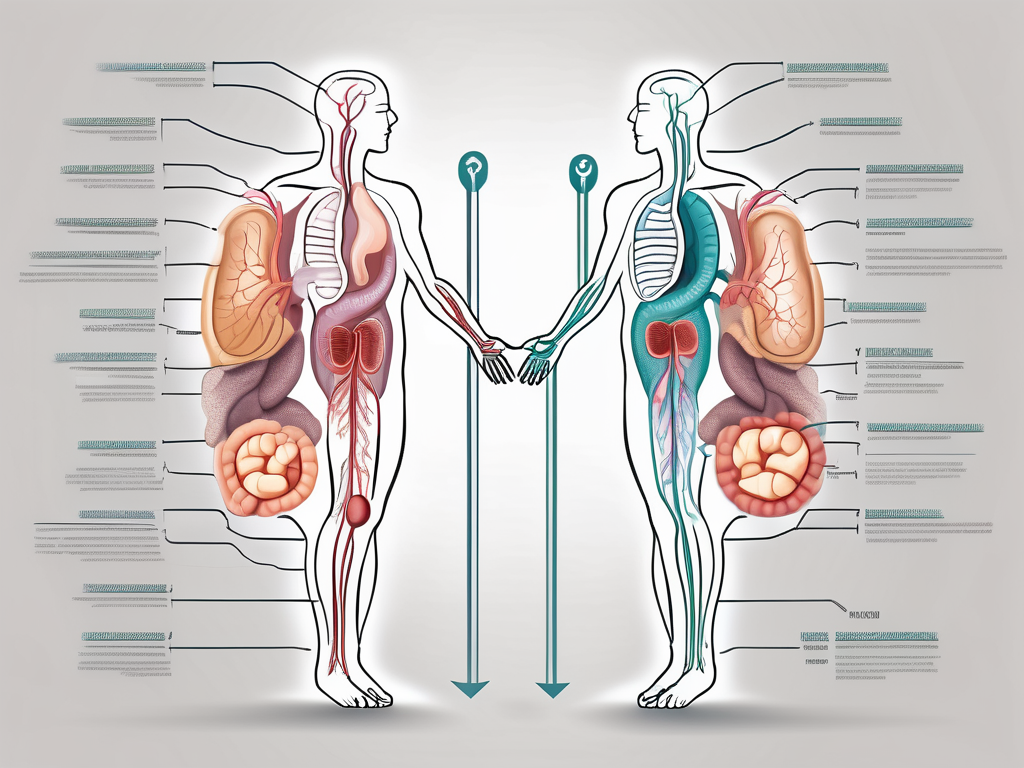
The parasympathetic nerve plays a crucial role in the function of the gut, affecting various aspects of digestive health. Understanding the intricate relationship between the parasympathetic nervous system and the digestive system is essential in comprehending the complexities of gut function and overall well-being.
Understanding the Parasympathetic Nervous System
In order to grasp the significance of the parasympathetic nerve in gut function, it is important to first understand the fundamentals of the parasympathetic nervous system. This branch of the autonomic nervous system is responsible for promoting rest, relaxation, and digestion, commonly known as the “rest and digest” response. Unlike the sympathetic nervous system, which activates the “fight or flight” response, the parasympathetic nervous system works in opposition, promoting a state of calm and allowing the body to focus on digesting food and ensuring efficient nutrient absorption.
The Anatomy of the Parasympathetic Nervous System
The parasympathetic nervous system primarily consists of two main components: the cranial nerves and the sacral nerves. The cranial nerves arise from the brainstem, with the vagus nerve being the major player in regulating gut function. It extends from the brainstem down to the abdomen, innervating various organs, including the stomach, small intestine, and colon. The sacral nerves, on the other hand, originate from the lower segments of the spinal cord and also contribute to the regulation of gut function, particularly in the pelvic organs.
The vagus nerve, also known as the tenth cranial nerve, is a long and complex nerve that plays a crucial role in the parasympathetic nervous system’s control over gut function. It carries signals from the brain to the various organs in the abdomen, providing precise instructions for digestion and nutrient absorption. The vagus nerve acts as a communication channel between the brain and the gut, ensuring that the digestive system functions optimally.
