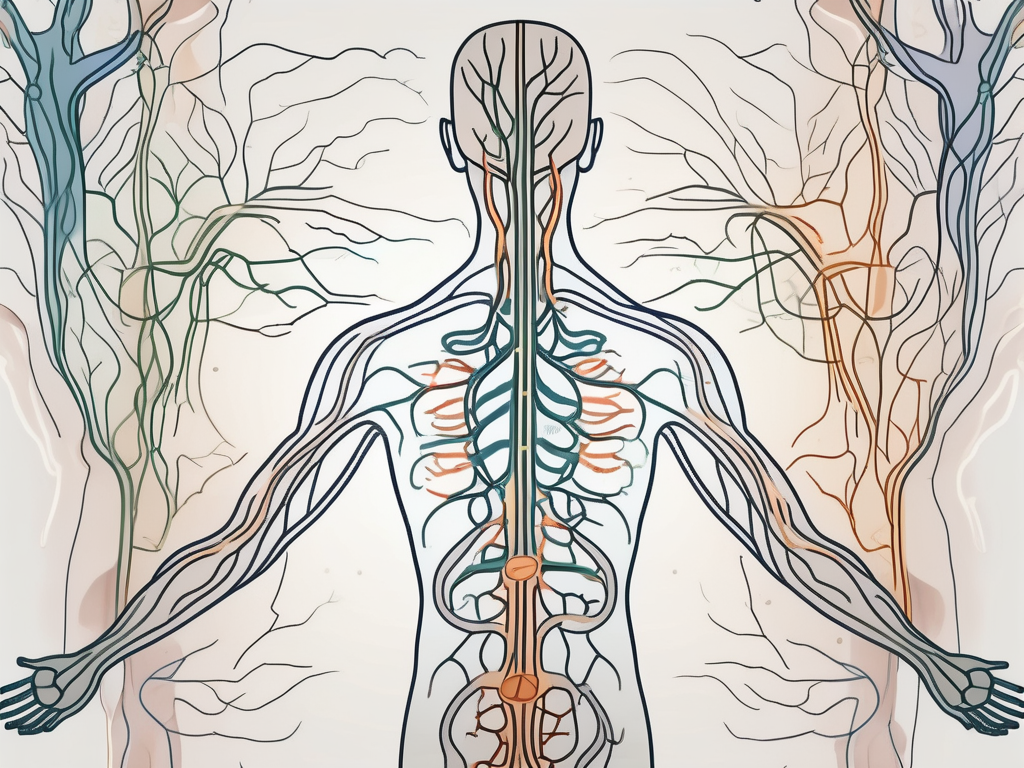
The nervous system is a complex and intricate network that plays a crucial role in regulating and coordinating various functions of the human body. It is responsible for everything from allowing us to move our muscles to controlling our heart rate and even influencing our emotions. Within the realm of the nervous system, there are two main divisions: the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems.
Introduction to the Nervous System
Before delving into the specifics of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems, it’s important to have a basic understanding of the nervous system as a whole. The nervous system is an intricate network of cells, tissues, and organs that work together to transmit signals and coordinate the functions of the body.
The nervous system is comprised of two main components: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS is like the command center, consisting of the brain and spinal cord. It is responsible for processing information, making decisions, and sending instructions to the rest of the body. The PNS, on the other hand, extends throughout the body and acts as a communication network, connecting the CNS to various organs, tissues, and cells.
The Role of the Nervous System in the Body
The overall function of the nervous system is to send and receive signals or messages throughout the body. It does this through the use of specialized cells called neurons. Neurons are the building blocks of the nervous system, and they are responsible for transmitting electrical impulses, also known as nerve impulses or action potentials.
Imagine a complex web of interconnected wires, each carrying important information. Just like these wires, neurons form intricate pathways known as nerve pathways. These pathways allow for communication between different parts of the body, ensuring that signals are transmitted accurately and efficiently.
Divisions of the Nervous System
Within the peripheral nervous system, there are two major divisions: the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system. The somatic nervous system is responsible for voluntary movements and actions, such as walking or picking up objects. It allows us to consciously control our skeletal muscles and interact with the external environment.
On the other hand, the autonomic nervous system is responsible for involuntary actions and processes that occur automatically, without conscious effort. It regulates vital functions such as heart rate, digestion, and breathing. This is where the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems come into play.
The sympathetic nervous system is often referred to as the “fight or flight” response. It prepares the body for action in times of stress or danger. When activated, it increases heart rate, dilates blood vessels, and releases stress hormones like adrenaline, allowing us to respond quickly and effectively to perceived threats.
Conversely, the parasympathetic nervous system is responsible for the body’s “rest and digest” response. It promotes relaxation, conserves energy, and facilitates processes such as digestion and healing. When activated, it slows down heart rate, constricts blood vessels, and enhances the body’s ability to rest and recover.
Understanding the intricate workings of the nervous system is crucial in comprehending the complexities of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. These two divisions work in harmony to maintain balance and ensure the body functions optimally in various situations.
