The parasympathetic nervous system is a crucial component of the autonomic nervous system, which controls important bodily functions. In order to fully comprehend the functions and effects of the parasympathetic nervous system, it is essential to have an overview of the nervous system as a whole.
An Overview of the Nervous System
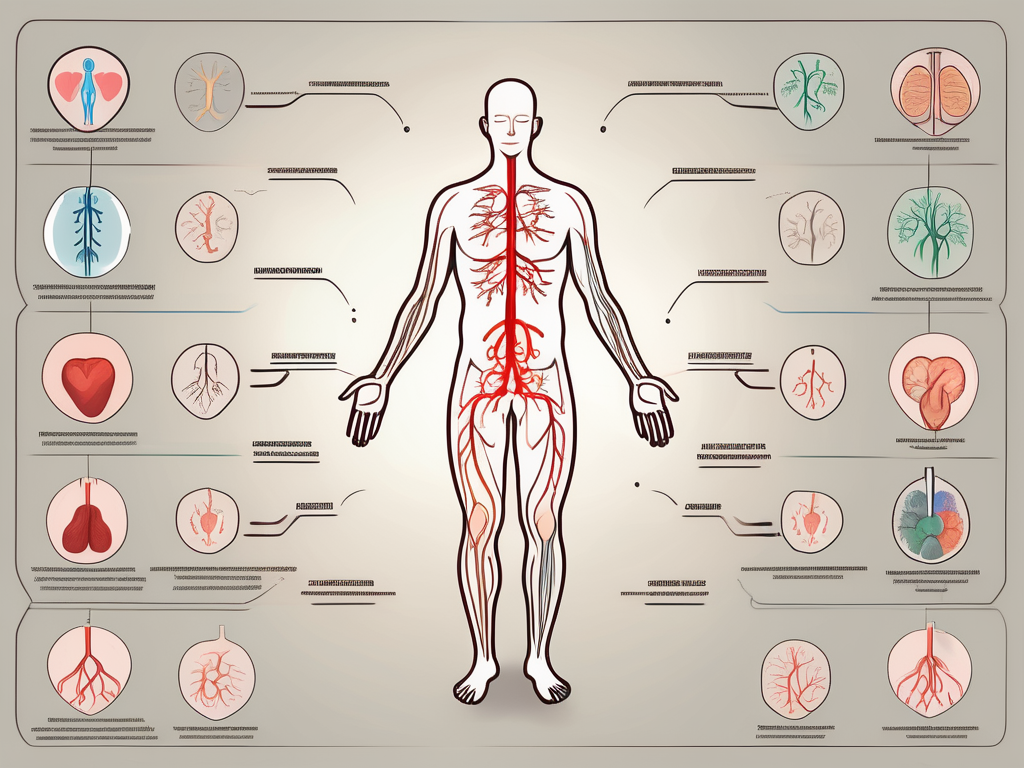
The nervous system is a complex network of cells responsible for transmitting electrical signals throughout the body. It is divided into two major divisions: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord. The brain, weighing about three pounds, is the control center of the nervous system. It is responsible for processing information received from the body and the environment, as well as sending instructions to the rest of the body. The spinal cord, a long, thin, tubular bundle of nerves, extends from the brain down the back and serves as a pathway for transmitting signals between the brain and the body.
The PNS, on the other hand, consists of nerves that extend beyond the brain and spinal cord, connecting them to the rest of the body. These nerves are like electrical wires, carrying messages back and forth between the CNS and the body’s organs, muscles, and tissues. They enable us to sense the world around us, control our movements, and carry out various bodily functions.
The Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems
The central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS) work together to ensure the proper functioning of the body. The CNS, consisting of the brain and spinal cord, serves as the command center. It processes information received from the sensory organs and sends out instructions to the muscles and glands, allowing us to move, think, and feel.
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is like a vast network of communication lines that branch out from the CNS to every part of the body. It includes the cranial nerves, which connect the brain to the head and neck, and the spinal nerves, which extend from the spinal cord to the rest of the body. These nerves transmit signals to and from the CNS, allowing us to interact with our environment and respond to stimuli.
