The parasympathetic nerve plays a crucial role in regulating heart rate. Understanding how this intricate system works is essential for grasping the mechanisms behind heart rate reduction. By exploring the connection between the parasympathetic nervous system and heart rate, we can gain insight into the biochemical processes that underlie this phenomenon. Furthermore, we will examine the impact of parasympathetic activity on overall health and explore techniques for enhancing parasympathetic activity in order to manage heart rate effectively.
Understanding the Parasympathetic Nervous System
The parasympathetic nervous system is one of the two primary divisions of the autonomic nervous system, which controls involuntary bodily functions. Its main role is to counterbalance the sympathetic nervous system, which responds to stress and prepares the body for physical exertion. In contrast, the parasympathetic nerves help maintain homeostasis, promoting a state of relaxation and conserving energy.
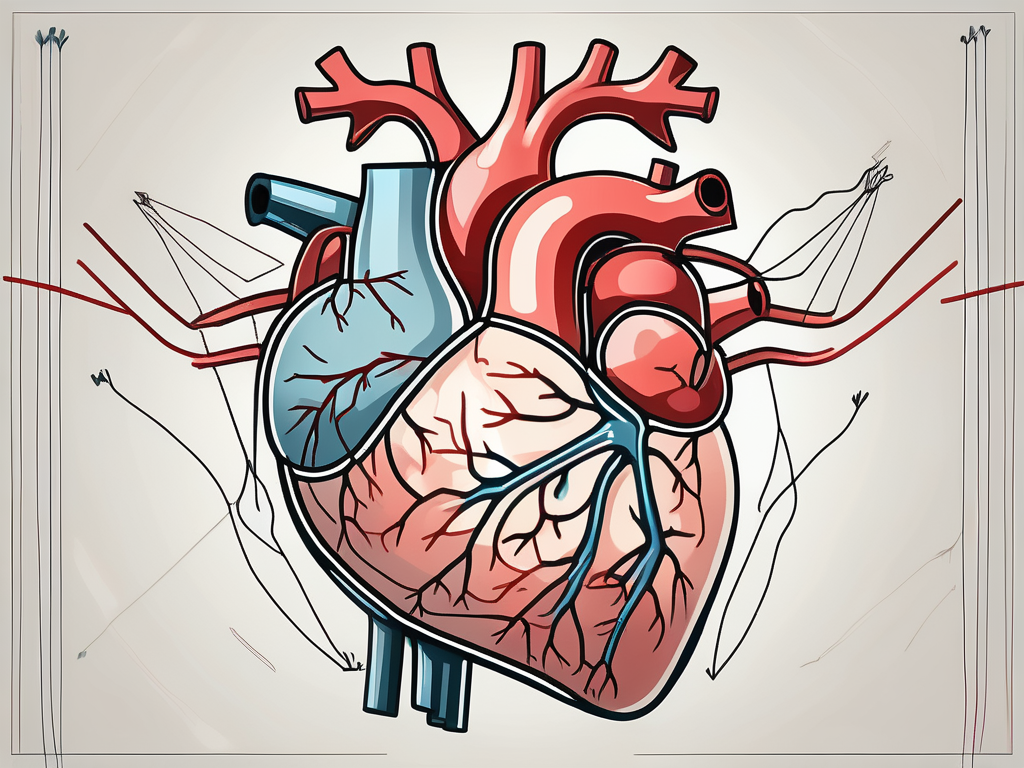
The parasympathetic nervous system primarily operates through the vagus nerve, also known as the tenth cranial nerve. Originating in the brainstem, this long and complex nerve extends all the way down to the abdomen, innervating various organs along the way, including the heart.
The parasympathetic nervous system encompasses a network of nerves that help regulate involuntary bodily functions. Its main function is to slow down heart rate, increase digestion, stimulate glandular secretions, and promote overall relaxation. By promoting rest and recovery, the parasympathetic nervous system helps maintain a balanced physiological state.
Specifically, the parasympathetic nerves release a neurotransmitter called acetylcholine, which binds to certain receptors in target organs, triggering a series of biochemical responses. These responses result in decreased heart rate, among other effects. Understanding this process is crucial for comprehending the role of the parasympathetic nerve in reducing heart rate.
The parasympathetic nervous system exerts its influence on the heart through various mechanisms. One of the key ways it decreases heart rate is by inhibiting the activity of the sinoatrial (SA) node, often referred to as the heart’s natural pacemaker. The SA node generates electrical impulses that regulate the heart’s rhythm, and the parasympathetic nerves slow down this process.
Additionally, parasympathetic activity reduces the conduction velocity of electrical signals throughout the heart, further contributing to a decreased heart rate. By suppressing the heart’s electrical activity, the parasympathetic nervous system promotes a state of relaxation, allowing the heart to beat more slowly and efficiently.