The Sympathetic Nervous System Explained
The sympathetic nervous system is often referred to as the “fight or flight” response system. It is activated in times of stress or danger and prepares the body to respond to these situations by increasing heart rate, blood pressure, and respiratory rate.
But what exactly happens when the sympathetic nervous system kicks into action? Let’s dive deeper into the fascinating world of this intricate system.
The Function of the Sympathetic Nervous System
When faced with a perceived threat, the sympathetic nervous system kicks into action, releasing adrenaline and other stress hormones into the bloodstream. These hormones stimulate various organs and tissues, allowing the body to respond quickly and efficiently.
Imagine you’re walking alone in a dark alley, and suddenly you hear a loud noise. Your heart starts pounding, your breathing becomes rapid, and your muscles tense up. These are all responses triggered by the sympathetic nervous system, preparing you to either fight off the danger or flee from it.
But the sympathetic nervous system does more than just prepare us for physical action. It also plays a vital role in increasing alertness, sharpening focus, and promoting survival instincts. It helps us react swiftly to dangerous situations, both physically and mentally.
Key Components of the Sympathetic Nervous System
The sympathetic nervous system is made up of a complex network of nerves that extend from the spinal cord to various parts of the body. It is connected to organs such as the heart, lungs, and digestive system.
One of the most important components of the sympathetic nervous system is the chain of ganglia, which are clusters of nerve cell bodies located on either side of the spinal cord. These ganglia allow for the rapid transmission of nerve impulses throughout the body.
Imagine these ganglia as the messengers that deliver urgent messages from the brain to different parts of the body. They ensure that the signals travel quickly and efficiently, allowing for an immediate response to any perceived threat.
Additionally, the sympathetic nervous system is closely intertwined with the adrenal glands, which sit on top of the kidneys. These glands play a crucial role in the stress response by releasing hormones like adrenaline into the bloodstream, further enhancing the body’s readiness for action.
So, the next time you find yourself in a stressful situation, remember the incredible work of the sympathetic nervous system. It is a remarkable system that ensures our survival and helps us navigate through life’s challenges with strength and resilience.
The Parasympathetic Nervous System Uncovered
While the sympathetic nervous system acts to prepare the body for action, the parasympathetic nervous system functions as its counterpart, responsible for bringing the body back to a state of relaxation and rest. It is often referred to as the “rest and digest” system.
Have you ever wondered how your body knows when it’s time to relax and unwind after a long day? Well, that’s where the parasympathetic nervous system comes into play. This intricate system works tirelessly behind the scenes to ensure that your body can recover and rejuvenate.
The parasympathetic nervous system helps to conserve energy and maintain normal bodily functions during periods of rest. It counteracts the effects of the sympathetic nervous system, slowing down the heart rate, promoting digestion, and allowing the body to repair and regenerate.
Imagine a symphony orchestra where each instrument plays a crucial role in creating a harmonious melody. Similarly, the parasympathetic nervous system orchestrates a symphony of bodily functions, ensuring that everything runs smoothly. It regulates various processes, such as stimulating the production of saliva to aid in digestion and promoting the release of tears to keep your eyes moist and healthy.
The Role of the Parasympathetic Nervous System
The parasympathetic nervous system is not just responsible for maintaining bodily functions; it also plays a vital role in promoting emotional well-being. When activated, this system helps to create a sense of calmness and tranquility, reducing stress and anxiety.
Think of a serene garden, where colorful flowers bloom, birds chirp, and a gentle breeze rustles the leaves. That’s the kind of atmosphere the parasympathetic nervous system strives to create within your body. By slowing down the heart rate and decreasing blood pressure, it allows you to experience a state of deep relaxation.
Furthermore, the parasympathetic nervous system is closely linked to processes such as sleep and sexual arousal. It helps prepare your body for a good night’s sleep by promoting the release of melatonin, the hormone that regulates sleep-wake cycles. Additionally, it plays a significant role in sexual arousal by increasing blood flow to the genital area, enhancing sensitivity and pleasure.
Understanding the Parasympathetic Nervous System Components
Similar to the sympathetic nervous system, the parasympathetic nervous system consists of a series of nerves that originate from both the brainstem and the lower spinal cord. These nerves, like branches of a tree, extend throughout the body, reaching various organs and tissues.
One of the key players in the parasympathetic response is the vagus nerve. This remarkable nerve, also known as the wanderer, wanders through the body, connecting to vital organs such as the heart, lungs, and digestive system. It acts as a messenger, relaying information between these organs and the brain.
When the vagus nerve is activated, it sets off a cascade of responses that promote relaxation and restoration. It slows down the heart rate, allowing it to beat at a steady rhythm. It also stimulates the smooth muscles in the digestive tract, promoting efficient digestion and absorption of nutrients.
Moreover, the vagus nerve has been found to play a crucial role in the mind-body connection. It has a direct influence on our emotional well-being, with studies showing that stimulating the vagus nerve can alleviate symptoms of depression and anxiety.
So, the next time you find yourself feeling calm and content, remember to thank your parasympathetic nervous system and its faithful companion, the vagus nerve. They work tirelessly to ensure your body and mind find balance and harmony in the midst of life’s chaos.