The Role of the Autonomic Nervous System
Within the peripheral nervous system (PNS), the autonomic nervous system plays a vital role in regulating automatic bodily functions. It controls processes that occur without conscious effort, such as heart rate, digestion, and stress response. The autonomic nervous system is further divided into two branches: the sympathetic and the parasympathetic nervous systems.
The sympathetic nervous system is responsible for the body’s “fight or flight” response. When faced with a perceived threat or danger, this system prepares the body for action by increasing heart rate, dilating the pupils, and releasing stress hormones like adrenaline. It helps us respond quickly in emergency situations, enabling us to either fight off the threat or flee from it.
On the other hand, the parasympathetic nervous system is responsible for the body’s “rest and digest” response. It promotes relaxation, conserves energy, and supports normal bodily functions. When activated, it slows down heart rate, constricts the pupils, and enhances digestion and nutrient absorption. It helps us rest, recover, and maintain a state of balance in our day-to-day lives.
In conclusion, the nervous system is a remarkable and intricate system that allows us to perceive the world, control our movements, and carry out various bodily functions. The central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system work together to ensure the proper functioning of our bodies, while the autonomic nervous system regulates automatic processes. Understanding the complexities of the nervous system can help us appreciate the incredible capabilities of the human body.
The Parasympathetic Nervous System Explained
The parasympathetic nervous system is one of the two branches of the autonomic nervous system. It counterbalances the sympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for the body’s “fight-or-flight” response. The parasympathetic nervous system, in contrast, promotes relaxation and restoration.
When we think of the parasympathetic nervous system, we often envision a calm and peaceful state. It is the system that helps us unwind after a long and stressful day, allowing our bodies to recover and rejuvenate. Let’s delve deeper into the anatomy and key functions of this remarkable system.
Anatomy of the Parasympathetic Nervous System
The parasympathetic nervous system arises from certain cranial and sacral nerves. It consists of nerves that branch out from the cranial nerves, originating in the brainstem, and the sacral nerves, arising from the lower spinal cord. These nerves innervate various organs and glands throughout the body.
One of the cranial nerves involved in the parasympathetic nervous system is the vagus nerve. This remarkable nerve extends from the brainstem to the abdomen, reaching multiple organs along the way, including the heart, lungs, stomach, and intestines. It plays a crucial role in regulating bodily functions and maintaining homeostasis.
The sacral nerves, on the other hand, emerge from the lower part of the spinal cord and innervate the pelvic organs, such as the bladder and reproductive organs. These nerves ensure the proper functioning of these vital systems, allowing us to experience normal urination and sexual arousal.
Key Functions of the Parasympathetic Nervous System
The parasympathetic nervous system is primarily responsible for regulating restorative bodily functions, such as digestion, urination, and sexual arousal. When it is activated, it promotes a state of relaxation and aids in conserving and restoring energy.
One of the significant roles of the parasympathetic nervous system is its involvement in digestion. When activated, it stimulates the secretion of digestive enzymes, increases blood flow to the digestive organs, and facilitates the process of digestion and absorption of nutrients. This system ensures that our bodies efficiently break down the food we consume, extracting essential nutrients to nourish our cells and tissues.
In addition to its digestive functions, the parasympathetic nervous system also plays a vital role in maintaining cardiovascular and respiratory health. It helps regulate heart rate, ensuring that it beats at a steady pace, promoting optimal blood circulation throughout the body. Furthermore, it supports normal respiratory rate, allowing us to breathe effortlessly and efficiently.
Furthermore, the parasympathetic nervous system is involved in maintaining proper bladder function. It helps regulate the contraction and relaxation of the bladder muscles, ensuring that urine is stored and released appropriately. This system allows us to maintain control over our urinary functions, preventing any discomfort or inconvenience.
The parasympathetic nervous system is a remarkable and essential part of our overall well-being. It works in harmony with the sympathetic nervous system, creating a delicate balance that allows our bodies to respond appropriately to different situations. Understanding its anatomy and functions helps us appreciate the intricate mechanisms that keep our bodies functioning optimally.
