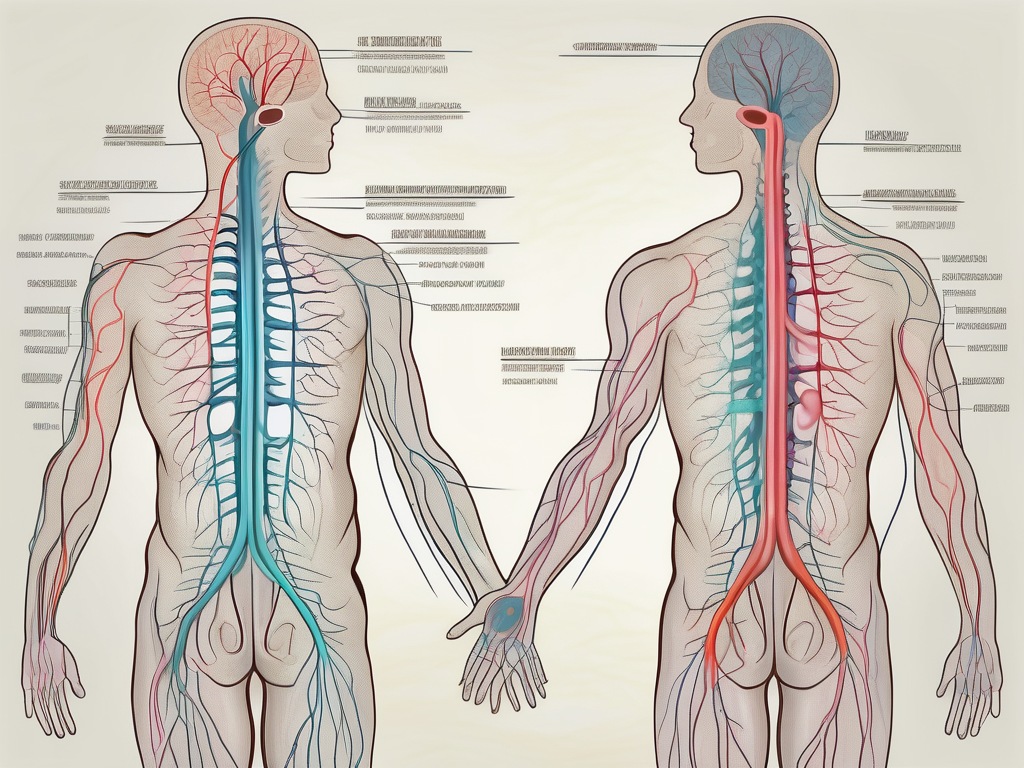
The parasympathetic nervous system, often referred to as the “rest and digest” system, plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance and harmony of our bodily functions. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve deep into the intricate workings of parasympathetic nerve fibers and explore their significance in our overall well-being.
Introduction to the Nervous System
Before we embark on our exploration of the parasympathetic nervous system, it is important to have a basic understanding of the nervous system as a whole. The nervous system is a complex network of nerve cells and fibers that facilitates communication between different parts of the body and the brain. It can be broadly divided into two main divisions: the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. While the central nervous system includes the brain and spinal cord, the peripheral nervous system comprises the nerves that extend from the central nervous system to the rest of the body.
Overview of the Nervous System
The nervous system acts as a control center for our body, allowing us to perform various voluntary and involuntary actions. It regulates vital functions such as breathing, heart rate, digestion, and even our thoughts and emotions. The intricate web of nerves enables the transmission of signals between different parts of the body, ensuring proper coordination and functioning.
Imagine a scenario where you are walking in a park, enjoying the fresh air and the beauty of nature. As you stroll along, your brain receives signals from your eyes, allowing you to see the vibrant colors of the flowers and the lush greenery surrounding you. Simultaneously, your peripheral nervous system is at work, coordinating the movement of your legs, ensuring that you maintain balance and avoid any obstacles on your path. Without the nervous system, this simple act of walking and experiencing the world around you would not be possible.