The Interplay Between Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Systems
Although the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems have distinct functions, they work in harmony to maintain a delicate balance within the body. This balance is critical for overall health and well-being.
The sympathetic nervous system is responsible for the body’s fight-or-flight response, which prepares the body for action in times of perceived danger or stress. On the other hand, the parasympathetic nervous system promotes rest and relaxation, allowing the body to recover and conserve energy.
Balancing Act: Sympathetic vs Parasympathetic
In a healthy individual, the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems work in opposition to one another, maintaining equilibrium. When the sympathetic nervous system is activated, the parasympathetic system acts to bring the body back to a state of rest and relaxation once the perceived threat or danger has passed.
For example, imagine a person encountering a wild animal in the woods. The sympathetic nervous system would kick in, increasing heart rate, dilating the pupils, and releasing stress hormones like adrenaline, preparing the individual to fight or flee. Once the danger has passed, the parasympathetic nervous system takes over, slowing down heart rate, constricting the pupils, and promoting digestion and healing.
It is essential for these two systems to work together in order to maintain optimal functioning of various bodily processes. They act as a dynamic duo, ensuring that the body can respond appropriately to different situations while also promoting recovery and restoration.
Impact of Imbalance Between the Two Systems
An imbalance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems can have significant effects on overall health. Chronic stress or prolonged activation of the sympathetic nervous system can lead to a range of health problems, including high blood pressure, heart disease, and gastrointestinal issues.
Conversely, an underactive sympathetic nervous system or an overactive parasympathetic nervous system can also have adverse effects. An underactive sympathetic system may result in a lack of energy, decreased motivation, and poor stress response. On the other hand, an overactive parasympathetic system may lead to excessive tiredness, digestion problems, and reduced heart rate.
It is important to note that maintaining a balance between these two systems is crucial for overall well-being. Various lifestyle factors, such as regular exercise, adequate sleep, and stress management techniques, can help promote this balance.
In conclusion, the interplay between the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems is a fascinating aspect of human physiology. These two systems work together to ensure that the body can respond to stressors while also promoting rest and recovery. Understanding this delicate balance can help individuals make informed decisions about their health and well-being.
The Role of Nerve Pathways in These Systems
Nerve pathways are crucial for the communication and transmission of nerve impulses within the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. These pathways play a vital role in ensuring the smooth functioning of these systems, allowing for the coordination of various physiological processes.
How Nerve Pathways Facilitate Communication
In both systems, nerve pathways allow for the transmission of signals from the central nervous system to the various organs and tissues throughout the body. These pathways consist of bundles of nerve fibers that carry the necessary information to initiate appropriate responses.
Within the sympathetic nervous system, nerve pathways primarily involve a series of interconnected ganglia that allow for rapid transmission of impulses. These ganglia serve as relay stations, facilitating the quick and efficient delivery of signals to their intended destinations. This rapid transmission is crucial in situations requiring immediate responses, such as the fight-or-flight response.
In contrast, the parasympathetic nervous system utilizes longer pathways involving both the vagus nerve and other nerves originating from the brainstem and lower spinal cord. These pathways are responsible for transmitting signals that promote rest, relaxation, and digestion. The vagus nerve, in particular, plays a significant role in regulating heart rate, breathing, and digestion.
The Importance of Healthy Nerve Pathways
Healthy nerve pathways are essential for the proper functioning of both the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. Any disruption or damage to these pathways can lead to impaired communication and a variety of health problems.
For example, in the sympathetic nervous system, damage to the nerve pathways can result in a dysregulated fight-or-flight response. This can lead to chronic stress, increased blood pressure, and a weakened immune system. Similarly, dysfunction in the parasympathetic nervous system’s pathways can cause digestive issues, irregular heart rate, and difficulty relaxing.
It’s important to note that maintaining healthy nerve pathways requires an overall healthy lifestyle, including proper nutrition, regular exercise, and stress management techniques. Adequate nutrition provides the necessary building blocks for nerve cell maintenance and repair, while regular exercise promotes blood flow and oxygenation, supporting the health of nerve pathways. Additionally, stress management techniques, such as meditation and deep breathing exercises, can help reduce chronic stress and promote the optimal functioning of these pathways.
In conclusion, nerve pathways play a critical role in facilitating communication within the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. These pathways allow for the transmission of signals from the central nervous system to various organs and tissues, ensuring the coordination of physiological processes. Maintaining healthy nerve pathways is essential for overall well-being and requires a holistic approach to health and wellness.
Conclusion: The Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Systems in Harmony
In conclusion, the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems are integral components of the overall nervous system. They work together to regulate various bodily functions, maintain balance, and adapt to different situations.
Understanding the components of these nerve pathways provides insight into how our bodies respond to stress, how we achieve rest and relaxation, and the importance of maintaining a healthy balance between the two systems.
While it’s fascinating to delve into the intricate workings of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems, it’s important to recognize that individual experiences can vary. If you have concerns about your nervous system or any related symptoms, it is always advised to consult with a qualified healthcare professional who can provide accurate diagnosis and guidance based on your specific circumstances.