The Effects of the Parasympathetic Nervous System
The parasympathetic nervous system plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions, exerting a profound impact on heart rate, digestion, stress response, and relaxation. Understanding the intricate workings of this system can provide valuable insights into maintaining optimal health and well-being.
Impact on Heart Rate and Digestion
When the parasympathetic nervous system is actively engaged, it works in harmony with the sympathetic nervous system to maintain a balanced heart rate. While the sympathetic nervous system prepares the body for action by increasing heart rate, the parasympathetic nervous system steps in to lower heart rate and promote relaxation. This delicate interplay ensures that the heart functions efficiently, adapting to the body’s needs.
In addition to its role in heart rate regulation, the parasympathetic nervous system also plays a vital role in digestion. It stimulates the digestive organs by increasing blood flow to these organs and activating digestive enzymes. This activation allows for efficient breakdown and absorption of nutrients, facilitating optimal digestion and nutrient utilization.
Role in Stress Response and Relaxation
The parasympathetic nervous system acts as a counterbalance to the stress response triggered by the sympathetic nervous system. When faced with a stressful event, the sympathetic nervous system activates the body’s fight-or-flight response, preparing it for action. However, once the threat has passed, the parasympathetic nervous system kicks in to restore the body to a state of relaxation.
By activating the parasympathetic nervous system, individuals can induce a relaxation response, leading to reduced stress levels and improved overall well-being. This can be achieved through various relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or engaging in activities that promote a sense of calm and tranquility.
Furthermore, chronic stress can have detrimental effects on physical and mental health. By actively engaging the parasympathetic nervous system through relaxation techniques, individuals can help mitigate the negative impact of stress, promoting a healthier and more balanced lifestyle.
In conclusion, the parasympathetic nervous system plays a vital role in regulating heart rate, digestion, stress response, and relaxation. Understanding its functions and learning how to activate it can have significant benefits for overall health and well-being. By prioritizing relaxation and incorporating techniques that promote parasympathetic activation into daily routines, individuals can optimize their physiological responses and enhance their overall quality of life.
Disorders Related to the Parasympathetic Nervous System
The parasympathetic nervous system plays a vital role in maintaining the body’s equilibrium and ensuring its proper functioning. However, like any other system in the body, it is susceptible to disorders that can disrupt its normal functioning.
One common disorder related to the parasympathetic nervous system is bradycardia, which is characterized by an abnormally slow heart rate. This condition can lead to fatigue, dizziness, and even fainting. Another disorder is gastroparesis, where the muscles in the stomach do not function properly, causing delayed digestion and symptoms like nausea, vomiting, and bloating.
Urinary problems can also arise from parasympathetic nervous system disorders. For instance, urinary retention, a condition where the bladder does not empty completely, can cause discomfort and increase the risk of urinary tract infections. On the other hand, overactive bladder, which is characterized by a sudden and frequent urge to urinate, can disrupt daily activities and affect quality of life.
Sexual dysfunction is another symptom that can be associated with parasympathetic nervous system disorders. Both men and women may experience a decrease in libido, difficulty achieving arousal or orgasm, and even pain during sexual intercourse. These issues can have a significant impact on relationships and overall well-being.
Symptoms of Parasympathetic Nervous System Disorders
Disorders related to the parasympathetic nervous system can manifest in various ways, affecting different parts of the body. In addition to the aforementioned symptoms, individuals may also experience issues such as excessive sweating, dry mouth, and blurred vision. These symptoms can vary in severity and may require medical attention to manage effectively.
Treatment Options for Parasympathetic Nervous System Disorders
If you suspect that you may be experiencing a disorder related to the parasympathetic nervous system, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional. They will be able to evaluate your symptoms, perform necessary tests, and provide an accurate diagnosis.
Treatment options for parasympathetic nervous system disorders will depend on the specific disorder and its underlying cause. In some cases, medication may be prescribed to manage symptoms and regulate the functioning of the parasympathetic nervous system. Lifestyle modifications, such as dietary changes and stress management techniques, can also play a significant role in improving symptoms and overall well-being.
