Spinal misalignment, also known as vertebral subluxation, is a condition that can have a profound impact on the parasympathetic nerve, a crucial component of our autonomic nervous system. Understanding the connection between spinal misalignment and the parasympathetic nerve is essential for anyone looking to maintain optimal health and well-being. In this article, we will explore the definition, causes, and symptoms of spinal misalignment, as well as delve into the role and function of the parasympathetic nerve. Additionally, we will discuss how spinal misalignment affects nervous system function, the potential health consequences associated with this condition, and the various treatment and prevention options available.
Understanding Spinal Misalignment
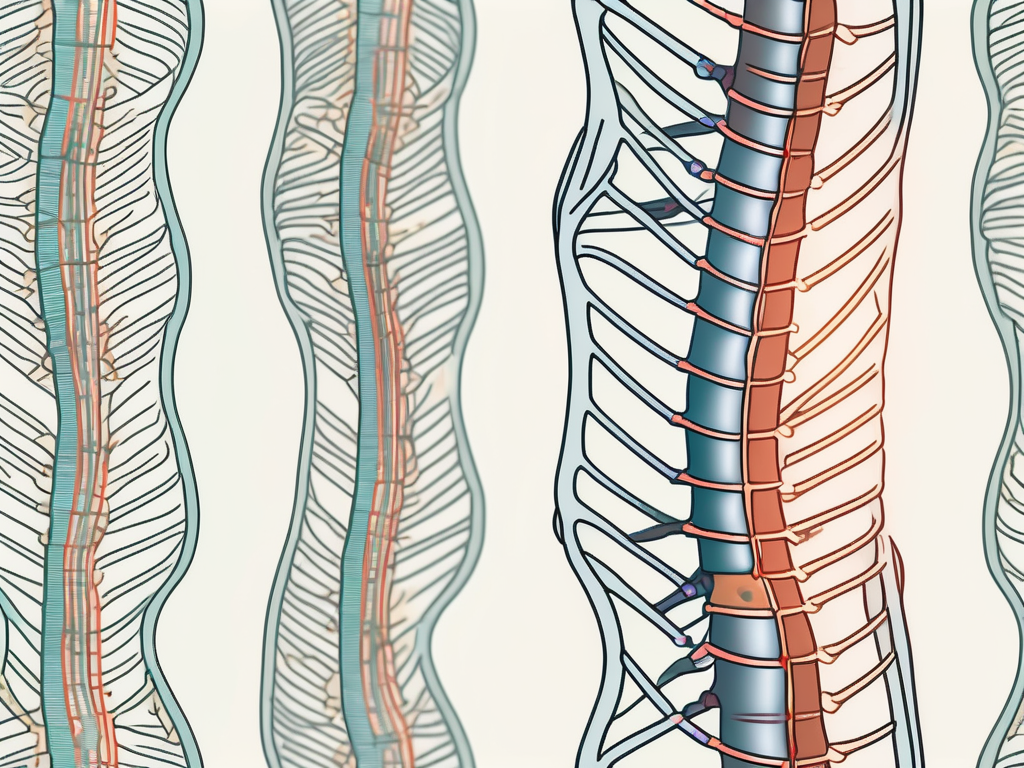
At its core, spinal misalignment refers to the improper alignment or positioning of the vertebrae in the spine. This misalignment can occur as a result of various factors, including trauma, poor posture, repetitive stress, and degenerative conditions. Regardless of the cause, spinal misalignment can negatively impact the parasympathetic nerve, which is responsible for regulating many vital bodily functions.
When the vertebrae are misaligned, they can put pressure on the surrounding nerves, including the parasympathetic nerve. This pressure disrupts the flow of communication between the brain and the body, leading to a host of potential health issues.
Definition and Causes of Spinal Misalignment
Spinal misalignment, or vertebral subluxation, is a condition where the vertebrae in the spine become misaligned or move out of their normal position. This often occurs due to trauma, such as a sports injury or car accident, but can also be caused by poor posture, repetitive stress, and degenerative conditions like arthritis.
When the vertebrae are misaligned, they can put pressure on the surrounding nerves, including the parasympathetic nerve. This pressure disrupts the flow of communication between the brain and the body, leading to a host of potential health issues.
It is important to note that spinal misalignment can occur at any age. In children, it can be caused by falls, sports injuries, or even the birthing process. In adults, it can be a result of poor posture, repetitive motions, or the natural wear and tear of the spine over time.
