The cranial parasympathetic nerve plays a crucial role in the overall functioning and regulation of the human body. Understanding its anatomy, functions, and potential disorders is essential for both medical professionals and individuals seeking to maintain optimal health. This comprehensive overview aims to shed light on the complexities of the cranial parasympathetic nerve, while also highlighting potential treatment options and future research directions. It is important to note that this article does not provide medical advice, and individuals experiencing any concerns or symptoms should consult with a qualified healthcare professional.
Understanding the Cranial Parasympathetic Nerve
The cranial parasympathetic nerve is a fascinating component of the parasympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for coordinating and regulating various bodily functions. It plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis and ensuring the optimal functioning of our body.
Anatomy and Structure of the Cranial Parasympathetic Nerve
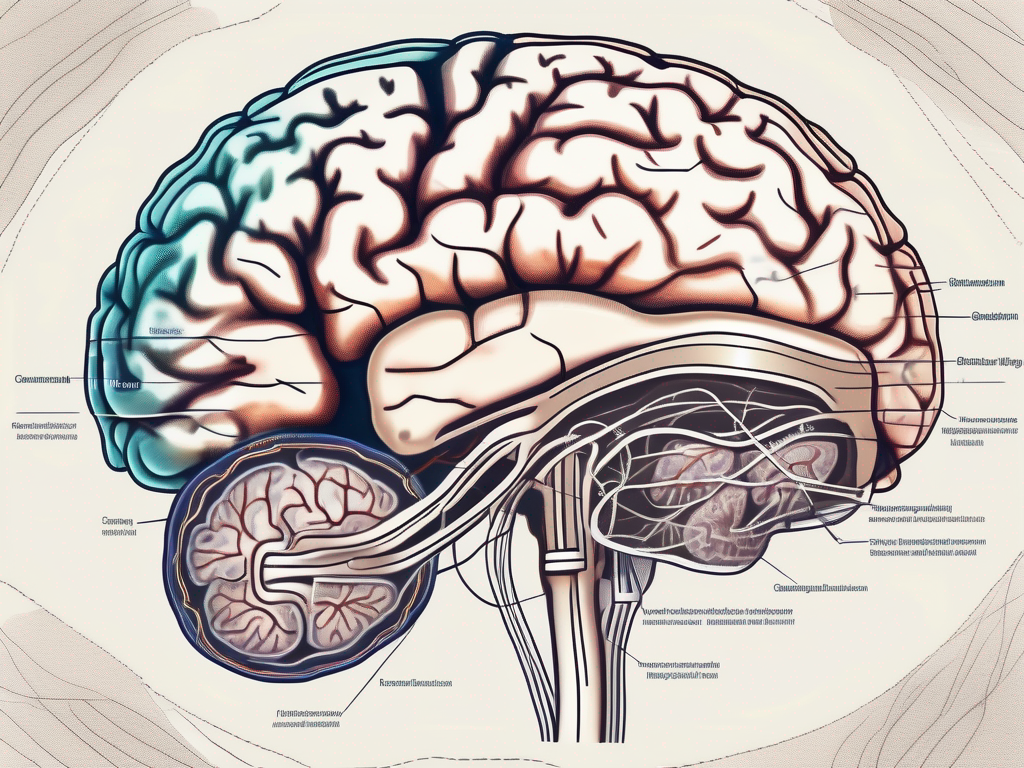
The cranial parasympathetic nerve consists of several cranial nerves, each originating in different regions of the brainstem. These cranial nerves include the oculomotor nerve (CN III), facial nerve (CN VII), glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX), and vagus nerve (CN X).
The oculomotor nerve, also known as CN III, controls pupil constriction, allowing our eyes to adjust to different lighting conditions. It is fascinating how this small nerve plays such a vital role in our visual perception and adaptation.
The facial nerve, or CN VII, is responsible for tear production and salivation. It enables us to shed tears when we are emotionally moved or when our eyes need lubrication. Additionally, it stimulates salivary glands, aiding in the digestion process.
The glossopharyngeal nerve, or CN IX, contributes to taste sensation and swallowing. It allows us to savor the flavors of our favorite foods and ensures that we can swallow them safely, preventing choking hazards.
The vagus nerve, also known as CN X, is a remarkable nerve that influences various bodily functions. It plays a crucial role in regulating heart rate, digestion, and respiratory processes. This nerve is responsible for the “rest and digest” response, promoting relaxation and optimal functioning of our body.
Functions of the Cranial Parasympathetic Nerve
The cranial parasympathetic nerve is involved in regulating important bodily functions, ensuring that they operate smoothly and efficiently.
One of its essential functions is digestion. Through the vagus nerve, the cranial parasympathetic nerve stimulates the secretion of digestive enzymes and increases blood flow to the gastrointestinal tract, promoting efficient digestion and nutrient absorption.