But the nervous system does much more than just enable us to walk and see. It is responsible for the complex processes that occur within our bodies, often without us even realizing it. For example, the nervous system regulates our heart rate, ensuring that it beats at a steady rhythm to pump blood throughout our bodies. It also controls our breathing, allowing us to take in oxygen and expel carbon dioxide. These functions are essential for our survival, and the nervous system plays a crucial role in maintaining them.
Divisions of the Nervous System
The peripheral nervous system can be further divided into the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system. While the somatic nervous system controls voluntary movements and sensory perception, the autonomic nervous system regulates involuntary functions.
Let’s delve deeper into the somatic nervous system. This division of the peripheral nervous system is responsible for our conscious movements and sensory experiences. It allows us to interact with the world around us, enabling us to walk, talk, and engage in various activities. For example, when you decide to raise your hand, it is the somatic nervous system that sends signals from your brain to the muscles in your arm, causing them to contract and lift your hand. Similarly, when you touch a hot surface, the somatic nervous system relays the sensation of heat to your brain, alerting you to the potential danger.
On the other hand, the autonomic nervous system controls involuntary functions that occur without conscious effort. It can be further divided into the sympathetic nervous system and the parasympathetic nervous system. The sympathetic nervous system is responsible for the body’s fight-or-flight response, preparing us for action in times of danger or stress. In contrast, the parasympathetic nervous system promotes rest and relaxation, allowing our bodies to recover and conserve energy.
Imagine you are faced with a sudden threat, such as a loud noise or a dangerous animal. Your sympathetic nervous system would kick into gear, increasing your heart rate, dilating your pupils, and releasing stress hormones such as adrenaline. These physiological changes prepare your body to either fight the threat or flee from it. On the other hand, when you are in a peaceful environment, such as lying in a hammock on a sunny day, your parasympathetic nervous system takes over, slowing down your heart rate, constricting your pupils, and promoting digestion and relaxation.
The divisions of the nervous system work in harmony to maintain homeostasis, a state of balance and stability within the body. They ensure that our bodies can adapt to different situations and respond appropriately to external stimuli. Without this intricate system, our bodies would be unable to function effectively, and our survival would be compromised.
Diving Deeper into the Parasympathetic Nervous System
Now that we have a foundational understanding of the nervous system, let’s focus our attention on the parasympathetic nervous system, one of the two main divisions of the autonomic nervous system. The parasympathetic system works in opposition to its counterpart, the sympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for the body’s fight-or-flight response.
Anatomy of the Parasympathetic Nervous System
The parasympathetic nervous system consists of cranial nerves originating from the brainstem and sacral nerves arising from the lower part of the spinal cord. These nerves carry signals to specific organs and tissues, promoting rest, relaxation, and recovery.
The cranial nerves involved in the parasympathetic system include the oculomotor nerve, facial nerve, glossopharyngeal nerve, and vagus nerve. These nerves innervate various structures, such as the eyes, salivary glands, heart, lungs, liver, and digestive organs. The sacral nerves, on the other hand, innervate the lower part of the digestive tract, bladder, and reproductive organs.
Each of these nerves has a specific function in regulating the parasympathetic response. For example, the oculomotor nerve controls the constriction of the pupil and the focusing of the lens in the eye. The facial nerve stimulates tear production and salivation. The glossopharyngeal nerve is responsible for the secretion of saliva and the contraction of the pharynx during swallowing. Lastly, the vagus nerve, the longest cranial nerve, innervates multiple organs, including the heart, lungs, liver, and digestive tract.
Functions of the Parasympathetic Nervous System
The primary function of the parasympathetic nervous system is to conserve energy and maintain a state of calmness in the body. It works in opposition to the sympathetic nervous system, which prepares the body for action during times of stress or danger. When the parasympathetic system is active, heart rate and blood pressure decrease, digestion and nutrient absorption improve, and overall relaxation is promoted.
