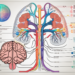
In today’s fast-paced world, stress and anxiety have become prevalent issues that can take a toll on our physical and mental health. One key aspect of our nervous system that is intimately linked to stress is the parasympathetic nerve. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into understanding the parasympathetic nervous system and explore techniques for calming it. It is important to note that this article provides general information and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. If you are experiencing chronic stress or any health concerns, it is always best to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance.
Understanding the Parasympathetic Nervous System
The parasympathetic nervous system is a branch of the autonomic nervous system, which controls various automatic bodily functions. It is responsible for bringing our bodies back to a state of rest and relaxation after facing stress or danger. Unlike its counterpart, the sympathetic nervous system, which triggers the fight-or-flight response, the parasympathetic nervous system promotes calmness and restoration.
When we encounter a stressful situation, such as a near miss while driving or a deadline at work, our sympathetic nervous system kicks into gear. It releases stress hormones like adrenaline and cortisol, preparing our bodies to either fight the threat or run away from it. This response is essential for our survival, as it enables us to react quickly and effectively in dangerous situations.
However, once the threat has passed, it is crucial for our bodies to return to a state of equilibrium. This is where the parasympathetic nervous system comes into play. It acts as a counterbalance to the sympathetic nervous system, helping us recover and restore our energy levels.
The Role of the Parasympathetic Nerve in the Body
The parasympathetic nerve plays a crucial role in maintaining balance and well-being. It regulates bodily functions such as heart rate, digestion, salivation, urination, and sexual arousal. When activated, it promotes relaxation, aids in digestion, and conserves energy.
For example, when we sit down to enjoy a meal, the parasympathetic nervous system is responsible for stimulating the production of digestive enzymes and increasing blood flow to the digestive organs. This allows our bodies to efficiently break down and absorb nutrients from the food we consume. Without the parasympathetic nerve’s influence, digestion would be compromised, leading to issues such as indigestion and nutrient deficiencies.
In addition to its role in digestion, the parasympathetic nervous system also plays a vital role in regulating heart rate. When we are in a state of rest, the parasympathetic nerve slows down our heart rate, allowing it to beat at a steady and relaxed pace. This helps conserve energy and promotes overall cardiovascular health.
The Connection Between the Parasympathetic Nerve and Stress
Chronic stress can disrupt the normal functioning of the parasympathetic nervous system, leading to imbalances in our body and mind. Prolonged activation of the sympathetic nervous system (which is often associated with stress) can inhibit the parasympathetic nerve’s ability to bring our bodies back to a state of equilibrium. This can result in various health issues, including cardiovascular problems, digestive disorders, and weakened immune function.
When we experience chronic stress, our bodies remain in a constant state of high alert. This prolonged activation of the sympathetic nervous system can lead to increased heart rate, elevated blood pressure, and impaired digestion. Additionally, the release of stress hormones can suppress the immune system, making us more susceptible to infections and illnesses.
It is essential to find ways to activate the parasympathetic nervous system and promote relaxation in our daily lives. Practices such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, yoga, and spending time in nature can all help stimulate the parasympathetic nerve and counteract the effects of chronic stress.
The Science Behind Calming the Parasympathetic Nerve
Understanding how stress affects the parasympathetic nerve allows us to explore strategies for calming it. By reducing stress levels and supporting the parasympathetic nervous system, individuals can enhance their overall well-being and lead healthier lives.
The Impact of Stress on the Parasympathetic Nerve
During times of stress, the body releases stress hormones such as cortisol and adrenaline, which can hinder the parasympathetic nervous system’s activity. This can lead to a variety of physical and mental health issues, including increased heart rate, elevated blood pressure, and heightened anxiety levels.
When stress hormones flood the body, the parasympathetic nerve, also known as the “rest and digest” system, is suppressed. This means that the body’s ability to relax, repair, and regenerate is compromised. As a result, individuals may experience difficulties in falling asleep, digestive problems, and a weakened immune system.
However, by managing stress through various techniques, such as lifestyle modifications, individuals can support the parasympathetic nerve and promote relaxation. This can have a profound impact on their overall well-being and quality of life.
The Biological Process of Calming the Nerve
Engaging in activities that promote relaxation can activate the parasympathetic nervous system, counterbalancing the negative effects of stress hormones. One effective technique is deep breathing exercises, which help activate the body’s relaxation response.
When we take slow, deep breaths, the diaphragm moves downward, allowing the lungs to expand fully. This triggers a relaxation response in the body, activating the parasympathetic nerve and promoting a sense of calmness and tranquility. Deep breathing exercises can be practiced anywhere and at any time, making them a convenient tool for stress management.