In addition to digestion, the cranial parasympathetic nerve also influences respiration. The vagus nerve plays a vital role in controlling the rate and depth of our breaths, ensuring that we receive an adequate supply of oxygen and expel carbon dioxide efficiently.
Furthermore, the cranial parasympathetic nerve contributes to heart rate regulation. The vagus nerve acts as a brake on the heart, slowing down the heart rate when necessary. This mechanism helps maintain a steady and balanced heartbeat, preventing irregularities and promoting cardiovascular health.
Another intriguing function of the cranial parasympathetic nerve is its involvement in glandular secretion. Through various cranial nerves, it stimulates the secretion of tears, saliva, and other essential fluids. These secretions play important roles in maintaining the health and functioning of our eyes, mouth, and other glands.
Overall, the cranial parasympathetic nerve is a complex and intricate system that ensures our body maintains a state of balance and optimal functioning. Imbalances or dysfunctions in this nerve can lead to a range of health issues that may require medical attention. Therefore, understanding the anatomy and functions of this nerve is crucial for maintaining our overall well-being.
The Parasympathetic Nervous System and Its Importance
The parasympathetic nervous system plays a vital role in maintaining the overall well-being of the body. It works in conjunction with the sympathetic nervous system to regulate bodily processes and ensure homeostasis. While the sympathetic nervous system prepares the body for fight or flight responses in stressful situations, the parasympathetic nervous system promotes relaxation and restoration.
Activation of the parasympathetic nervous system results in a cascade of physiological responses that are essential for optimal bodily function. One of the key effects of parasympathetic activation is the decrease in heart rate. This reduction in heart rate allows the body to conserve energy and promotes a state of calmness. Additionally, the parasympathetic nervous system causes the pupils to constrict, which helps to improve visual acuity and focus.
Another important function of the parasympathetic nervous system is its role in enhancing digestive processes. When activated, it increases the secretion of digestive enzymes and stimulates the smooth muscles in the gastrointestinal tract, promoting efficient digestion and absorption of nutrients. This is crucial for maintaining a healthy digestive system and ensuring proper nutrient utilization.
In addition to its effects on the heart and digestion, the parasympathetic nervous system also plays a role in regulating blood flow to various organs. When activated, it promotes vasodilation, allowing for increased blood flow to organs such as the liver, kidneys, and digestive system. This increased blood flow ensures that these organs receive an adequate supply of oxygen and nutrients, facilitating their optimal functioning.
Furthermore, the parasympathetic nervous system helps to relax the bronchial muscles in the respiratory system. This relaxation allows for easier and more efficient breathing, ensuring that the body receives an adequate supply of oxygen. It also helps to reduce respiratory distress and improve overall lung function.
The Parasympathetic Nervous System vs. the Sympathetic Nervous System
It is important to understand the distinction between the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems. While the parasympathetic nervous system promotes rest, digestion, and relaxation, the sympathetic nervous system triggers the body’s fight or flight response in times of stress or danger.
The sympathetic nervous system prepares the body for immediate action by increasing heart rate, dilating pupils, and redirecting blood flow to the muscles. This response is crucial for survival in threatening situations. On the other hand, the parasympathetic nervous system counteracts the effects of the sympathetic nervous system, promoting a state of rest and recovery.
Both systems work harmoniously to ensure the body responds appropriately to environmental cues, allowing balance between periods of alertness and rest. However, imbalances or chronic activation of the sympathetic nervous system can lead to various health implications, underscoring the importance of a well-functioning parasympathetic nervous system.
In conclusion, the parasympathetic nervous system is a crucial component of the autonomic nervous system. Its activation promotes relaxation, digestion, and restoration, allowing the body to maintain homeostasis. Understanding the role of the parasympathetic nervous system is essential for optimizing overall health and well-being.
The Cranial Parasympathetic Nerve and Health
The cranial parasympathetic nerve plays a crucial role in maintaining the overall health and functioning of the body. This nerve, also known as the cranial nerve, is responsible for regulating various bodily functions, including tear production, salivation, taste perception, digestion, and heart rate regulation.
Disorders Associated with the Cranial Parasympathetic Nerve
Several disorders can affect the cranial parasympathetic nerve and its associated cranial nerves. One common disorder is facial palsy, which occurs when there is damage or dysfunction to the cranial nerve responsible for facial movement. Facial palsy can result in facial paralysis, making it difficult for individuals to control their facial muscles and express emotions.
In addition to facial palsy, disorders affecting the cranial parasympathetic nerve can also lead to impairments in tear production or salivation. This can cause dry eyes or difficulty swallowing, making it challenging for individuals to perform everyday tasks and enjoy a comfortable quality of life.
