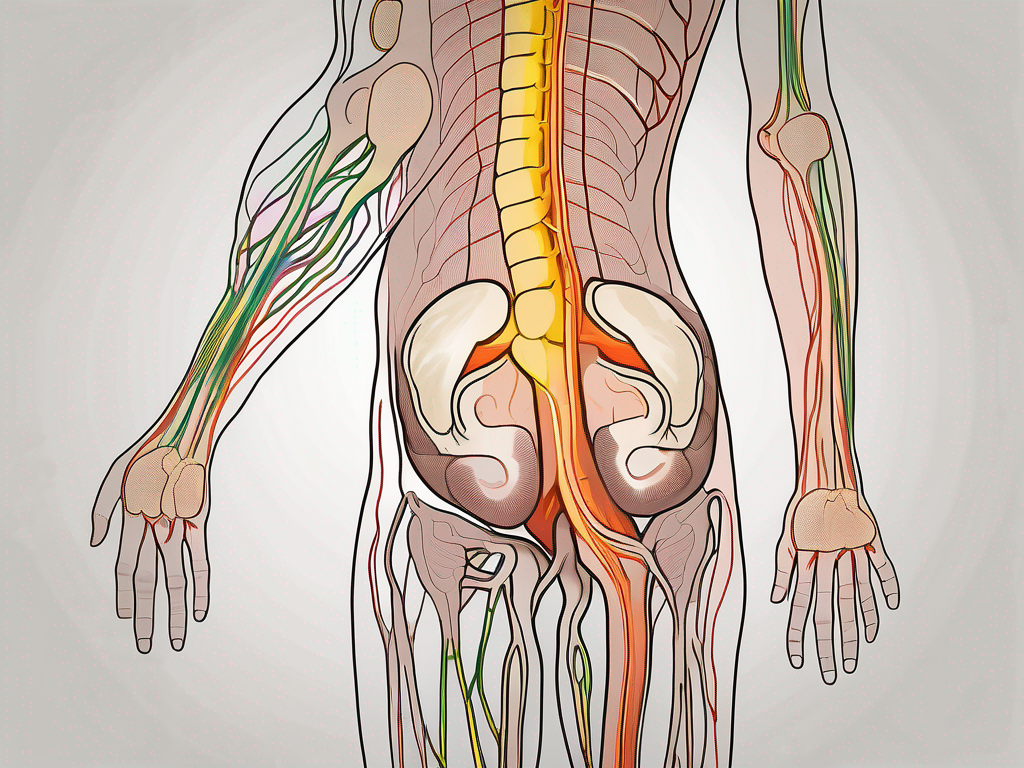
The parasympathetic nervous system is a complex network of nerves that plays a vital role in maintaining the body’s overall health and well-being. While its functions are widespread throughout the body, in this article, we will focus on understanding parasympathetic nerve endings specifically in the buttocks.
The Basics of Parasympathetic Nervous System
The parasympathetic nervous system is a division of the autonomic nervous system, responsible for controlling the body’s functions at rest and promoting a state of relaxation. It works in opposition to the sympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for the body’s fight-or-flight response.
The parasympathetic nervous system is a complex network of nerves that extends throughout the body, with its main control center located in the brainstem. This system is responsible for regulating various bodily processes, ensuring that they function optimally even when the body is at rest.
One of the primary functions of the parasympathetic nervous system is to conserve energy. When the body is in a state of rest, it is essential to minimize energy expenditure and focus on replenishing resources. The parasympathetic nervous system achieves this by slowing down heart rate, reducing blood pressure, and promoting digestion.
Defining the Parasympathetic Nervous System
The parasympathetic nervous system is primarily responsible for conserving energy, promoting digestion, and maintaining bodily functions. It is often referred to as the “rest and digest” system because it helps the body relax and recover after periods of stress or exertion.
When the parasympathetic nervous system is activated, it sends signals to various organs and tissues to stimulate their functions. For example, it stimulates the salivary glands to produce saliva, which aids in the digestion process. It also increases the activity of the digestive organs, such as the stomach and intestines, to break down food and absorb nutrients efficiently.
In addition to its role in digestion, the parasympathetic nervous system also regulates other bodily functions, such as urination and defecation. It signals the bladder to contract and the sphincter muscles to relax, allowing for the elimination of waste products from the body.
