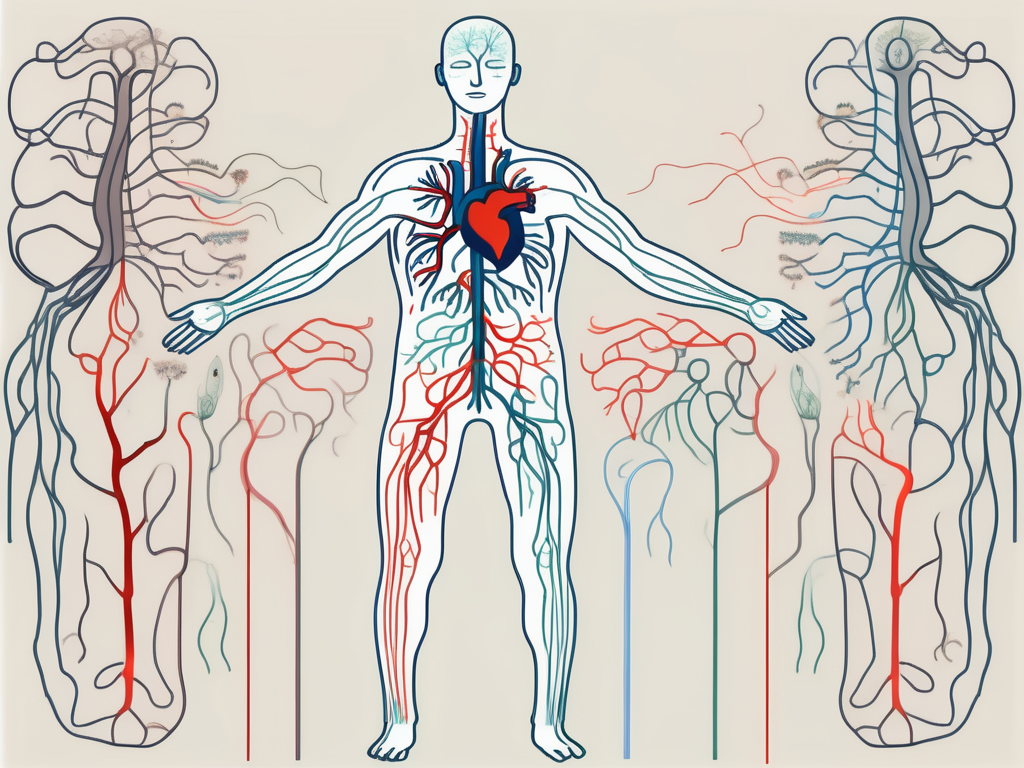
The parasympathetic nervous system plays a crucial role in regulating various physiological processes within the body. Understanding its functions and mechanisms is essential for comprehending the impact it has on our overall health and well-being. In this article, we will explore the intricate workings of the parasympathetic nervous system, its influence on different body systems, its role in stress response, and future research directions in the field.
Understanding the Parasympathetic Nervous System
The parasympathetic nervous system is one of the two main divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the other being the sympathetic nervous system. While the sympathetic nervous system is responsible for the “fight or flight” response, the parasympathetic nervous system promotes relaxation and restoration. It is often referred to as the “rest and digest” system.
The parasympathetic nervous system plays a crucial role in maintaining the body’s overall well-being. It is responsible for regulating various bodily functions, including heart rate, digestion, and respiratory rate. By doing so, it helps to maintain homeostasis, ensuring that the body functions optimally in different situations.
When the body is under stress, the sympathetic nervous system becomes active, preparing the body for action. However, once the threat or stressor has passed, the parasympathetic nervous system takes over, allowing the body to relax and recover.
The Role and Function of the Parasympathetic Nervous System
The primary role of the parasympathetic nervous system is to maintain homeostasis by regulating various bodily functions. One of its key functions is controlling heart rate. When the body is at rest, the parasympathetic nervous system slows down the heart rate, promoting a state of relaxation. This is essential for conserving energy and allowing the body to recover.