In addition to deep breathing, meditation is another powerful practice that can calm the parasympathetic nerve. By focusing the mind and redirecting attention away from stressors, meditation helps activate the body’s relaxation response. Regular meditation practice has been shown to reduce anxiety, improve sleep quality, and enhance overall well-being.
Spending time in nature is also a wonderful way to support the parasympathetic nerve. Being in natural environments has been found to reduce stress levels and promote relaxation. Whether it’s taking a walk in a park, hiking in the mountains, or simply sitting by the beach, immersing ourselves in nature can have a profound impact on our nervous system, allowing us to unwind and recharge.
By incorporating these practices into our daily routines, we can improve our body’s resilience to stress and enhance our overall well-being. It’s important to remember that calming the parasympathetic nerve is not a one-time fix, but rather an ongoing process that requires consistent effort and self-care. With dedication and practice, we can create a harmonious balance between our body and mind, leading to a healthier and more fulfilling life.
Techniques for Calming the Parasympathetic Nerve
There are numerous techniques that can help calm the parasympathetic nerve and promote a sense of relaxation. Let’s explore some of these techniques below:
Breathing Exercises and Their Effects
Deep breathing exercises, such as diaphragmatic breathing or alternate nostril breathing, have been shown to activate the parasympathetic nervous system. By focusing on slow, deep breaths, we can stimulate the relaxation response and reduce stress levels. Incorporating these breathing exercises into our daily routines can be immensely beneficial for calming the parasympathetic nerve.
Diaphragmatic breathing, also known as belly breathing, involves taking deep breaths that fully engage the diaphragm. This technique allows for a greater intake of oxygen, which helps to calm the parasympathetic nerve. By consciously directing our breath to the lower abdomen, we can activate the relaxation response and promote a sense of calmness throughout our body.
Another effective breathing exercise is alternate nostril breathing. This technique involves closing one nostril with a finger and inhaling deeply through the other nostril, then switching sides and exhaling through the opposite nostril. This rhythmic breathing pattern helps balance the flow of energy in the body and activates the parasympathetic nervous system, leading to a state of relaxation and tranquility.
The Role of Meditation in Calming the Nerve
Meditation is a practice that has been used for centuries to promote relaxation and reduce stress. Engaging in regular meditation sessions can help lower anxiety levels and support the parasympathetic nervous system. By dedicating a few minutes each day to cultivating a sense of mindfulness, we can bring about a state of calmness and tranquility.
During meditation, we focus our attention on the present moment, allowing thoughts and worries to pass by without judgment. This practice helps to quiet the mind and activate the parasympathetic nervous system, which in turn promotes a sense of relaxation and well-being. By incorporating meditation into our daily routine, we can develop a greater sense of self-awareness and cultivate a peaceful state of mind.
There are various meditation techniques to choose from, including mindfulness meditation, loving-kindness meditation, and transcendental meditation. Each technique offers its own unique benefits, but all share the common goal of calming the parasympathetic nerve and promoting a state of inner peace.
During mindfulness meditation, we focus our attention on the sensations of the breath, the body, or a specific object of focus. This practice helps to anchor our awareness in the present moment and reduce the influence of stress and anxiety on our nervous system. By regularly practicing mindfulness meditation, we can train our minds to become more resilient to stress and cultivate a sense of calmness in our daily lives.
Loving-kindness meditation involves directing well-wishes and compassion towards ourselves and others. By cultivating feelings of love, kindness, and empathy, we activate the parasympathetic nervous system and promote a sense of connection and well-being. This practice not only calms the parasympathetic nerve but also enhances our relationships and overall sense of happiness.
Transcendental meditation is a technique that involves silently repeating a mantra, a specific word or phrase, to quiet the mind and induce a state of deep relaxation. By focusing our attention on the mantra, we can bypass the constant stream of thoughts and activate the parasympathetic nervous system. This technique has been shown to reduce stress, lower blood pressure, and promote a sense of inner peace and clarity.
Dietary Influence on the Parasympathetic Nerve
Our diet can play a significant role in supporting the health of our nervous system, including the parasympathetic nerve. While specific foods cannot directly calm the nerve, certain nutrients can promote relaxation and well-being. It is important to maintain a well-balanced diet that includes a variety of foods.
One group of foods that can aid in calming the nerve are those rich in magnesium. Leafy greens, such as spinach and kale, as well as nuts and seeds, like almonds and pumpkin seeds, are excellent sources of this mineral. Magnesium helps relax muscles and promote calmness, making it beneficial for the parasympathetic nerve.
In addition to magnesium-rich foods, incorporating omega-3 fatty acids into your diet can also support brain health and reduce stress levels. Fatty fish, such as salmon and mackerel, as well as flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts, are all good sources of omega-3s. These fatty acids have been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties and can contribute to a sense of well-being.