The Function of the Parasympathetic Nervous System
The parasympathetic nervous system exerts its influence on the gut through a myriad of mechanisms. One of its main functions is to stimulate the secretion of digestive enzymes and increase blood flow to the digestive organs, ensuring optimal digestion and nutrient absorption. This intricate process involves the release of various neurotransmitters, such as acetylcholine, which act as chemical messengers between nerve cells and target organs.
Acetylcholine, a key neurotransmitter in the parasympathetic nervous system, binds to specific receptors in the gastrointestinal tract, triggering a cascade of events that enhance gut function. It stimulates the release of enzymes from the salivary glands, pancreas, and stomach, aiding in the breakdown of food into smaller, absorbable molecules. Additionally, acetylcholine promotes the relaxation of the smooth muscles in the gastrointestinal tract, allowing for the efficient movement of food through the digestive system.
Furthermore, the parasympathetic nervous system plays a vital role in regulating gut motility. It coordinates the rhythmic contractions of the muscles in the gastrointestinal tract, known as peristalsis, which propel food along the digestive system. These contractions are essential for the proper mixing and digestion of food, as well as the elimination of waste through regular bowel movements. The parasympathetic nervous system ensures that this process occurs smoothly, preventing issues such as constipation and promoting overall gut health.
In addition to its role in digestion, the parasympathetic nervous system also influences other bodily functions. It regulates heart rate, respiratory rate, and blood pressure, helping to maintain homeostasis and balance within the body. Moreover, it promotes relaxation and reduces stress, which can have a positive impact on overall well-being.
In conclusion, the parasympathetic nervous system is a crucial component of gut function. Its intricate control over digestion, nutrient absorption, and gut motility ensures that the body can efficiently process food and maintain optimal gut health. Understanding the anatomy and function of the parasympathetic nervous system provides valuable insights into the complex mechanisms that govern our digestive processes.
The Parasympathetic Nerve and the Digestive System
The connection between the parasympathetic nerve and the digestive system is vital in maintaining gut health. This intricate relationship ensures that digestion and absorption occur efficiently, providing the body with the necessary nutrients for optimal functioning.
The Connection Between the Parasympathetic Nerve and the Gut
The parasympathetic nerve influences the gut through a complex network of communication that involves neurotransmitters and receptors. When activated, the vagus nerve releases acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that stimulates the release of digestive enzymes from glands in the gut. This process facilitates effective breakdown of food and absorption of nutrients.
In addition to acetylcholine, other neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine also play a role in the parasympathetic regulation of the digestive system. These neurotransmitters help modulate gut motility, enhance nutrient absorption, and promote a sense of well-being during digestion.
Furthermore, the parasympathetic nerve promotes the relaxation of the muscles in the gastrointestinal tract, allowing for the coordinated movement of food through various stages of digestion. This ensures that food is propelled efficiently through the stomach, small intestine, and colon, preventing issues such as delayed gastric emptying or intestinal dysmotility.
The Impact of the Parasympathetic Nerve on Digestion
Proper digestion is crucial for overall gut health, and the parasympathetic nerve plays a prominent role in this process. The stimulation of digestive enzyme secretion by the parasympathetic nerve ensures the breakdown of complex nutrients into smaller, more absorbable molecules. This allows for efficient absorption of nutrients and prevents malnutrition or other nutrient deficiencies that may arise from impaired digestion.
In addition to enzyme secretion, the parasympathetic nerve also influences the release of hormones that regulate digestion. For example, it stimulates the release of gastrin, a hormone that promotes the secretion of gastric acid and enhances the motility of the stomach. This coordinated hormonal response ensures that digestion proceeds smoothly and efficiently.
The parasympathetic nerve also affects the production of gastric acid, which aids in the breakdown of proteins. Optimal gastric acid secretion is vital in preventing conditions such as acid reflux or gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), which can cause discomfort and damage to the esophagus.
Furthermore, the parasympathetic nerve helps regulate the balance of gut microbiota, which are the trillions of microorganisms that reside in the digestive tract. These microorganisms play a crucial role in digestion, nutrient absorption, and immune function. The parasympathetic nerve promotes a healthy gut microbiome by modulating gut motility, promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria, and preventing the overgrowth of harmful pathogens.