In addition to heart rate regulation, the parasympathetic nervous system also plays a vital role in digestion. It stimulates the production of digestive enzymes and increases blood flow to the digestive organs, promoting efficient digestion and nutrient absorption. This is why it is often referred to as the “rest and digest” system.
Furthermore, the parasympathetic nervous system is involved in regulating respiratory rate. When the body is in a relaxed state, it slows down the breathing rate, allowing for deeper and more efficient breathing. This helps to oxygenate the body and promote a sense of calm.
Key Components of the Parasympathetic Nervous System
The parasympathetic nervous system is composed of a complex network of nerves and ganglia. These nerves extend from the brainstem and sacral region of the spinal cord to various organs throughout the body.
Cranial nerves, such as the vagus nerve, play a significant role in transmitting parasympathetic signals to different organs. The vagus nerve, in particular, is responsible for regulating many vital functions, including heart rate, digestion, and respiratory rate. It carries parasympathetic signals from the brain to the heart, lungs, stomach, and other organs.
When the parasympathetic nervous system is activated, it releases acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that binds to receptors on target cells, initiating specific physiological responses. These responses can vary depending on the organ or tissue involved.
Overall, the parasympathetic nervous system is a crucial part of the autonomic nervous system, working in opposition to the sympathetic nervous system to maintain balance and promote overall well-being. By understanding its role and function, we can appreciate the importance of relaxation and restoration in our daily lives.
The Parasympathetic Nervous System and Physiological Regulation
One of the essential functions of the parasympathetic nervous system is to promote the rest and digest response, which prepares the body for optimal digestion and absorption of nutrients. This response is initiated during periods of relaxation, allowing the body to conserve energy and focus on essential metabolic processes.
The parasympathetic nervous system plays a crucial role in maintaining the body’s homeostasis, or internal balance. It works in conjunction with the sympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for the fight or flight response. While the sympathetic nervous system prepares the body for action and stress, the parasympathetic nervous system helps restore calm and balance.
The Parasympathetic Nervous System in Rest and Digest Response
When the parasympathetic nervous system is activated, it stimulates the release of digestive enzymes and increases blood flow to the digestive organs, promoting efficient digestion. Additionally, it helps relax smooth muscles in the gastrointestinal tract, facilitating the movement of food through the digestive system.
During the rest and digest response, the body experiences a multitude of physiological changes. Salivation increases, aiding in the breakdown of food in the mouth. The stomach produces gastric juices, including hydrochloric acid and pepsin, which help break down proteins. The pancreas releases digestive enzymes, such as amylase, lipase, and proteases, to further break down carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, respectively.
Furthermore, the parasympathetic nervous system stimulates the gallbladder to release bile, which aids in the digestion and absorption of fats. The small intestine, a vital site for nutrient absorption, experiences increased blood flow, ensuring efficient nutrient uptake.
The Influence of Parasympathetic Nervous System on Heart Rate
The parasympathetic nervous system has a significant impact on heart rate regulation. It slows down the heart rate and reduces the force of its contractions, which helps conserve energy. This effect allows the heart to function efficiently during periods of rest and relaxation.
Heart rate is controlled by the sinoatrial (SA) node, often referred to as the natural pacemaker of the heart. The parasympathetic nervous system exerts its influence on heart rate through the release of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that binds to receptors in the SA node. This binding slows down the electrical impulses generated by the SA node, resulting in a decreased heart rate.
Moreover, the parasympathetic nervous system also influences the conduction of electrical signals through the atrioventricular (AV) node, which further contributes to heart rate regulation. By reducing the heart’s workload and oxygen demand, the parasympathetic nervous system helps maintain cardiovascular health.
The Parasympathetic Nervous System’s Role in Energy Conservation
Energy conservation is critical for the overall health and well-being of an individual. The parasympathetic nervous system promotes energy conservation by reducing unnecessary bodily functions during restful periods. By conserving energy, the body can allocate resources to essential processes, such as growth, repair, and immune function.