Function and Role of the Parasympathetic Nervous System
The parasympathetic nervous system controls various bodily processes, including heart rate, blood pressure, digestion, and elimination. It also plays a crucial role in promoting calmness, relaxation, and maintaining homeostasis.
When the parasympathetic nervous system is activated, it counteracts the effects of the sympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for the body’s fight-or-flight response. This balance between the two systems is essential for maintaining overall well-being and ensuring that the body can respond appropriately to different situations.
Furthermore, the parasympathetic nervous system is involved in regulating sleep and promoting restful sleep patterns. It helps to slow down brain activity, decrease muscle tension, and promote a sense of calmness, all of which are necessary for a good night’s sleep.
In summary, the parasympathetic nervous system is a vital component of the autonomic nervous system, responsible for controlling the body’s functions at rest. It conserves energy, promotes digestion, and maintains bodily functions, ensuring that the body can relax and recover after periods of stress or exertion. Understanding the role of the parasympathetic nervous system is crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being.
Anatomy of the Buttocks
To understand the parasympathetic nerve endings in the buttocks, it’s important to have a basic understanding of the anatomical structures in this area.
The buttocks, or gluteal region, consist of several muscles, including the gluteus maximus, gluteus medius, and gluteus minimus. These muscles are innervated by the sciatic nerve, which is the longest and thickest nerve in the body.
The gluteus maximus is the largest muscle in the buttocks and is responsible for the extension and rotation of the hip joint. It is innervated by the inferior gluteal nerve, a branch of the sciatic nerve. The gluteus medius and gluteus minimus are smaller muscles that are responsible for abduction and rotation of the hip joint. They are innervated by the superior gluteal nerve, also a branch of the sciatic nerve.
Muscular Structure and Nerve Distribution
The gluteus maximus, located superficially in the buttocks, is a powerful muscle that helps maintain an upright posture and aids in activities such as walking, running, and climbing stairs. It originates from the ilium, sacrum, and coccyx and inserts into the femur. The sciatic nerve, which originates from the lower back, splits into two branches – the tibial nerve and the common fibular nerve. The tibial nerve supplies the gluteus maximus, while the common fibular nerve supplies the other gluteal muscles.
The gluteus medius and gluteus minimus are located deep within the buttocks, beneath the gluteus maximus. They both arise from the ilium and insert into the greater trochanter of the femur. These muscles are responsible for stabilizing the pelvis during walking and running, preventing the opposite hip from dropping when standing on one leg. The superior gluteal nerve, a branch of the sciatic nerve, provides the necessary innervation for these muscles to function properly.
Role of Nerves in the Buttocks
The nerves in the buttocks play a crucial role in various functions, such as providing motor control to the gluteal muscles and sensory information from the skin in the area. Additionally, the parasympathetic nerve endings in the buttocks have specific roles in regulating certain bodily functions.
Parasympathetic nerve endings are part of the autonomic nervous system, which controls involuntary bodily functions. These nerve endings in the buttocks are involved in regulating processes such as digestion, urination, and sexual arousal. When stimulated, they can cause relaxation of the smooth muscles in the digestive tract, leading to increased peristalsis and improved digestion. They can also promote bladder emptying by relaxing the muscles of the urinary bladder, allowing for efficient urination.
Furthermore, the parasympathetic nerve endings in the buttocks are involved in sexual arousal. When stimulated, they can increase blood flow to the genital area, leading to enhanced sexual sensations and pleasure.
In conclusion, the buttocks are a complex anatomical region consisting of multiple muscles and nerves. Understanding the muscular structure and nerve distribution in this area is essential to comprehend the role of parasympathetic nerve endings in regulating various bodily functions.
Parasympathetic Nerve Endings in the Buttocks
The buttocks are not just a cushion for sitting, but also home to a network of parasympathetic nerve endings. These nerve endings have unique locations and distributions throughout this region, playing a crucial role in various bodily functions.
Location and Distribution
Let’s dive deeper into the location and distribution of these parasympathetic nerve endings in the buttocks. They are found in close proximity to key anatomical structures, including the pelvic floor muscles and the rectum. This strategic placement allows for efficient communication between these nerve endings and the surrounding structures.
Originating from the sacral region of the spinal cord, these nerve endings extend their delicate fibers throughout the buttocks, forming an intricate network. Their distribution is not random but rather precisely organized to ensure proper functioning of the associated bodily processes.