In summary, the parasympathetic nerve and the digestive system have a complex and intricate relationship. The parasympathetic nerve influences various aspects of digestion, including enzyme secretion, muscle relaxation, hormone release, gastric acid production, and gut microbiota balance. This connection ensures optimal gut health and efficient nutrient absorption, contributing to overall well-being and vitality.
The Parasympathetic Nerve and Gut Health
The role of the parasympathetic nerve extends beyond digestion and plays a vital role in maintaining overall gut health. Several aspects of gut function that impact overall well-being are influenced by the parasympathetic nervous system.
The parasympathetic nerve, also known as the “rest and digest” system, works in opposition to the sympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for the body’s “fight or flight” response. While the sympathetic nervous system prepares the body for action, the parasympathetic nervous system helps the body relax and recover.
The Role of the Parasympathetic Nerve in Gut Motility
The parasympathetic nerve contributes to the regulation of gut motility, ensuring the appropriate movement of food through the digestive system. This prevents issues such as constipation or diarrhea and helps maintain regular bowel movements.
When the parasympathetic nerve is activated, it stimulates the release of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that promotes smooth muscle contractions in the digestive tract. These contractions, known as peristalsis, propel food forward and aid in the breakdown and absorption of nutrients.
However, disruptions in parasympathetic nerve function can result in dysmotility disorders, leading to discomfort and compromised gut health. Conditions such as gastroparesis, where the stomach muscles do not contract properly, can be caused by dysfunction in the parasympathetic nervous system.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional if you experience persistent or severe changes in bowel habits, as these may be indicative of an underlying condition that requires medical attention.
The Parasympathetic Nerve and Nutrient Absorption
Efficient nutrient absorption is essential for optimal health, and the parasympathetic nerve plays a crucial role in this process. By promoting the secretion of digestive enzymes and stimulating blood flow to the digestive organs, the parasympathetic nerve ensures that nutrients from food are effectively absorbed into the bloodstream.
When the parasympathetic nerve is activated, it triggers the release of saliva, gastric juices, and pancreatic enzymes, which aid in the breakdown of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. This breakdown allows for easier absorption of nutrients in the small intestine.
In addition, the parasympathetic nerve stimulates blood vessels in the digestive system, increasing blood flow to the intestines. This enhanced blood flow helps transport nutrients across the intestinal wall and into the bloodstream.
If you have concerns about nutrient absorption or suspect nutrient deficiencies, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional who can assess your specific needs and provide appropriate guidance. Nutrient deficiencies can lead to a variety of health issues, including fatigue, weakened immune function, and impaired cognitive function.
In conclusion, the parasympathetic nerve plays a crucial role in maintaining gut health. From regulating gut motility to promoting efficient nutrient absorption, this branch of the autonomic nervous system ensures that our digestive system functions optimally. By understanding the importance of the parasympathetic nerve in gut health, we can take steps to support its function and maintain overall well-being.
Disorders Related to Parasympathetic Nerve Dysfunction
When the parasympathetic nerve does not function optimally, it can lead to various disorders that impact gut health. These conditions can cause significant discomfort and require medical intervention in order to manage symptoms effectively.
Parasympathetic nerve dysfunction refers to a disruption in the normal functioning of the parasympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for regulating the body’s rest and digest response. This system plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of various bodily functions, including digestion, heart rate, and blood pressure.
One disorder associated with parasympathetic nerve dysfunction is gastroparesis, a condition characterized by delayed gastric emptying. In individuals with gastroparesis, the muscles of the stomach do not contract properly, leading to a delay in the movement of food from the stomach to the small intestine. This can result in symptoms such as bloating, nausea, vomiting, and a feeling of fullness even after consuming small amounts of food.
Symptoms of Parasympathetic Nerve Dysfunction in the Gut
Parasympathetic nerve dysfunction can manifest in various ways within the gut. Symptoms such as bloating, abdominal pain, alternating diarrhea and constipation, and delayed gastric emptying may indicate underlying dysregulation of the parasympathetic nervous system.
In addition to these symptoms, individuals with parasympathetic nerve dysfunction may also experience changes in appetite, weight loss, and malnutrition due to the impaired digestion and absorption of nutrients. The gut-brain connection is also affected, leading to an increased risk of developing mental health conditions such as anxiety and depression.