Complex carbohydrates are another important component of a diet that supports the parasympathetic nerve. Whole grains, such as quinoa and brown rice, as well as fruits like bananas and apples, provide a steady release of energy and can help stabilize mood. These carbohydrates are digested more slowly, preventing sudden spikes and crashes in blood sugar levels, which can impact the nervous system.
In addition to specific foods, herbal teas can also aid in relaxation and support the parasympathetic nerve. Chamomile and lavender teas, in particular, have soothing properties that can help calm the mind and promote a sense of well-being. Enjoying a warm cup of herbal tea in the evening can be a comforting ritual that supports your nervous system.
The Impact of Hydration on the Nervous System
Proper hydration is crucial for overall health, including the optimal functioning of the nervous system. Drinking an adequate amount of water throughout the day helps to maintain hydration levels and support the parasympathetic nerve.
When it comes to hydration, it is important to be mindful of your beverage choices. While water is the best choice for staying hydrated, other fluids can also contribute to your daily intake. However, it is advisable to limit the consumption of caffeine and alcohol, as they can have dehydrating effects on the body.
Caffeine, found in coffee, tea, and some soft drinks, acts as a diuretic, increasing urine production and potentially leading to dehydration if consumed in excess. Similarly, alcohol can also have a dehydrating effect on the body, as it increases urine output and impairs the body’s ability to retain water.
To ensure optimal hydration, it is recommended to drink water throughout the day and listen to your body’s thirst signals. Remember that staying hydrated is not only important for your overall health but also for the proper functioning of your nervous system, including the parasympathetic nerve.
Physical Activities and the Parasympathetic Nerve
Engaging in physical activities can have a profound impact on our nervous system, including the parasympathetic nerve. Let’s explore some activities that can help promote relaxation:
The Benefits of Yoga for the Nervous System
Yoga is a mind-body practice that combines physical postures, breath control, and meditation. The gentle movements and focused breathing techniques in yoga can activate the parasympathetic nervous system, promoting relaxation and reducing stress. Regular yoga practice can also improve flexibility, strength, and overall well-being.
How Regular Exercise Contributes to Nerve Health
Engaging in regular exercise, such as brisk walking, jogging, or cycling, can have a positive impact on the nervous system. Physical activity helps to reduce stress hormones, promote the release of endorphins (the body’s natural mood boosters), and support the parasympathetic nerve. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week to reap these benefits.
The Importance of Sleep in Nerve Health
Adequate sleep plays a crucial role in maintaining overall nerve health and supporting the parasympathetic nervous system. Lack of sleep can lead to increased stress levels, impaired cognitive function, and reduced immune function. It is essential to prioritize good sleep hygiene and establish a consistent sleep routine for optimal nervous system health.
The Relationship Between Sleep and the Parasympathetic Nerve
During sleep, the parasympathetic nervous system becomes more active, promoting rest and restoration. Sufficient sleep allows the body to repair and rejuvenate itself. Establishing a consistent sleep schedule, creating a peaceful sleep environment, and practicing relaxation techniques before bedtime can contribute to better sleep quality and support the parasympathetic nerve.
Tips for Improving Sleep for Better Nerve Health
- Create a relaxing bedtime routine, such as reading a book or taking a warm bath.
- Avoid electronic devices and stimulating activities before bed.
- Maintain a comfortable sleep environment that is dark, quiet, and cool.
- Limit caffeine intake, especially in the afternoon and evening.
- Exercise regularly but avoid intense physical activity close to bedtime.
Long-term Strategies for Maintaining Parasympathetic Nerve Health
While the techniques mentioned above can provide temporary relief from stress and promote nerve relaxation, adopting long-term strategies is key to maintaining parasympathetic nerve health. These strategies involve making lifestyle changes and seeking professional guidance when necessary.
The Role of Regular Check-ups in Nerve Health
Regular check-ups with healthcare professionals, such as primary care physicians or neurologists, are essential for monitoring overall nerve health. These medical professionals can provide personalized guidance and interventions, if needed, to support the parasympathetic nervous system. Seeking professional advice is especially crucial for individuals with pre-existing medical conditions or those experiencing severe and persistent symptoms.
Lifestyle Changes for a Healthy Nervous System
Adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, stress management techniques, and adequate sleep can support the parasympathetic nerve and promote overall nerve health. Engaging in activities that bring joy and practicing self-care are also integral parts of a holistic approach to maintaining nerve well-being.
In conclusion, understanding the parasympathetic nervous system and its connection to stress is crucial for promoting overall well-being. By incorporating various techniques such as breathing exercises, meditation, adequate sleep, and adopting a healthy lifestyle, individuals can support the parasympathetic nerve and manage stress levels effectively. However, it is important to remember that everyone’s needs and circumstances are unique, and consulting with a healthcare professional is always advised for personalized guidance.