Function and Significance
The parasympathetic nerve endings in the buttocks serve a vital role in regulating various functions, which are essential for our overall well-being.
One of their primary functions is to control bowel movements. When these nerve endings are stimulated, they send signals to the muscles of the rectum, initiating the process of defecation. Without their proper functioning, individuals may experience difficulties in passing stool, leading to conditions such as constipation.
In addition to bowel movements, these nerve endings also play a crucial role in bladder control. When the bladder is full, the parasympathetic nerve endings in the buttocks are responsible for triggering the urge to urinate. They coordinate with the muscles of the bladder, allowing for the efficient release of urine. Dysfunction or damage to these nerve endings can result in urinary incontinence, where individuals struggle to control their bladder, leading to embarrassing situations and a decreased quality of life.
Furthermore, the parasympathetic nerve endings in the buttocks are involved in sexual arousal. When stimulated, they initiate a cascade of events that lead to increased blood flow to the genital area, contributing to sexual pleasure and the ability to achieve and maintain an erection in males. Dysfunction in these nerve endings can lead to erectile dysfunction, a condition that affects the sexual health and well-being of individuals.
It is important to highlight the significance of these nerve endings in the buttocks. Dysfunction or damage to them can result in various conditions such as fecal or urinary incontinence, erectile dysfunction, and even pelvic pain. These conditions can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life, making it essential to understand and appreciate the role of the parasympathetic nerve endings in this region.
In conclusion, the parasympathetic nerve endings in the buttocks are not just a mere anatomical detail but rather a complex network that regulates vital bodily functions. Their strategic location and distribution, coupled with their role in controlling bowel movements, bladder control, and sexual arousal, highlight their significance. Understanding the importance of these nerve endings can help in diagnosing and treating various conditions that may arise from their dysfunction or damage.
Disorders Related to Parasympathetic Nerve Endings in the Buttocks
Disorders affecting the parasympathetic nerve endings in the buttocks can have a significant impact on an individual’s quality of life. The parasympathetic nervous system plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions, including digestion, sexual function, and bladder control. When these nerve endings are disrupted or damaged, it can lead to a range of symptoms and complications.
One common symptom of parasympathetic nerve-related disorders is difficulty controlling bowel or bladder movements. This can manifest as urinary or fecal incontinence, where individuals may experience leakage or complete loss of control over these bodily functions. The embarrassment and social stigma associated with these symptoms can significantly affect a person’s self-esteem and overall well-being.
In addition to bowel and bladder dysfunction, sexual dysfunction is another prevalent symptom of disorders related to parasympathetic nerve endings in the buttocks. Individuals may experience difficulties achieving or maintaining an erection, decreased sexual desire, or problems with orgasm. These issues can strain relationships and lead to emotional distress.
Chronic pelvic pain is another common symptom experienced by individuals with parasympathetic nerve-related disorders. This pain can be persistent and debilitating, affecting daily activities and overall quality of life. The exact cause of pelvic pain can vary, ranging from nerve damage to inflammation or muscle dysfunction.
There are several potential causes of disorders related to parasympathetic nerve endings in the buttocks. Nerve damage can occur due to trauma, such as a fall or injury to the lower back or pelvic region. Infections, such as urinary tract infections or sexually transmitted infections, can also affect the nerves in this area. Additionally, underlying medical conditions like diabetes, multiple sclerosis, or spinal cord injuries can contribute to parasympathetic nerve dysfunction.
If you experience any of the symptoms associated with parasympathetic nerve-related disorders, it is crucial to seek medical attention and consult with a healthcare professional. A thorough medical evaluation, including imaging tests and specialized examinations, can help determine the underlying cause of your symptoms. It is important to remember that early diagnosis and intervention can lead to better outcomes and improved quality of life.
The treatment options for disorders related to parasympathetic nerve endings in the buttocks may include medication, physical therapy, lifestyle modifications, or surgical interventions. Medications can help manage symptoms like pain or bladder dysfunction. Physical therapy techniques, such as pelvic floor exercises or biofeedback, can strengthen the muscles and improve bladder or bowel control. Lifestyle modifications, such as dietary changes or stress management techniques, can also play a significant role in symptom management. In severe cases, surgical interventions may be necessary to repair damaged nerves or correct underlying structural issues.