Additionally, certain lifestyle factors can contribute to spinal misalignment. For example, sitting for long periods, especially with poor posture, can put undue stress on the spine and increase the risk of misalignment. Similarly, engaging in activities that involve repetitive motions, such as heavy lifting or playing certain sports, can also lead to spinal misalignment.
Common Symptoms of Spinal Misalignment
Spinal misalignment can manifest in a variety of ways, and the symptoms can vary from person to person. Some common signs of spinal misalignment include:
- Chronic back or neck pain: Misaligned vertebrae can cause chronic pain in the affected area. This pain may be dull and achy or sharp and shooting, depending on the severity of the misalignment.
- Headaches and migraines: The pressure on the nerves caused by spinal misalignment can lead to frequent headaches and migraines. These headaches may be accompanied by neck pain or stiffness.
- Numbness or tingling in the extremities: When the nerves in the spine are compressed due to misalignment, it can result in numbness or tingling sensations in the arms, hands, legs, or feet.
- Poor posture: Misalignment in the spine can affect the overall alignment of the body, leading to poor posture. This can cause additional strain on the muscles and joints, further exacerbating the issue.
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan. They can perform a thorough examination, which may include imaging tests like X-rays or MRI scans, to determine the extent of the misalignment and develop an individualized treatment approach.
The Parasympathetic Nerve Explained
The parasympathetic nerve is one of the two branches of the autonomic nervous system, which controls involuntary bodily functions. It works in opposition to the sympathetic nerve, which is responsible for the body’s fight-or-flight response. The parasympathetic nerve promotes rest and relaxation, regulates digestion, and supports many other vital bodily functions.
The parasympathetic nerve plays a crucial role in regulating bodily functions such as heart rate, digestion, and respiratory rate. It promotes a state of calm and rest, allowing the body to recover and repair. When the parasympathetic nerve is functioning optimally, the body can maintain a healthy balance and adapt to stressors efficiently.
However, when spinal misalignment occurs, it can disrupt the communication between the brain and the parasympathetic nerve, leading to a dysregulation of these vital functions.
The anatomy of the parasympathetic nerve is fascinating and complex. It originates in the brain and travels down the spinal cord, where it branches out and innervates various organs and tissues. This intricate network of nerves and neurotransmitters allows the parasympathetic nerve to regulate bodily functions systematically.
Let’s delve deeper into the role and function of the parasympathetic nerve. One of its primary responsibilities is to regulate heart rate. When the body is in a state of rest, the parasympathetic nerve slows down the heart rate, ensuring that it beats at a steady and healthy pace. This is crucial for maintaining cardiovascular health and preventing conditions such as hypertension and heart disease.
In addition to heart rate regulation, the parasympathetic nerve also plays a vital role in digestion. It stimulates the production of digestive enzymes and increases blood flow to the digestive organs, promoting efficient digestion and nutrient absorption. When the parasympathetic nerve is functioning optimally, individuals experience regular bowel movements, reduced bloating, and improved overall digestive health.
Furthermore, the parasympathetic nerve is involved in respiratory regulation. It helps to slow down the breathing rate and deepen the breath, allowing for efficient oxygen exchange in the lungs. This is essential for maintaining healthy lung function and overall respiratory health.
Another fascinating aspect of the parasympathetic nerve is its involvement in sexual arousal and reproduction. It plays a crucial role in the physiological responses associated with sexual activity, such as increased blood flow to the genital area and the release of sexual hormones. Dysfunction of the parasympathetic nerve can lead to sexual health issues, including erectile dysfunction and decreased libido.
Overall, the parasympathetic nerve is a vital component of the autonomic nervous system, ensuring that the body functions optimally in a state of rest and relaxation. Its intricate network of nerves and neurotransmitters allows for the regulation of various bodily functions, including heart rate, digestion, respiratory rate, and sexual arousal. Understanding the role and function of the parasympathetic nerve is crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being.
The Connection Between the Spine and the Parasympathetic Nerve
The spine serves as the protective housing for the spinal cord, which is an extension of the central nervous system. It plays a critical role in facilitating communication between the brain and the body. When spinal misalignment occurs, it can profoundly affect the parasympathetic nerve and its ability to function optimally.
The parasympathetic nerve is part of the autonomic nervous system, which controls involuntary bodily functions such as digestion, sleep, and immune response. It works in opposition to the sympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for the body’s fight-or-flight response. The parasympathetic nerve helps the body rest, digest, and recover from stress.