During the rest and digest response, the parasympathetic nervous system inhibits non-essential activities that consume energy. For example, it decreases the production of stress hormones, such as cortisol, which are involved in the fight or flight response. By doing so, the parasympathetic nervous system helps prevent excessive wear and tear on the body’s tissues and organs.
Furthermore, the parasympathetic nervous system promotes relaxation and sleep, allowing the body to recharge and restore energy levels. It also supports the immune system by enhancing the production of immune cells and antibodies, which play a crucial role in defending against pathogens and maintaining overall health.
In conclusion, the parasympathetic nervous system is a vital component of physiological regulation. It promotes the rest and digest response, influences heart rate regulation, and plays a crucial role in energy conservation. By understanding the functions and mechanisms of the parasympathetic nervous system, we can appreciate its importance in maintaining overall health and well-being.
The Impact of Parasympathetic Nerve Regulation on Various Body Systems
The parasympathetic nervous system exerts its influence on different body systems to maintain homeostasis and promote overall physiological balance.
The parasympathetic nervous system, also known as the “rest and digest” system, is responsible for promoting relaxation and conserving energy. It works in opposition to the sympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for the “fight or flight” response.
When the parasympathetic nervous system is activated, it has a profound effect on various body systems, including the cardiovascular system, the digestive system, and the respiratory system.
The Effect on the Cardiovascular System
Activation of the parasympathetic nervous system causes vasodilation, which leads to a decrease in blood pressure. This response is vital for maintaining optimal blood flow to various organs and tissues. By reducing the workload on the heart, the parasympathetic nervous system helps to prevent cardiovascular diseases such as hypertension and heart failure.
However, in certain pathological conditions, excessive parasympathetic activity may lead to bradycardia or fainting, necessitating medical intervention. It is important to strike a balance between sympathetic and parasympathetic activity to ensure proper cardiovascular function.
The Impact on the Digestive System
The parasympathetic nervous system plays a crucial role in regulating digestion and nutrient absorption. By increasing blood flow to the digestive organs and enhancing the secretion of digestive enzymes, it ensures efficient breakdown and absorption of nutrients.
In addition to promoting digestion, the parasympathetic nervous system also stimulates the release of bile from the gallbladder, which aids in the breakdown and absorption of fats. It also promotes peristalsis, the rhythmic contractions of the digestive tract that help propel food through the system.
However, it is essential to note that digestive disorders may require medical treatment and dietary modifications. Conditions such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) may disrupt the normal functioning of the digestive system and require specialized care.
The Influence on the Respiratory System
The parasympathetic nervous system helps regulate the respiratory rate and depth by controlling the smooth muscles in the airways and lungs. During restful periods, it promotes a slower and deeper breathing pattern, allowing for efficient gas exchange.
In addition to controlling the rate and depth of breathing, the parasympathetic nervous system also plays a role in regulating the diameter of the airways. It causes bronchoconstriction, which reduces airflow, and mucus secretion, which helps to trap foreign particles and protect the respiratory system.
However, respiratory disorders should always be evaluated and managed under the guidance of a healthcare professional. Conditions such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and pneumonia require specialized treatment to ensure proper respiratory function.
In conclusion, the parasympathetic nervous system plays a vital role in maintaining homeostasis and promoting overall physiological balance. Its influence on the cardiovascular system, digestive system, and respiratory system is crucial for optimal functioning. However, it is important to recognize that excessive parasympathetic activity or disruptions in its regulation can lead to pathological conditions that require medical intervention. By understanding the impact of parasympathetic nerve regulation on various body systems, healthcare professionals can better diagnose and manage related disorders.
The Parasympathetic Nervous System and Stress Response
Stress is an inevitable part of life, and the parasympathetic nervous system plays a significant role in managing its effects on the body.
When we encounter stress, our body’s stress response system kicks into action. This system is composed of various physiological and psychological processes that help us cope with challenging situations. One crucial component of this system is the parasympathetic nervous system.
The Role of Parasympathetic Nervous System in Stress Management
The parasympathetic nervous system helps counteract the effects of stress by promoting relaxation and reducing the body’s physiological response to stressors. It acts as the body’s natural calming mechanism, allowing us to recover from stressful situations and return to a state of balance.
