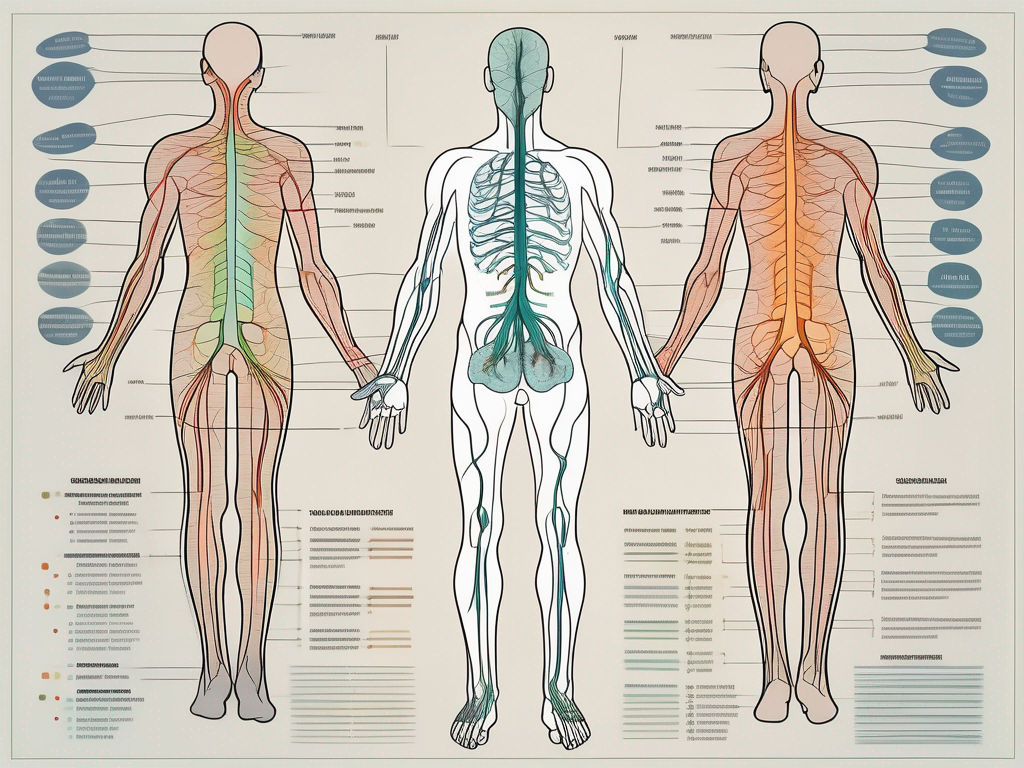
The parasympathetic nervous system is a complex network of nerves in the body that plays a vital role in maintaining our overall health and well-being. One important component of this system is the sacral parasympathetic nerve route, which is responsible for regulating various bodily functions. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the intricacies of the sacral parasympathetic nerve route and its significance in our daily lives.
Understanding the Parasympathetic Nervous System
The parasympathetic nervous system is a division of the autonomic nervous system, which is responsible for controlling involuntary bodily functions. It works in conjunction with the sympathetic nervous system to maintain homeostasis and ensure that our physiological processes remain in balance. While the sympathetic nervous system triggers the “fight-or-flight” response, the parasympathetic nervous system promotes relaxation and rest, helping the body conserve energy.
When the parasympathetic nervous system is activated, a series of intricate processes occur within the body. One of its primary roles is to counterbalance the effects of the sympathetic nervous system, regulating essential bodily functions such as heart rate, digestion, urination, and sexual arousal. By activating the parasympathetic nervous system, our body undergoes processes that promote relaxation, digestion, and restoration.
The Role of the Parasympathetic Nervous System
Let’s dive deeper into the role of the parasympathetic nervous system. When we are in a state of relaxation, the parasympathetic nervous system takes charge, allowing our body to rest and recover. It slows down our heart rate, reducing the need for oxygen and conserving energy. This is why our heart rate decreases when we are in a calm state, such as during meditation or deep sleep.
In addition to regulating heart rate, the parasympathetic nervous system also plays a crucial role in digestion. When we eat a meal, the parasympathetic nervous system stimulates the production of digestive enzymes and increases blood flow to the digestive organs. This allows for the efficient breakdown and absorption of nutrients, ensuring that our body receives the necessary fuel to function optimally.