Furthermore, the parasympathetic system plays a crucial role in various bodily functions. For instance, it stimulates the production of saliva, which aids in the digestion of food. It also promotes the release of digestive enzymes and increases blood flow to the digestive organs, enhancing nutrient absorption. Additionally, the parasympathetic system stimulates the contraction of the bladder muscles, facilitating urination.
It is essential to note that the parasympathetic nervous system not only maintains physiological balance but also influences our mental and emotional well-being. By fostering a state of rest and tranquility, the parasympathetic system allows us to experience moments of peace and rejuvenation. It helps reduce anxiety, promote mental clarity, and improve overall mood.
In conclusion, the parasympathetic nervous system, with its intricate network of cranial and sacral nerves, plays a vital role in maintaining the body’s equilibrium. By promoting rest, relaxation, and recovery, it allows us to experience moments of calmness and rejuvenation, both physically and mentally.
The Role of Parasympathetic Nerve Fibers
At the core of the parasympathetic nervous system are specialized nerve fibers that carry signals from the central nervous system to various organs and tissues throughout the body. These parasympathetic nerve fibers play a significant role in regulating bodily functions and ensuring optimal performance.
Parasympathetic nerve fibers are part of the autonomic nervous system, which controls involuntary actions such as heart rate, digestion, and breathing. They work in opposition to the sympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for the “fight or flight” response. While the sympathetic nervous system prepares the body for action, the parasympathetic nervous system promotes relaxation and restoration.
How Parasympathetic Nerve Fibers Work
Parasympathetic nerve fibers release a neurotransmitter called acetylcholine, which binds to specific receptors on target tissues and organs. This binding triggers a cascade of events that lead to relaxation and enhanced functioning. For example, in the gastrointestinal system, parasympathetic stimulation increases digestive enzyme secretion, improves gut motility, and enhances nutrient absorption.
When the body is in a relaxed state, parasympathetic nerve fibers are active. They slow down the heart rate, reduce blood pressure, and promote digestion. This allows the body to conserve energy and focus on essential functions such as nutrient absorption and waste elimination. The parasympathetic nervous system also plays a crucial role in sexual arousal, as it is responsible for the release of nitric oxide, which relaxes blood vessels and increases blood flow to the genital area.
The Importance of Parasympathetic Nerve Fibers
Parasympathetic nerve fibers are vital for maintaining homeostasis in our bodies. They counterbalance the effects of the sympathetic nervous system, ensuring a harmonious equilibrium between rest and activity. By promoting relaxation and supporting essential bodily functions, parasympathetic nerve fibers contribute to our overall health and well-being.
In addition to their role in digestion and sexual arousal, parasympathetic nerve fibers also play a crucial role in other bodily functions. They help regulate bladder and bowel movements, control salivation and tear production, and promote the secretion of digestive juices in the stomach and pancreas. Furthermore, the parasympathetic nervous system is involved in controlling pupil constriction, which helps with focusing on nearby objects.
Imbalances in the parasympathetic nervous system can lead to various health issues. For example, overactivity of parasympathetic nerve fibers may result in excessive salivation, frequent urination, and slow heart rate. On the other hand, underactivity of these fibers can lead to dry mouth, constipation, and rapid heart rate.
Understanding the role of parasympathetic nerve fibers is essential for maintaining a healthy lifestyle. By adopting relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, and yoga, we can activate our parasympathetic nervous system and promote overall well-being. Taking care of our parasympathetic nerve fibers is crucial for achieving a balanced and healthy life.
Disorders Related to Parasympathetic Nerve Fibers
While the parasympathetic nervous system is generally reliable and efficient, certain disorders or imbalances can disrupt its functioning. It is crucial to be aware of these conditions to seek timely medical attention and ensure proper management.