In addition to medication and lifestyle modifications, various therapies may be recommended to address the underlying cause of the disorder. For example, physical therapy can help improve muscle function and coordination in individuals with urinary problems. Cognitive-behavioral therapy may be beneficial for managing anxiety or stress-related sexual dysfunction.
It is important to remember that each individual’s experience with a parasympathetic nervous system disorder is unique, and treatment plans should be tailored to their specific needs. Regular follow-ups with healthcare professionals are essential to monitor progress, adjust treatment as necessary, and ensure optimal management of symptoms.
The Parasympathetic Nervous System and Overall Health
Achieving a balanced nervous system is vital for maintaining optimal health and well-being. Both the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems need to work in harmony.
The parasympathetic nervous system, often referred to as the “rest and digest” system, is responsible for promoting relaxation, conserving energy, and restoring the body to a state of calmness. It works in opposition to the sympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for the “fight or flight” response.
When the parasympathetic nervous system is activated, several physiological changes occur in the body. The heart rate slows down, blood pressure decreases, digestion and nutrient absorption increase, and the body enters a state of deep relaxation. This state is essential for the body to repair and regenerate cells, boost the immune system, and promote overall well-being.
Importance of a Balanced Nervous System
A balanced nervous system allows for efficient regulation of bodily functions, promotes resilience to stress, and enhances overall vitality. It is important to adopt holistic approaches to support the nervous system, including proper nutrition, regular exercise, adequate sleep, stress management techniques, and engaging in activities that promote relaxation.
Proper nutrition plays a crucial role in supporting the parasympathetic nervous system. Consuming a diet rich in whole foods, including fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats, provides the necessary nutrients for optimal nervous system function. Additionally, certain foods, such as chamomile tea, dark chocolate, and leafy greens, have been shown to have calming effects on the body.
Regular exercise is another important aspect of maintaining a balanced nervous system. Engaging in activities like yoga, tai chi, or gentle aerobic exercises can help activate the parasympathetic nervous system and promote relaxation. Exercise also stimulates the release of endorphins, which are natural mood boosters that can help reduce stress and anxiety.
Adequate sleep is crucial for the restoration and rejuvenation of the nervous system. During sleep, the body repairs damaged tissues, consolidates memories, and regulates hormone production. Creating a relaxing bedtime routine, ensuring a comfortable sleep environment, and practicing good sleep hygiene can contribute to a restful night’s sleep and support the parasympathetic nervous system.
Lifestyle Changes to Support the Parasympathetic Nervous System
To support the parasympathetic nervous system, individuals can incorporate various lifestyle changes. These may include practicing mindfulness and relaxation techniques, engaging in activities that promote a sense of calmness and tranquility, and fostering healthy relationships and social connections.
Mindfulness and relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, and progressive muscle relaxation, can help activate the parasympathetic nervous system and induce a state of relaxation. These practices can be incorporated into daily routines, allowing individuals to manage stress and promote overall well-being.
Engaging in activities that promote a sense of calmness and tranquility can also support the parasympathetic nervous system. This may include spending time in nature, listening to soothing music, practicing hobbies or creative outlets, or taking warm baths. These activities can help reduce stress levels, promote relaxation, and enhance overall mental and emotional well-being.
Fostering healthy relationships and social connections is another important aspect of supporting the parasympathetic nervous system. Spending time with loved ones, engaging in meaningful conversations, and participating in social activities can help reduce feelings of loneliness and isolation, which can negatively impact overall health and well-being.
Additionally, adopting a well-balanced diet, staying hydrated, and getting regular exercise can contribute to the overall health of the parasympathetic nervous system. A diet rich in nutrients, hydration, and physical activity supports the body’s natural ability to maintain balance and promote optimal nervous system function.
In conclusion, understanding the functions and effects of the parasympathetic nervous system is crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being. It plays a pivotal role in promoting relaxation, regulating heart rate and digestion, and counterbalancing the stress response. By adopting lifestyle changes that support the parasympathetic nervous system, individuals can optimize their nervous system function and enhance their quality of life. If you have concerns or suspect a disorder related to the parasympathetic nervous system, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.