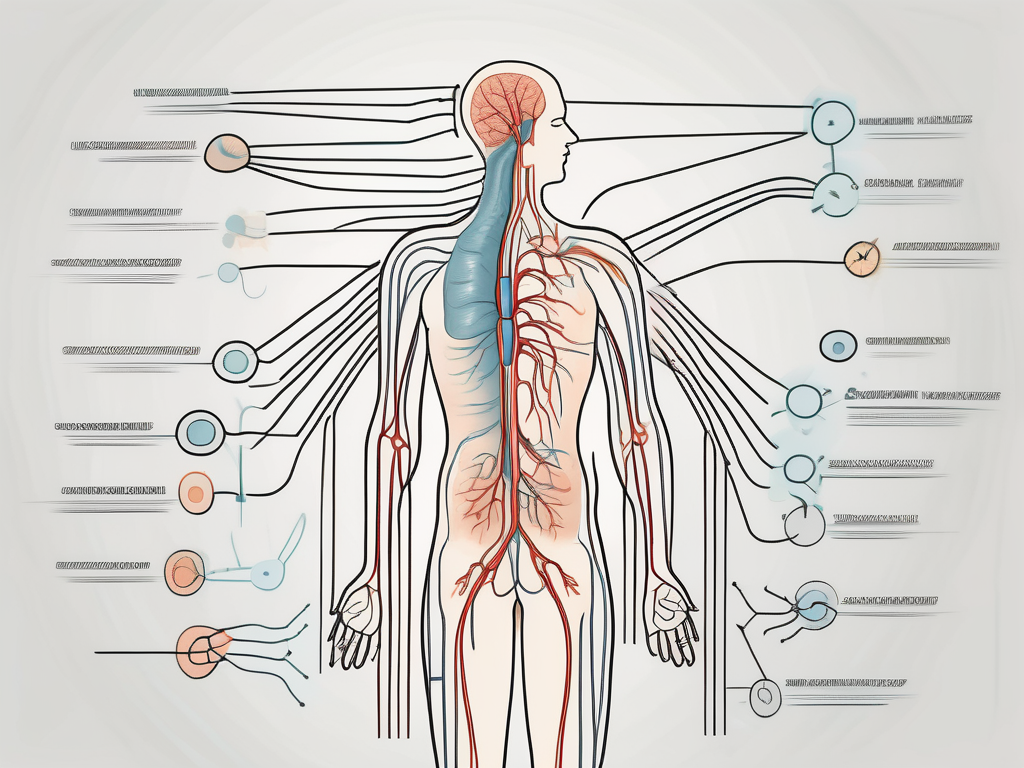
The parasympathetic nervous system, a crucial component of our autonomic nervous system, plays a significant role in regulating various bodily functions. Its impact on our overall health and well-being cannot be overstated. Understanding the intricacies of parasympathetic nerve regulation can provide us with valuable insights into the inner workings of our bodies and how they respond to different stimuli.
Understanding the Parasympathetic Nervous System
Before delving into the impact of parasympathetic nerve regulation, it is important to grasp a comprehensive understanding of the parasympathetic nervous system itself. Situated within the autonomic nervous system, the parasympathetic branch functions to counterbalance the sympathetic branch, which is responsible for our “fight or flight” response.
While the sympathetic branch prepares our bodies for quick action, the parasympathetic branch acts as its counterpart, promoting relaxation, digestion, and restorative processes. Together, these two branches maintain a delicate balance that allows our bodies to efficiently respond to various situations.
The parasympathetic nervous system, often referred to as the “rest and digest” system, plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis. It is responsible for conserving and restoring energy, ensuring that our bodies remain in a state of equilibrium. By slowing down heart rate, reducing blood pressure, and decreasing the release of stress hormones, the parasympathetic system aids in promoting calmness and relaxation.
The Role of the Parasympathetic Nervous System
One of the primary roles of the parasympathetic nervous system is to conserve and restore energy. It counteracts the stress response triggered by the sympathetic nervous system, ensuring that our bodies remain in a state of equilibrium. By slowing down heart rate, reducing blood pressure, and decreasing the release of stress hormones, the parasympathetic system aids in promoting calmness and relaxation.
In addition to its role in maintaining homeostasis, the parasympathetic nervous system actively regulates vital bodily functions. One of its key functions is digestion. It controls the muscles that aid in digestion, stimulating saliva production and promoting the release of digestive enzymes. This ensures that the food we consume is properly broken down and absorbed by the body, providing us with the necessary nutrients for optimal health.
Furthermore, the parasympathetic branch influences reproductive processes. It promotes sexual arousal by increasing blood flow to the genital area, facilitating the physiological changes necessary for sexual activity. This branch also plays a role in urination, stimulating bladder contraction to ensure proper emptying and prevent urinary retention.