It is important to seek medical advice if you experience persistent or worsening symptoms that affect your quality of life. A healthcare professional can evaluate your symptoms, perform relevant tests, and offer appropriate guidance to help manage your condition.
Treatment and Management of Parasympathetic Nerve Dysfunction
The treatment and management of conditions related to parasympathetic nerve dysfunction involve a multidisciplinary approach that may include lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, stress management techniques, and medications if necessary. Consulting with a healthcare professional who specializes in gastrointestinal disorders is crucial in order to develop an individualized treatment plan that addresses your specific needs.
Lifestyle modifications may include regular exercise, which can help stimulate the parasympathetic nervous system and improve gut motility. Dietary changes may involve avoiding trigger foods that exacerbate symptoms, such as fatty or spicy foods, and opting for a diet rich in fiber to promote regular bowel movements.
Stress management techniques, such as mindfulness meditation and deep breathing exercises, can also be beneficial in reducing the impact of stress on the parasympathetic nervous system. In some cases, medications may be prescribed to help regulate gut motility and manage symptoms.
It is important to note that the treatment and management of parasympathetic nerve dysfunction may vary depending on the underlying cause and individual factors. Therefore, it is essential to work closely with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate approach for your specific condition.
The Future of Parasympathetic Nerve Research
Advancements in medical research continue to shed light on the complex relationship between the parasympathetic nerve and gut function, offering potential avenues for improved understanding and treatment of various gut-related disorders.
The parasympathetic nerve, also known as the “rest and digest” system, is a crucial component of the autonomic nervous system. It controls many vital functions in the body, including digestion, nutrient absorption, and regulation of gastrointestinal motility. The intricate interplay between the parasympathetic nerve and the gut is a topic of great interest to researchers and healthcare professionals alike.
Current Research on the Parasympathetic Nerve and Gut Function
Ongoing studies are aimed at unraveling the intricate mechanisms underlying parasympathetic nerve function and its impact on gut health. Researchers are exploring the potential therapeutic applications of neuromodulation techniques, such as vagus nerve stimulation, in the management of conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease, irritable bowel syndrome, and gastrointestinal motility disorders.
One area of research focuses on the role of the parasympathetic nerve in the gut-brain axis, a bidirectional communication system between the gut and the brain. It is believed that disruptions in this axis may contribute to the development of gut-related disorders. By understanding the specific pathways through which the parasympathetic nerve communicates with the gut, researchers hope to identify novel targets for intervention.
Another area of interest is the influence of the parasympathetic nerve on gut microbiota, the trillions of microorganisms that inhabit the gastrointestinal tract. Emerging evidence suggests that the parasympathetic nerve may play a role in shaping the composition and function of gut microbiota, which in turn can impact overall gut health. This line of research holds promise for the development of microbiota-based therapies for gut-related disorders.
Potential Implications for Gastrointestinal Health and Disease Treatment
The insights gained from ongoing research on the parasympathetic nerve could have significant implications for the development of targeted therapies for various gut-related disorders. By understanding the precise mechanisms through which the parasympathetic nerve influences gut function, novel treatment modalities may emerge, providing hope for better outcomes and improved quality of life for individuals affected by these conditions.
For example, vagus nerve stimulation, a technique currently used in the treatment of epilepsy and depression, shows promise as a potential therapy for gut-related disorders. By modulating the activity of the parasympathetic nerve, researchers believe that it may be possible to alleviate symptoms and improve gut function in conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease and irritable bowel syndrome.
Furthermore, a deeper understanding of the parasympathetic nerve’s role in the gut-brain axis may open up new avenues for the development of psychobiotics, which are live bacteria that can positively influence mental health. By targeting the parasympathetic nerve-gut-brain axis, researchers hope to develop innovative therapies that address both the physical and psychological aspects of gut-related disorders.
In conclusion, the parasympathetic nerve plays a crucial role in gut function, impacting various aspects of digestion, nutrient absorption, and overall gut health. Understanding the intricate relationship between the parasympathetic nervous system and the digestive system provides valuable insights for healthcare professionals and researchers alike. If you have concerns regarding your gut function or experience symptoms suggestive of parasympathetic nerve dysfunction, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional who can assess your situation and provide appropriate guidance.