It is important to note that while the parasympathetic nervous system predominantly decreases heart rate, it does not solely govern heart function. The sympathetic nervous system, with its fight-or-flight response, also plays a significant role in regulating heart rate and can override the parasympathetic influence in certain situations.
The parasympathetic nervous system not only affects the heart but also has widespread effects on other organs in the body. For example, it stimulates glandular secretions, such as saliva production, gastric acid secretion, and pancreatic enzyme release, which aid in digestion. Additionally, it promotes smooth muscle contraction in the gastrointestinal tract, facilitating the movement of food through the digestive system.
Furthermore, the parasympathetic nervous system promotes relaxation and rest by constricting the pupils of the eyes, facilitating near vision and reducing the amount of light entering the eyes. It also stimulates bronchoconstriction, which narrows the airways in the lungs, helping to conserve energy and promote a calm state.
Another important function of the parasympathetic nervous system is its role in sexual arousal and reproduction. It is responsible for the release of nitric oxide, a vasodilator that relaxes the smooth muscles in the blood vessels of the genital organs, allowing for increased blood flow and engorgement. This physiological response is crucial for sexual function and pleasure.
In summary, the parasympathetic nervous system is a vital component of the autonomic nervous system, working in opposition to the sympathetic nervous system to maintain homeostasis and promote relaxation. Its effects on the heart, digestion, glandular secretions, and various other organs contribute to overall physiological balance and well-being.
The Connection Between the Parasympathetic Nerve and Heart Rate
Understanding how the parasympathetic nerve influences heart rate requires a closer look at the biochemical processes at play. Firstly, the vagus nerve releases acetylcholine, which binds to muscarinic receptors located on the heart’s cells. This binding triggers a signaling cascade that results in the opening of potassium channels and the closure of calcium channels, ultimately leading to a decreased heart rate.
However, the relationship between the parasympathetic nerve and heart rate goes beyond this basic understanding. Let’s delve deeper into the intricacies of how the parasympathetic nervous system influences heart rate regulation.
How the Parasympathetic Nerve Influences Heart Rate
When the parasympathetic nervous system is activated, the vagus nerve releases acetylcholine, which binds to muscarinic receptors in the sinoatrial node. Through a complex series of intracellular reactions, this binding inhibits the production of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP), a signaling molecule that is responsible for increasing heart rate.
By reducing cAMP levels, the parasympathetic nervous system indirectly slows down the heart rate. This intricate process underscores the complexity of the regulatory mechanisms behind heart rate reduction and highlights the integral role of the parasympathetic nerve in this physiological response.
But what exactly happens at the cellular level to bring about this heart rate reduction? Let’s explore the biochemical process behind this fascinating phenomenon.
The Biochemical Process Behind Heart Rate Reduction
Decreasing heart rate involves a complex interplay of biochemical processes within the heart’s cells. The binding of acetylcholine to muscarinic receptors initiates a signaling cascade that ultimately leads to the activation of potassium channels. This activation allows potassium ions to flow out of the cells, hyperpolarizing them and making it more difficult for the heart to generate electrical impulses.
Furthermore, the binding of acetylcholine inhibits the opening of calcium channels, which are responsible for the entry of calcium ions into the cells. Calcium ions play a crucial role in the heart’s electrical activity, and their inhibition further contributes to a reduced heart rate.
By modulating these intricate biochemical processes, the parasympathetic nervous system is able to significantly decrease heart rate, promoting a state of relaxation and calm.
It is important to note that the parasympathetic nervous system does not act alone in regulating heart rate. The sympathetic nervous system, often referred to as the “fight-or-flight” response, also plays a role in modulating heart rate. While the parasympathetic nervous system slows down heart rate, the sympathetic nervous system speeds it up, creating a delicate balance between the two systems.
In conclusion, the connection between the parasympathetic nerve and heart rate is a fascinating interplay of biochemical processes. Through the release of acetylcholine and subsequent activation of potassium channels and inhibition of calcium channels, the parasympathetic nervous system exerts its influence on heart rate reduction. This intricate dance of cellular reactions highlights the complexity of the human body and its ability to finely regulate physiological responses.
The Impact of Parasympathetic Activity on Overall Health
Beyond its role in regulating heart rate, parasympathetic activity has a profound impact on overall health. Maintaining a healthy balance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems is essential for optimal physiological functioning.
Parasympathetic activity not only affects cardiovascular health but also plays a crucial role in various other aspects of well-being. Let’s explore some of the additional ways in which parasympathetic activity influences our overall health.
Parasympathetic Activity and Cardiovascular Health
Enhancing parasympathetic activity can have significant cardiovascular benefits. By reducing heart rate and blood pressure, parasympathetic stimulation helps relieve strain on the heart, potentially reducing the risk of heart disease and other cardiovascular conditions. Additionally, parasympathetic activity promotes vasodilation, leading to improved blood flow and oxygen delivery to the body’s tissues.