Key Functions of the Parasympathetic Nervous System
The parasympathetic nervous system actively regulates vital bodily functions, including digestion, reproduction, and urination. It controls the muscles that aid in digestion, stimulating saliva production and promoting the release of digestive enzymes. Additionally, it promotes sexual arousal by increasing blood flow to the genital area and stimulates bladder contraction for proper emptying.
Furthermore, the parasympathetic branch influences ocular health by controlling the constriction of the pupil and the shape of the lens. This ensures optimal vision and protects the eyes from harmful external factors.
Overall, the parasympathetic nervous system plays a crucial role in maintaining our overall well-being. By counteracting the effects of the sympathetic nervous system, it promotes relaxation, digestion, and restorative processes. Understanding the intricate workings of this branch of the autonomic nervous system allows us to appreciate the complexity of our body’s responses and the importance of maintaining a healthy balance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems.
The Science of Parasympathetic Nerve Regulation
Understanding the mechanism of parasympathetic nerve regulation is essential in comprehending its impact on our health and well-being. This intricate system primarily operates through the vagus nerve, also known as the tenth cranial nerve. The vagus nerve extends from the brainstem to various organs, playing a crucial role in transmitting signals that stimulate the parasympathetic response.
The parasympathetic nervous system, often referred to as the “rest and digest” system, is responsible for promoting relaxation and restoring bodily functions after moments of stress or arousal. It acts as a counterbalance to the sympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for the body’s “fight or flight” response.
The Mechanism of Parasympathetic Nerve Regulation
When the body encounters a stimulus that requires a parasympathetic response, the vagus nerve releases acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that signals surrounding tissues and organs. This leads to a cascade of reactions, resulting in the relaxation and restoration of bodily functions. For instance, the release of acetylcholine may slow down heart rate, increase digestive enzyme production, and enhance blood flow to the digestive organs.
Furthermore, the parasympathetic nervous system influences the gastrointestinal tract, playing a crucial role in digestion and nutrient absorption. It stimulates the production of digestive enzymes, promotes peristalsis (the rhythmic contractions of the digestive tract), and increases blood flow to the digestive organs, ensuring optimal nutrient breakdown and absorption.
In addition to its effects on the digestive system, the parasympathetic branch also plays a significant role in promoting urinary and reproductive functions. It stimulates the bladder to contract, facilitating the elimination of waste products, and enhances sexual arousal and reproductive processes.
The Relationship between Parasympathetic Nerve Regulation and Body Functions
The parasympathetic nervous system closely interacts with various bodily systems to maintain harmony within the body. It collaborates with the cardiovascular system to regulate heart rate, blood pressure, and blood vessel constriction, ensuring efficient circulation throughout the body. Moreover, it influences the respiratory system, playing a role in controlling breathing patterns and optimizing lung function.
Additionally, the parasympathetic branch works in tandem with the endocrine system, aiding in hormone regulation and secretion. By modulating the release of hormones such as insulin and cortisol, it supports metabolic processes and stress response regulation.
Furthermore, the parasympathetic nervous system has been shown to have a profound impact on mental health and emotional well-being. Activation of the parasympathetic response promotes a state of calmness and relaxation, helping to alleviate symptoms of anxiety, stress, and depression. It also plays a role in promoting restful sleep and enhancing cognitive function.
In conclusion, the parasympathetic nervous system and its regulation through the vagus nerve are integral to maintaining overall health and well-being. Understanding the intricate mechanisms by which it operates allows us to appreciate its impact on various bodily functions and opens avenues for therapeutic interventions aimed at promoting balance and harmony within the body.
The Impact of Parasympathetic Nerve Regulation on Health
Parasympathetic nerve regulation has profound implications for both our mental and physical health. Finding balance and nurturing the parasympathetic response can significantly contribute to overall well-being.
When it comes to mental health, the parasympathetic nervous system plays a significant role in managing stress and anxiety. By activating the relaxation response, it counteracts the physiological effects of stress, leading to a sense of calmness and tranquility. Engaging in activities that promote parasympathetic activation, such as mindfulness exercises, deep breathing techniques, and meditation, can have a positive impact on mental health and assist in stress management.
However, it is essential to note that parasympathetic nerve regulation should complement professional mental health care. While these techniques can be beneficial, if experiencing prolonged or severe mental health challenges, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or therapist for appropriate guidance and support.
Turning our attention to physical health, the impact of parasympathetic nerve regulation extends beyond mental well-being and influences various aspects of our physical well-being. Adequate parasympathetic stimulation supports healthy digestion and efficient nutrient absorption, contributing to optimal gastrointestinal function.
In addition to digestive health, the parasympathetic branch aids in maintaining an ideal heart rate and blood pressure, which are crucial for cardiovascular health. By lowering heart rate and blood pressure, parasympathetic nerve regulation can reduce the risk of hypertension and other cardiovascular diseases.
Furthermore, the parasympathetic system has been linked to immune function modulation. Research suggests that its activation encourages a balanced immune response, potentially reducing the risk of chronic inflammation and associated conditions.