Furthermore, the parasympathetic nervous system is involved in the process of urination. When the bladder is full, the parasympathetic nervous system signals the bladder muscles to contract and the sphincter muscles to relax, allowing urine to be expelled from the body. This process is essential for maintaining the balance of fluids and eliminating waste products from our system.
Lastly, the parasympathetic nervous system also plays a role in sexual arousal. When we are in a state of relaxation and intimacy, the parasympathetic nervous system triggers the release of neurotransmitters that promote sexual desire and arousal. It increases blood flow to the genital area, leading to engorgement and heightened sensitivity.
Key Components of the Parasympathetic Nervous System
The parasympathetic nervous system consists of several key components that work together to ensure its proper functioning. One of these components is the cranial nerves, which arise from the brainstem and innervate structures in the head and neck. These cranial nerves play a vital role in controlling functions such as eye movement, facial expressions, and salivation.
Another important component of the parasympathetic nervous system is the sacral nerves. These nerves originate from the lower spinal cord and supply the pelvic organs, including the bladder, reproductive organs, and parts of the digestive system. They are responsible for regulating functions such as urination, sexual arousal, and bowel movements.
Overall, the parasympathetic nervous system is a crucial part of our autonomic nervous system. It works hand in hand with the sympathetic nervous system to maintain balance and ensure the smooth functioning of our bodily processes. By understanding the role and components of the parasympathetic nervous system, we can appreciate the intricate mechanisms that allow our body to rest, digest, and restore itself.
The Sacral Component of the Parasympathetic Nervous System
Within the parasympathetic nervous system, the sacral component plays a crucial role in governing important bodily functions related to the lower abdomen and pelvis. Understanding the anatomy and functions of the sacral parasympathetic nerve route is paramount in comprehending its impact on our overall well-being.
The sacral component of the parasympathetic nervous system is an intricate network of nerves that originates from the sacral spinal cord. It travels through the pelvic region, intricately distributing its nerve fibers to the reproductive organs, bladder, and rectum. These intricate fibers transmit signals that regulate the contractions of smooth muscles, controlling bladder emptying, bowel movements, and sexual functions.
Anatomy of the Sacral Parasympathetic Nerve Route
The sacral parasympathetic nerve route originates from the sacral spinal cord, specifically from the S2 to S4 segments. These segments are responsible for transmitting signals that regulate various bodily functions related to the lower abdomen and pelvis. As the nerve route travels through the pelvic region, it branches out and distributes its intricate network of nerve fibers to different organs, ensuring their proper functioning.
One of the key destinations of the sacral parasympathetic nerve route is the bladder. The nerve fibers innervate the detrusor muscle, which is responsible for the contraction and relaxation of the bladder wall. Through the intricate network of nerves, the sacral parasympathetic nerve route ensures that the bladder can contract and expel urine efficiently.
In addition to the bladder, the sacral parasympathetic nerve route also plays a vital role in the reproductive system. The nerve fibers innervate the erectile tissue in both males and females, facilitating sexual arousal and orgasm. This intricate network ensures the proper functioning of the reproductive system, allowing for pleasurable sexual experiences.
Furthermore, the sacral parasympathetic nerve route extends its influence to the rectum. The nerve fibers regulate the smooth muscle contractions in the rectal wall, promoting efficient bowel movements and elimination. This ensures proper digestion and prevents complications such as constipation.
Functions of the Sacral Parasympathetic Nerve Route
The sacral parasympathetic nerve route plays a crucial role in several important bodily functions. One of its primary functions is the control of micturition, the process of emptying the bladder. When the bladder is full, the nerve fibers in the sacral parasympathetic nerve route transmit signals that trigger the contraction of the detrusor muscle, allowing the bladder to expel urine. This intricate coordination ensures that the bladder functions properly and prevents urinary retention.
In addition to controlling micturition, the sacral parasympathetic nerve route also facilitates sexual arousal and orgasm. The nerve fibers in this network innervate the erectile tissue in the genitals, allowing for increased blood flow and engorgement. This leads to sexual arousal and ultimately orgasm, ensuring the proper functioning of the reproductive system and promoting sexual satisfaction.