Furthermore, studies have shown that parasympathetic activity can help regulate cholesterol levels and decrease the formation of blood clots, further protecting against cardiovascular diseases. This intricate interplay between the parasympathetic nervous system and cardiovascular health highlights the importance of nurturing parasympathetic activity.
However, it is important to note that individual needs may vary, and it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any specific parasympathetic stimulation techniques or interventions. They can provide personalized advice based on your unique medical history, ensuring that any interventions are safe and appropriate for your individual circumstances.
Stress, the Parasympathetic Nerve, and Heart Rate
One of the key factors influencing parasympathetic activity is stress. During periods of heightened stress, the sympathetic nervous system dominates, leading to an increase in heart rate and blood pressure. Conversely, engaging the parasympathetic nervous system through various techniques can promote relaxation and counteract the effects of stress.
Techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, and gentle physical activity can help activate the parasympathetic nervous system, leading to a decrease in heart rate and a sense of calm. Moreover, the activation of the parasympathetic nervous system during these relaxation techniques triggers the release of endorphins, which are natural painkillers and mood enhancers.
It is important to incorporate stress management techniques into our daily routines to support parasympathetic activity and overall well-being. By doing so, we can reduce the negative impact of chronic stress on our health and enhance our body’s ability to recover and rejuvenate.
However, it is important to remember that while these techniques can be beneficial, they are not a substitute for professional medical advice. If you are experiencing persistent or severe symptoms related to heart rate or any other health concerns, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional. They can conduct a thorough evaluation and provide appropriate guidance tailored to your specific needs.
In conclusion, parasympathetic activity plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health, particularly in cardiovascular health and stress management. By understanding the impact of parasympathetic activity and incorporating techniques to enhance it, we can support our body’s natural healing processes and promote optimal well-being.
Modulating the Parasympathetic Nervous System
Given the significant impact of parasympathetic activity on heart rate and overall health, it is valuable to explore techniques for enhancing parasympathetic activity in a safe and effective manner.
The parasympathetic nervous system, often referred to as the “rest and digest” system, plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis in the body. It counterbalances the sympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for the “fight or flight” response. When the parasympathetic nervous system is activated, heart rate decreases, blood pressure lowers, and digestion and other restorative processes are facilitated.
Techniques for Enhancing Parasympathetic Activity
- Deep Breathing: Engaging in slow, deep breaths can activate the parasympathetic nervous system and promote relaxation. Take deep breaths in through the nose, allowing the abdomen to expand, and exhale slowly through the mouth, focusing on elongating the out-breath. This technique not only enhances parasympathetic activity but also helps reduce stress and anxiety.
- Meditation: Regular meditation practice can help activate the parasympathetic nervous system and reduce stress. Find a quiet and comfortable space, close your eyes, and focus on your breath or a calming visualization. As you cultivate a state of mindfulness, the parasympathetic response is triggered, leading to a sense of calm and well-being.
- Yoga and Tai Chi: These gentle forms of exercise combine movement, breath, and mindfulness, promoting relaxation and parasympathetic activation. Incorporating these practices into your routine can have long-lasting benefits for heart rate management. The slow, deliberate movements in yoga and tai chi help synchronize the breath with the body, enhancing parasympathetic activity and fostering a sense of inner peace.
It is crucial to approach these techniques with an understanding that individual experiences and needs may vary. What works for one person may not work for another. It is always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new practices or interventions, particularly if you have pre-existing medical conditions or concerns. They can provide personalized guidance and ensure that these techniques are suitable for your specific situation.
The Future of Heart Rate Management Through the Parasympathetic Nerve
The field of heart rate management continues to evolve, and researchers are exploring new ways to modulate the parasympathetic nervous system to optimize heart health. Advances in areas such as biofeedback, neurostimulation, and pharmacology hold promise for future interventions.
Biofeedback, for example, is a technique that allows individuals to gain awareness and control over their physiological processes, including heart rate. By providing real-time feedback on heart rate variability, individuals can learn to regulate their parasympathetic activity and improve heart rate management.
Neurostimulation involves the use of electrical or magnetic stimulation to target specific areas of the nervous system. Researchers are investigating the potential of neuromodulation techniques to enhance parasympathetic activity and improve heart rate regulation.
Pharmacology also plays a role in the future of heart rate management. Scientists are studying the development of drugs that specifically target the parasympathetic nervous system, aiming to enhance its activity and provide more effective treatment options for individuals with heart rate abnormalities.
However, it is important to emphasize that any emerging techniques or treatments should be thoroughly evaluated and their safety and efficacy established through rigorous scientific research. Consulting with healthcare professionals and experts in the field is crucial to ensure the adoption of evidence-based and suitable interventions.
Overall, the role of the parasympathetic nerve in reducing heart rate cannot be understated. By understanding the mechanisms behind its function, exploring the impact of parasympathetic activity on overall health, and learning techniques to enhance parasympathetic activity, individuals can take an active role in promoting heart health and well-being. As always, consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and guidance tailored to your unique needs.