How Spinal Misalignment Affects Nervous System Function
When the vertebrae in the spine become misaligned, they can put pressure on the spinal cord and the surrounding nerves. This pressure disrupts the flow of information between the brain and the parasympathetic nerve, leading to the dysregulation of bodily functions. As a result, individuals may experience a variety of health issues, including digestive problems, sleep disturbances, and weakened immune function.
For example, misalignment in the upper cervical spine can interfere with the parasympathetic nerve’s control over digestion. This can lead to symptoms such as acid reflux, bloating, and constipation. Similarly, misalignment in the thoracic spine can affect the nerve’s ability to regulate heart rate and blood pressure, potentially contributing to cardiovascular problems.
It is crucial to note that spinal misalignment should be properly diagnosed and treated by a qualified healthcare professional. They can perform a thorough examination, which may include imaging studies, to determine the extent of misalignment and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
The Impact of Spinal Health on Parasympathetic Activity
Maintaining a healthy spine is crucial for supporting optimal parasympathetic activity. Regular chiropractic care, along with other preventative measures like proper posture and exercise, can help promote spinal health. When the spine is properly aligned, it allows for optimal communication between the brain and the parasympathetic nerve, supporting overall well-being.
Chiropractic adjustments, which involve gentle manipulations of the spine, can help realign the vertebrae and relieve pressure on the spinal cord and nerves. This can restore proper communication between the brain and the parasympathetic nerve, allowing for improved function of the autonomic nervous system.
In addition to chiropractic care, maintaining good posture is essential for spinal health. Poor posture can lead to spinal misalignment over time, which can negatively impact the parasympathetic nerve. Engaging in exercises that strengthen the core muscles and promote proper alignment can also contribute to spinal health and support the optimal functioning of the parasympathetic nerve.
In conclusion, the connection between the spine and the parasympathetic nerve is crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being. Spinal misalignment can disrupt the flow of information between the brain and the parasympathetic nerve, leading to various health issues. However, with proper diagnosis and treatment, including chiropractic care and lifestyle modifications, individuals can support spinal health and optimize parasympathetic activity.
Potential Health Consequences of Spinal Misalignment
Spinal misalignment can have widespread consequences on overall health and well-being. Understanding these potential health implications is essential for individuals seeking to prioritize their spinal health and overall quality of life.
When it comes to spinal misalignment, the consequences extend far beyond just discomfort. Let’s dive deeper into some of the potential health issues that can arise from this condition.
Chronic Pain and Discomfort
One of the most apparent consequences of spinal misalignment is chronic pain and discomfort. As the misaligned vertebrae put pressure on the nerves, it can lead to persistent pain in the affected area. This pain may radiate to other parts of the body and significantly impact daily activities and quality of life.
Imagine waking up every morning with a throbbing pain in your lower back or a shooting pain down your leg. Simple tasks like bending over to tie your shoes or sitting for extended periods become excruciating. The constant discomfort can take a toll on your physical and mental well-being, affecting your ability to enjoy life to the fullest.
If you are suffering from chronic pain, it is important to seek professional medical advice to pinpoint the cause and discuss appropriate treatment options. Ignoring the issue can lead to further complications and a decline in overall health.
Digestive Issues and Immune System Impact
The parasympathetic nerve plays a vital role in regulating digestion and supporting a healthy immune system. When spinal misalignment affects the parasympathetic nerve, it can lead to digestive issues such as acid reflux, constipation, and bloating. Furthermore, impaired parasympathetic function can compromise the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections and illnesses.
Have you ever experienced frequent bouts of heartburn or struggled with irregular bowel movements? These uncomfortable digestive issues can be linked to spinal misalignment. The misaligned vertebrae can disrupt the normal flow of nerve signals that control the digestive system, leading to various gastrointestinal problems.
Additionally, a compromised immune system can make it harder for your body to fight off infections and viruses. This means you may find yourself falling ill more often or taking longer to recover from illnesses. Prioritizing spinal health and seeking appropriate treatment can help restore proper parasympathetic function and support overall well-being.
Mental Health Implications
Spinal misalignment can also have a significant impact on mental health. When the spine is misaligned, it can disrupt the balance of neurotransmitters and hormones that regulate mood and emotional well-being. This disruption can contribute to symptoms of anxiety, depression, and irritability.