However, it is important to note that treatment plans can vary depending on the specific diagnosis and individual circumstances. Consulting with a healthcare professional who specializes in these disorders is essential to develop an appropriate treatment plan tailored to your needs. They can provide guidance, support, and access to resources that can help you manage your symptoms and improve your overall well-being.
The Impact of Parasympathetic Nerve Endings on Overall Health
The parasympathetic nerve endings in the buttocks not only affect specific functions in this area but also have a significant impact on overall health and well-being.
The parasympathetic nervous system, which includes the nerve endings in the buttocks, plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis in the body. It is responsible for the rest and digest response, counterbalancing the fight or flight response of the sympathetic nervous system. This delicate balance is essential for optimal health and well-being.
Connection to Other Body Systems
The parasympathetic nervous system has extensive connections with other body systems, including the cardiovascular, digestive, and reproductive systems. These connections allow for seamless communication and coordination between different organs and tissues, ensuring proper functioning and overall health.
In the cardiovascular system, the parasympathetic nerve endings help regulate heart rate and blood pressure. They work in harmony with the sympathetic nervous system to maintain a steady heart rhythm and prevent excessive fluctuations in blood pressure. This balance is crucial for cardiovascular health and the prevention of conditions such as hypertension and heart disease.
Similarly, in the digestive system, the parasympathetic nerve endings play a vital role in promoting efficient digestion and absorption of nutrients. They stimulate the production of digestive enzymes and increase blood flow to the gastrointestinal tract, enhancing the breakdown and absorption of food. This ensures proper nutrient uptake and supports overall digestive health.
The parasympathetic nerve endings also have a significant impact on the reproductive system. They contribute to sexual arousal and facilitate the release of reproductive hormones. By regulating blood flow to the genital area and promoting relaxation, these nerve endings play a crucial role in sexual function and reproductive health.
Importance in Maintaining Health and Well-being
The parasympathetic nerve endings in the buttocks help regulate essential bodily functions, promote relaxation, and support overall psychological well-being. By ensuring proper control over bowel, bladder, and sexual functions, these nerve endings contribute to a higher quality of life.
When the parasympathetic nerve endings are functioning optimally, they promote relaxation and reduce stress levels. This has a positive impact on mental health, helping to alleviate anxiety and depression. Additionally, the parasympathetic nervous system stimulates the release of endorphins, which are natural painkillers and mood enhancers.
Proper control over bowel and bladder functions is crucial for maintaining comfort and preventing complications such as urinary incontinence or constipation. The parasympathetic nerve endings in the buttocks ensure the coordination of these functions, allowing for regular and efficient elimination.
Furthermore, the parasympathetic nerve endings play a role in sexual function and satisfaction. By regulating blood flow to the genital area and facilitating sexual arousal, they contribute to a fulfilling and enjoyable sex life.
In conclusion, the parasympathetic nerve endings in the buttocks have far-reaching effects on overall health and well-being. Their connections to various body systems and their role in maintaining essential bodily functions make them a vital component of optimal health. By understanding and nurturing these nerve endings, we can support our overall well-being and lead healthier, more fulfilling lives.
Future Research Directions in Parasympathetic Nerve Endings
Despite advancements in understanding parasympathetic nerve endings in the buttocks, there are still several avenues for future research that hold great potential for breakthroughs in this area.
Current Limitations and Challenges
Current research on parasympathetic nerve endings in the buttocks faces challenges such as limited understanding of specific nerve pathways, complex interactions with other nerve systems, and the need for further clinical studies to validate findings.
Potential Breakthroughs and Developments
Future research can focus on identifying novel therapeutic targets, leveraging emerging technologies for diagnostic purposes, and exploring non-invasive treatment modalities for disorders affecting parasympathetic nerve endings in the buttocks. Continued research efforts have the potential to improve our understanding of these nerve endings and offer more effective treatment options.
In conclusion, understanding parasympathetic nerve endings in the buttocks is essential for comprehending the intricate network that governs various bodily functions. Disorders affecting these nerve endings can have a significant impact on an individual’s quality of life. It is crucial to seek medical advice and consult with a healthcare professional if you experience any related symptoms. By furthering our knowledge through research, we can hope to improve diagnosis, treatment, and overall outcomes for individuals with conditions related to parasympathetic nerve endings in the buttocks.