Furthermore, some disorders may interfere with the ability to perceive taste sensations. This can greatly impact an individual’s enjoyment of food and beverages, as well as their overall nutritional intake. Additionally, dysfunction of the cranial parasympathetic nerve can disrupt important bodily functions such as digestion and heart rate regulation, leading to gastrointestinal issues and abnormal heart rhythms.
It is important to note that the diagnosis and management of these disorders should be left to qualified healthcare professionals. They have the expertise to perform comprehensive evaluations, develop individualized treatment plans, and provide appropriate guidance for individuals experiencing symptoms or concerns.
Impact of Cranial Parasympathetic Nerve Dysfunction
Dysfunction or damage to the cranial parasympathetic nerve can have significant impacts on an individual’s quality of life. The effects of this dysfunction can vary depending on the specific disorder and the extent of nerve damage.
One common symptom of cranial parasympathetic nerve dysfunction is dry eyes. When tear production is impaired, individuals may experience discomfort, blurred vision, and an increased risk of eye infections. Difficulty swallowing, another common symptom, can make it challenging to eat and drink, leading to malnutrition and dehydration if not properly managed.
Impaired digestion is another consequence of cranial parasympathetic nerve dysfunction. This can result in symptoms such as bloating, abdominal pain, and irregular bowel movements. In severe cases, it may even lead to malabsorption of nutrients and weight loss.
Abnormal heart rate is yet another possible effect of cranial parasympathetic nerve dysfunction. The parasympathetic nervous system plays a crucial role in regulating heart rate, and any disruption to this system can cause the heart to beat too fast or too slow. This can lead to symptoms such as palpitations, dizziness, and shortness of breath.
Recognizing and addressing these issues promptly is paramount to prevent further complications and improve the overall well-being of affected individuals. Seeking medical advice and undergoing appropriate diagnostic procedures is crucial for effective management and treatment. Healthcare professionals may recommend a combination of medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications to alleviate symptoms and restore normal functioning of the cranial parasympathetic nerve.
Treatment and Management of Cranial Parasympathetic Nerve Disorders
The treatment and management of cranial parasympathetic nerve disorders can be complex and multifaceted. It is important for healthcare professionals to develop customized treatment plans that address the specific needs and goals of each individual patient. These plans may vary depending on the underlying cause, specific symptoms, and individual patient factors.
One common approach to treating cranial parasympathetic nerve disorders is the use of medications. These medications are often prescribed to manage symptoms such as dry eyes or inhibited salivation. By targeting the underlying cause of these symptoms, medications can help individuals find relief and improve their overall quality of life.
In addition to medications, physical therapies can also play a crucial role in the treatment and management of cranial parasympathetic nerve disorders. For example, swallowing exercises or speech therapy can help individuals regain or enhance their ability to eat, drink, or communicate effectively. These therapies can be tailored to the specific needs of each patient, allowing for a personalized approach to treatment.
In some cases, surgical interventions may be necessary to address structural abnormalities or alleviate persistent symptoms. These procedures are typically reserved for rare cases where other treatment options have been unsuccessful. Surgical interventions are performed by skilled healthcare professionals who specialize in the treatment of cranial parasympathetic nerve disorders.
While current treatment options for cranial parasympathetic nerve disorders can be effective, ongoing research is focused on exploring new treatment modalities and deepening our understanding of the cranial parasympathetic nerve. This research aims to identify potential interventions for disorders affecting this essential component of our autonomic nervous system.
Future Research Directions in Cranial Parasympathetic Nerve Health
As medical and scientific knowledge advances, future research in cranial parasympathetic nerve health will continue to expand our understanding of this complex system. One area of focus is the investigation of novel therapies that can provide targeted and effective treatment for cranial parasympathetic nerve disorders.
Another important research direction is the refinement of diagnostic techniques. By improving our ability to accurately diagnose cranial parasympathetic nerve disorders, healthcare professionals can develop more precise treatment plans and improve patient outcomes.
Additionally, researchers are exploring strategies to enhance nerve regeneration and overall nerve health. This includes investigating potential therapies that can promote the growth and repair of damaged cranial parasympathetic nerves, leading to improved function and symptom relief.
Collaborations between healthcare professionals and researchers are critical in advancing our knowledge of cranial parasympathetic nerve disorders and improving their management. By working together, these experts can share insights, exchange ideas, and develop innovative approaches to treatment.
In conclusion, the treatment and management of cranial parasympathetic nerve disorders require a comprehensive and individualized approach. Medications, physical therapies, and surgical interventions may all play a role in addressing these disorders. Ongoing research is focused on expanding our understanding of the cranial parasympathetic nerve and identifying new treatment options. By staying at the forefront of medical advancements, healthcare professionals can provide the best possible care for individuals with cranial parasympathetic nerve disorders.
It is important to emphasize that this expanded article does not provide medical advice, and consulting with a qualified healthcare professional is necessary for accurate diagnosis, treatment, and personalized management plans.