Imagine feeling constantly on edge, overwhelmed by anxiety, or experiencing persistent feelings of sadness. These mental health symptoms can be linked to spinal misalignment. The misaligned vertebrae can interfere with the normal communication between the brain and the body, affecting the release and regulation of important mood-regulating chemicals.
If you are experiencing mental health symptoms, it is essential to reach out to a mental health professional, in addition to addressing any potential spinal misalignment. Taking a holistic approach to your well-being can help you find relief and regain control over your mental and emotional state.
In conclusion, spinal misalignment can have far-reaching consequences on your health. From chronic pain and discomfort to digestive issues, immune system impact, and mental health implications, it is crucial to prioritize your spinal health. Seeking appropriate treatment and taking proactive steps to maintain a healthy spine can significantly improve your overall quality of life.
Treatment and Prevention of Spinal Misalignment
Spinal misalignment, also known as vertebral subluxation, can cause a range of symptoms and discomfort. Fortunately, there are various treatment and prevention options available to address this issue. It is important to work with a qualified healthcare professional to develop an individualized plan based on your specific needs and condition.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options
Many individuals find relief from spinal misalignment through non-surgical treatment options such as chiropractic care, physical therapy, and massage therapy. These treatments focus on realigning the spine and relieving the pressure on the affected nerves, allowing for improved function and pain reduction.
Chiropractic care involves the manual manipulation of the spine to correct misalignments. This hands-on approach can help restore proper alignment, relieve tension, and promote overall spinal health. Physical therapy, on the other hand, utilizes targeted exercises and stretches to strengthen the muscles surrounding the spine and improve flexibility. By addressing muscle imbalances and weakness, physical therapy can help prevent further misalignment and promote long-term spinal health.
Massage therapy, often used in conjunction with chiropractic care and physical therapy, can provide additional relief by reducing muscle tension, improving blood circulation, and promoting relaxation. This hands-on therapy can help alleviate pain and discomfort associated with spinal misalignment.
It is important to note that these non-surgical treatments should be performed by licensed professionals who specialize in spinal health and have extensive experience in the field. This ensures that you receive safe and effective care tailored to your specific needs.
The Role of Physical Therapy and Exercise
In addition to chiropractic care, physical therapy can play a significant role in the treatment and prevention of spinal misalignment. A trained physical therapist can provide exercises and stretches specifically designed to target the affected areas and strengthen the surrounding muscles, reducing the risk of further misalignment.
Engaging in regular exercise, such as core-strengthening exercises and activities that promote proper posture, can also support spinal health and reduce the risk of misalignment. Strong core muscles provide stability and support to the spine, helping to maintain proper alignment and reduce the strain on the vertebral joints.
Furthermore, activities that promote proper posture, such as yoga and Pilates, can help improve spinal alignment and reduce the risk of misalignment. These exercises focus on strengthening the muscles that support the spine and promoting body awareness, which can contribute to better posture and spinal health.
Preventative Measures for Spinal Health
Prevention is always better than cure when it comes to spinal misalignment. By practicing good posture, maintaining a healthy weight, and engaging in regular physical activity, individuals can reduce the risk of spinal misalignment and support optimal spinal health.
Proper posture is essential for maintaining spinal alignment. It is important to be mindful of your posture throughout the day, whether you are sitting, standing, or walking. Avoid slouching or hunching over, and make an effort to keep your spine in a neutral position. Using ergonomic chairs and supportive pillows can also help maintain good posture and reduce the risk of misalignment.
Maintaining a healthy weight is another crucial aspect of spinal health. Excess weight can put additional stress on the spine, increasing the risk of misalignment and related complications. By adopting a balanced diet and engaging in regular exercise, individuals can achieve and maintain a healthy weight, reducing the strain on their spines.
Additionally, ergonomics play a significant role in spinal health. Ensuring proper ergonomics at workstations and during daily activities can help minimize stress on the spine and reduce the risk of misalignment. This includes using ergonomic chairs and desks, positioning computer monitors at eye level, and taking regular breaks to stretch and move around.
In conclusion, spinal misalignment can have a profound impact on the parasympathetic nerve, which regulates many vital bodily functions. Understanding the connection between spinal health and the parasympathetic nerve is crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being. By seeking appropriate treatment, practicing preventative measures, and working with qualified healthcare professionals, individuals can take control of their spinal health and optimize their quality of life. Remember, if you are experiencing symptoms or suspect spinal misalignment, consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan tailored to your specific needs.