Overall, nurturing and supporting the parasympathetic response through various techniques and practices can have a significant impact on both our mental and physical health. By finding balance and engaging in activities that promote parasympathetic activation, we can enhance our overall well-being and lead healthier lives.
The Potential of Parasympathetic Nerve Regulation in Medicine
The remarkable potential of parasympathetic nerve regulation has sparked interest in medical research and therapeutic applications. Medical professionals and researchers are exploring the possibilities of leveraging this system to improve health outcomes and develop innovative treatments.
Parasympathetic nerve regulation plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis in the body. This branch of the autonomic nervous system is responsible for the “rest and digest” response, which counterbalances the “fight or flight” response of the sympathetic nervous system. By activating the parasympathetic system, the body can conserve energy, promote digestion, and enhance overall well-being.
Therapeutic Applications of Parasympathetic Nerve Regulation
The field of bioelectronic medicine is actively investigating the potential of neuromodulation to harness the power of the parasympathetic nervous system. By delivering targeted electrical or chemical stimuli to specific nerves, researchers aim to modulate parasympathetic responses for therapeutic purposes. This approach shows promise in treating various conditions, including chronic pain, inflammatory disorders, and cardiovascular diseases.
For example, in the realm of chronic pain management, researchers are exploring the use of vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) to alleviate symptoms. VNS involves the implantation of a device that delivers electrical impulses to the vagus nerve, a major parasympathetic nerve. These electrical signals can help regulate pain perception and reduce the reliance on traditional pain medications.
Inflammatory disorders, such as rheumatoid arthritis and Crohn’s disease, also hold potential for parasympathetic nerve regulation-based therapies. By modulating the parasympathetic system, researchers aim to dampen the inflammatory response and alleviate symptoms associated with these conditions. This approach offers a promising alternative to conventional immunosuppressive treatments, which often come with significant side effects.
Furthermore, cardiovascular diseases, including hypertension and heart failure, are being targeted through parasympathetic nerve regulation. Researchers are exploring techniques to enhance parasympathetic activity and promote heart rate variability, which can have a positive impact on cardiac function and overall cardiovascular health.
Future Directions in Parasympathetic Nerve Regulation Research
As our understanding of the parasympathetic nervous system expands, so does the potential for groundbreaking research. Scientists are continuously exploring new avenues to optimize parasympathetic nerve regulation and its impact on health. Future research may focus on developing non-invasive techniques, refining neuromodulation strategies, and uncovering novel therapeutic targets.
Non-invasive techniques, such as transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation (tVNS), are being investigated as a more accessible alternative to invasive procedures. tVNS involves the application of electrical stimulation to the skin overlying the vagus nerve, allowing for potential therapeutic benefits without the need for surgical implantation.
Refining neuromodulation strategies is another area of active research. Scientists are working on improving the precision and specificity of electrical or chemical stimuli delivery to target specific parasympathetic pathways. This fine-tuning of neuromodulation techniques can lead to more effective and personalized treatments for various conditions.
Moreover, uncovering novel therapeutic targets within the parasympathetic nervous system is an exciting avenue for future research. By identifying specific receptors, neurotransmitters, or signaling pathways, researchers can develop targeted therapies that modulate parasympathetic responses with greater precision and efficacy.
In conclusion, the potential of parasympathetic nerve regulation in medicine is vast and promising. From bioelectronic medicine to non-invasive techniques and novel therapeutic targets, researchers are actively exploring ways to harness the power of the parasympathetic nervous system for improved health outcomes. As our understanding deepens, the future holds exciting possibilities for leveraging parasympathetic nerve regulation in innovative and transformative ways.
Conclusion: The Significance of Parasympathetic Nerve Regulation
Through its multifaceted influence on our mental and physical well-being, parasympathetic nerve regulation holds immense importance in understanding the intricacies of the human body. Recognizing the vital role it plays in maintaining overall health empowers individuals to prioritize activities that promote relaxation, rejuvenation, and balance. However, it is always prudent to consult with medical professionals for personalized advice and guidance tailored to individual circumstances.
Recap of Parasympathetic Nerve Regulation Impact
To recap, the parasympathetic nervous system is responsible for restoring and conserving energy, promoting relaxation, digestion, and reproductive functions. It counteracts the sympathetic nervous system, which orchestrates the “fight or flight” response.
Parasympathetic nerve regulation encompasses various bodily systems, including the cardiovascular, respiratory, and endocrine systems. It influences heart rate, blood circulation, breathing patterns, and hormonal balance.
The Future of Parasympathetic Nerve Regulation
The future of parasympathetic nerve regulation holds exciting possibilities in the fields of bioelectronic medicine and neuromodulation. Ongoing research and advancements may lead to innovative therapies and applications that leverage the power of the parasympathetic system to enhance health outcomes.
As we continue to explore the potential of parasympathetic nerve regulation, it is essential to approach these advances with caution and consult with healthcare professionals for individualized advice. Unlocking the full impact of this intricate system requires a collaborative effort between medical experts, researchers, and individuals seeking to optimize their well-being.