Lastly, the sacral parasympathetic nerve route regulates bowel movements. The nerve fibers in this network control the contractions of the rectal wall, facilitating efficient digestion and elimination. When the rectum is filled with stool, the nerve fibers transmit signals that trigger the relaxation of the internal anal sphincter and the contraction of the rectal wall, promoting bowel movements. This intricate coordination ensures proper digestion and prevents complications such as constipation.
The Connection Between the Sacral Parasympathetic Nerve Route and the Body
Understanding how the sacral parasympathetic nerve route influences the body provides valuable insights into the intricate connections between various bodily functions and our overall well-being.
The sacral parasympathetic nerve route, also known as the sacral outflow, originates from the sacral region of the spinal cord. It is part of the autonomic nervous system, which controls involuntary bodily functions. This nerve route plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis and ensuring the proper functioning of several vital processes.
The Sacral Parasympathetic Nerve Route and Digestion
Optimal digestion is essential for the body to absorb nutrients and maintain overall health. The sacral parasympathetic nerve route plays a vital role in promoting digestion by regulating the movement of food through the gastrointestinal tract and promoting the secretion of digestive enzymes.
When food enters the stomach, the sacral parasympathetic nerve route stimulates the release of gastric acid and digestive enzymes, such as amylase and lipase, from the salivary glands, pancreas, and liver. These enzymes break down carbohydrates, fats, and proteins into smaller molecules that can be easily absorbed by the body.
Furthermore, the sacral parasympathetic nerve route controls the peristaltic movements of the intestines, which propel food forward and aid in the absorption of nutrients. Any disruption in this process can lead to digestive disorders, such as constipation or irritable bowel syndrome.
If you experience ongoing digestive issues, consulting with your healthcare provider is recommended. They can evaluate the functioning of your sacral parasympathetic nerve route and provide appropriate treatment options to alleviate your symptoms and improve your digestive health.
The Sacral Parasympathetic Nerve Route and Urination
The sacral parasympathetic nerve route also plays a crucial role in the regulation of urination. It controls the detrusor muscle, which is responsible for bladder contraction during urination. Additionally, it relaxes the muscles in the urethra to allow the smooth flow of urine.
When the bladder is full, the sacral parasympathetic nerve route sends signals to the detrusor muscle, causing it to contract and expel urine from the body. Simultaneously, it inhibits the contraction of the sphincter muscles in the urethra, allowing urine to pass through without obstruction.
Dysfunction of the sacral parasympathetic nerve route may result in urinary retention or urinary incontinence. Urinary retention occurs when the bladder does not empty completely, leading to a constant feeling of urgency and discomfort. On the other hand, urinary incontinence refers to the involuntary leakage of urine, which can significantly impact a person’s quality of life.
If you experience persistent urinary problems, it is crucial to seek medical advice. A healthcare professional can assess the functioning of your sacral parasympathetic nerve route and recommend appropriate interventions, such as medication, pelvic floor exercises, or other therapeutic approaches, to help manage your condition effectively.
In conclusion, the sacral parasympathetic nerve route plays a vital role in digestion and urination. It regulates the movement of food through the gastrointestinal tract, promotes the secretion of digestive enzymes, and controls bladder contraction and urethral relaxation during urination. Understanding the intricate connections between this nerve route and various bodily functions can provide valuable insights into maintaining optimal health and seeking appropriate medical care when necessary.
Disorders Related to the Sacral Parasympathetic Nerve Route
While the sacral parasympathetic nerve route performs vital functions, certain disorders can affect its proper functioning and lead to various health issues. The sacral parasympathetic nerve route, also known as the pelvic splanchnic nerves, plays a crucial role in regulating the functions of the pelvic organs, including the bladder, bowel, and sexual organs.
The sacral parasympathetic nerve route is responsible for controlling the involuntary actions of these organs, such as emptying the bladder and bowels, achieving and maintaining an erection, and experiencing sexual pleasure. When this nerve route is disrupted or damaged, it can result in a range of disorders that significantly impact an individual’s quality of life.