When the parasympathetic nervous system is activated, it releases neurotransmitters such as acetylcholine, which slows down the heart rate, dilates blood vessels, and stimulates digestion. These actions help conserve energy and redirect resources towards restorative processes.
Additionally, the parasympathetic nervous system stimulates the release of hormones like oxytocin, often referred to as the “love hormone.” Oxytocin promotes feelings of trust, relaxation, and bonding, further enhancing the body’s ability to manage stress.
The Parasympathetic Nervous System’s Impact on Stress-Related Disorders
Imbalances in the parasympathetic nervous system can contribute to the development of stress-related disorders such as anxiety and depression. Chronic stress can disrupt the delicate balance between the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems, leading to an overactive stress response and a reduced ability to relax and recover.
Seeking professional help from a healthcare provider is crucial in managing these conditions effectively. They can provide guidance on various techniques and therapies that can help rebalance the parasympathetic nervous system, such as mindfulness practices, deep breathing exercises, and relaxation techniques.
Furthermore, engaging in activities that promote overall well-being, such as regular exercise, adequate sleep, and a healthy diet, can also support the functioning of the parasympathetic nervous system and improve stress management.
In conclusion, the parasympathetic nervous system plays a vital role in managing the body’s response to stress. By activating the “rest and digest” response, it helps restore equilibrium and foster a sense of calmness. Understanding the impact of the parasympathetic nervous system on stress-related disorders can guide individuals in seeking appropriate support and implementing strategies to promote overall well-being.
Future Research Directions in Parasympathetic Nerve Regulation
Continued research in the field of parasympathetic nerve regulation holds promise for the development of new therapeutic approaches and a deeper understanding of the intricacies of our physiological responses.
The parasympathetic nervous system, often referred to as the “rest and digest” system, is responsible for promoting relaxation, conserving energy, and maintaining homeostasis in the body. While its importance is well-established, there are still many avenues for exploration and discovery in this fascinating field.
Potential Therapeutic Applications
Exploring the potential therapeutic applications of parasympathetic nerve regulation has the potential to revolutionize various medical fields. From stress management techniques to targeted treatments for specific pathological conditions, the possibilities are vast.
For example, researchers are investigating the use of parasympathetic nerve stimulation as a non-invasive treatment for anxiety disorders. By modulating the activity of the parasympathetic nervous system, it may be possible to alleviate symptoms such as excessive worry, restlessness, and rapid heartbeat.
Furthermore, studies have shown that parasympathetic nerve regulation plays a crucial role in digestive health. Dysfunction of the parasympathetic system has been linked to conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and gastroparesis. By understanding the mechanisms underlying these disorders, researchers can develop targeted therapies to restore proper parasympathetic function and improve patients’ quality of life.
Unanswered Questions and Areas for Further Study
Despite considerable progress in the understanding of the parasympathetic nervous system, numerous unanswered questions warrant further investigation. Researchers continue to explore areas such as the link between the parasympathetic system and mental health, as well as the influence of lifestyle factors on its functioning.
One intriguing area of research is the role of the parasympathetic nervous system in emotional regulation. Studies have suggested that the parasympathetic system may play a role in modulating emotional responses, such as fear and anxiety. Understanding this connection could have significant implications for the development of novel treatments for mood disorders.
Additionally, lifestyle factors such as diet, exercise, and sleep have been shown to influence parasympathetic nerve regulation. Researchers are actively investigating how these factors interact with the parasympathetic system and whether interventions targeting lifestyle modifications can enhance parasympathetic function and overall well-being.
In conclusion, the parasympathetic nervous system plays a critical role in regulating physiological processes and maintaining overall health. Its impact on different body systems, stress response, and potential therapeutic applications make it an area of continuous research and exploration. As our understanding of this intricate system deepens, new opportunities for intervention and improved healthcare outcomes may arise. If you have concerns about your parasympathetic nerve regulation or any physiological issues, it is always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional who can provide personalized guidance and advice.