Common Disorders and Their Symptoms
Disorders related to the sacral parasympathetic nerve route may manifest as urinary and bowel dysfunction, sexual dysfunction, or pelvic pain. One common disorder is overactive bladder, which is characterized by a frequent and urgent need to urinate, often accompanied by urinary incontinence. This condition can be disruptive and embarrassing, causing individuals to limit their activities and social interactions.
Another disorder that can occur is erectile dysfunction, which is the inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for sexual intercourse. This can lead to feelings of frustration, low self-esteem, and strain on relationships. Additionally, fecal incontinence, the inability to control bowel movements, can also occur as a result of sacral parasympathetic nerve route disorders, causing embarrassment and a loss of confidence.
If you experience any of these symptoms persistently, it is advisable to seek medical evaluation and guidance. A healthcare professional can conduct a thorough assessment to determine the underlying cause of your symptoms and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Diagnostic Techniques for Sacral Parasympathetic Nerve Route Disorders
Diagnosing disorders related to the sacral parasympathetic nerve route often requires a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional. The diagnostic process typically begins with a detailed medical history and physical examination. During the physical examination, the healthcare provider may assess the function of the pelvic organs, such as checking for muscle strength and reflexes.
In addition to the physical examination, various tests may be employed to assess the functionality of the nerves and pelvic organs. Urodynamic studies are commonly used to evaluate bladder function and assess how well the bladder and urethra are working together. This test involves measuring urine flow rate, bladder pressure, and muscle activity during urination.
Electromyography (EMG) is another diagnostic technique that may be used to evaluate the function of the pelvic floor muscles and the nerves that control them. This test involves inserting small electrodes into the muscles to measure their electrical activity. EMG can help identify any abnormalities or dysfunction in the pelvic floor muscles.
In some cases, imaging techniques such as ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or computed tomography (CT) scans may be utilized to visualize the pelvic organs and identify any structural abnormalities or lesions that could be contributing to the symptoms.
Consulting with a healthcare provider will help determine the most appropriate diagnostic approach for your specific condition. They will consider your symptoms, medical history, and any previous test results to develop an individualized diagnostic plan.
Treatment and Management of Sacral Parasympathetic Nerve Route Disorders
Management of sacral parasympathetic nerve route disorders aims to alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life. While specific treatment options may vary depending on the underlying condition, a combination of medical treatments, therapies, and lifestyle changes is often recommended.
Medical Treatments and Therapies
Medical treatments may include medications to manage symptoms such as urinary frequency or erectile dysfunction. Physical therapy, biofeedback, and electrical stimulation may also be beneficial in enhancing muscle function and improving pelvic floor strength. The most appropriate treatment approach will depend on the specific disorder and should be determined in consultation with a healthcare professional.
Lifestyle Changes and Self-Care Strategies
Adopting certain lifestyle changes can help alleviate symptoms and manage sacral parasympathetic nerve route disorders. These may include dietary modifications, pelvic floor exercises, stress management techniques, and maintaining a healthy weight. It is essential to consult with a healthcare provider or specialist to develop an individualized plan that suits your needs and goals.
Future Research Directions in Sacral Parasympathetic Nerve Route
As medical knowledge and technology continue to advance, there is ongoing research into further understanding and treating disorders related to the sacral parasympathetic nerve route.
Emerging Techniques in Diagnosis
New diagnostic techniques, such as advanced imaging modalities, genetic testing, and molecular profiling, hold promise for improving diagnostic accuracy and identifying subtypes of disorders affecting the sacral parasympathetic nerve route. These advancements may lead to more targeted and personalized treatment approaches in the future.
Potential Therapies on the Horizon
Ongoing research includes exploring novel treatment modalities, such as neuromodulation techniques and stem cell therapies, to restore functionality and alleviate symptoms in sacral parasympathetic nerve route disorders. While these approaches are still in the experimental stage, they offer hope for future advancements in treatment options.
In conclusion, the sacral parasympathetic nerve route is a vital component of the parasympathetic nervous system that regulates various essential bodily functions. Understanding its anatomy, functions, and potential disorders provides valuable insights into maintaining our overall health and well-being. If you experience symptoms related to the sacral parasympathetic nerve route, it is crucial to consult with healthcare professionals who can provide appropriate evaluation, diagnosis, and guidance tailored to your specific needs.