The parasympathetic nervous system plays a vital role in maintaining homeostasis in the body. It is responsible for regulating various bodily functions, including digestion, heart rate, and bladder control. However, when there is a dysfunction in the parasympathetic nerve fibers, it can lead to a range of disorders and symptoms.
Common Disorders and Their Symptoms
One common disorder related to parasympathetic nerve fibers is dysautonomia. Dysautonomia is a condition characterized by an impaired autonomic nervous system, which includes both the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions. This disorder can result in a wide range of symptoms, including irregular heart rate, digestive disturbances, impaired bladder control, dizziness, and even fainting spells.
Another disorder that can affect the parasympathetic nervous system is irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). IBS is a gastrointestinal disorder that causes abdominal pain, bloating, and changes in bowel habits. The parasympathetic nervous system plays a crucial role in regulating the digestive process, and any dysfunction in this system can contribute to the development of IBS.
Treatment and Management of Disorders
If you suspect that you may be experiencing any issues related to the parasympathetic nervous system, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional who can provide an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment options. The treatment and management of disorders related to parasympathetic nerve fibers depend on the specific condition and its underlying cause.
In the case of dysautonomia, treatment may involve a combination of lifestyle modifications and medications. Lifestyle modifications may include regular exercise, stress management techniques, and dietary changes. Medications, such as beta-blockers or anticholinergic drugs, may be prescribed to help regulate heart rate and manage other symptoms.
For individuals with irritable bowel syndrome, treatment may focus on managing symptoms and improving overall gut health. This can involve dietary modifications, such as avoiding trigger foods, increasing fiber intake, and incorporating probiotics into the diet. Stress management techniques, such as relaxation exercises or cognitive-behavioral therapy, may also be beneficial in managing symptoms.
In some cases, additional interventions may be necessary to restore balance in the parasympathetic nervous system. These interventions may include physical therapy, biofeedback, or even surgical procedures, depending on the severity and underlying cause of the disorder.
It is important to remember that each individual’s experience with disorders related to parasympathetic nerve fibers may vary. Therefore, a personalized approach to treatment and management is essential to address the specific needs and symptoms of each person.
In conclusion, disorders related to parasympathetic nerve fibers can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. Seeking timely medical attention and proper management is crucial to alleviate symptoms and restore balance in the parasympathetic nervous system. By understanding these disorders and their symptoms, individuals can take proactive steps towards their well-being and overall health.
The Future of Parasympathetic Nerve Research
The field of parasympathetic nerve research is continuously evolving, with scientists dedicated to unraveling its mysteries and potential applications. These ongoing efforts hold promise for discoveries that could revolutionize healthcare and enhance our understanding of the human body.
Current Trends in Research
Current research in parasympathetic nerve fibers focuses on understanding the underlying mechanisms of their function and exploring potential therapeutic targets. Scientists are investigating the connection between the parasympathetic system and various health conditions, including anxiety, depression, and gastrointestinal disorders, with the aim of developing more effective treatments.
One area of current research interest is the role of the parasympathetic nervous system in mental health disorders. Studies have shown that imbalances in the parasympathetic system can contribute to the development and progression of anxiety and depression. Researchers are using advanced imaging techniques, such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), to map the activity of the parasympathetic nerves in individuals with these conditions. By identifying specific patterns of activity, scientists hope to develop targeted interventions that can restore balance to the parasympathetic system and alleviate symptoms.
In addition to mental health, researchers are also exploring the role of the parasympathetic system in gastrointestinal disorders. The parasympathetic nerves play a crucial role in regulating digestion and gut motility. Dysfunction in this system can lead to conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and gastroparesis. Scientists are investigating novel therapeutic approaches, such as neurostimulation, to modulate the activity of the parasympathetic nerves and restore normal gut function. Early studies have shown promising results, with some patients experiencing significant improvements in symptoms.
Potential Breakthroughs and Discoveries
While it is impossible to predict the exact nature of future breakthroughs in parasympathetic nerve research, emerging technologies such as neurostimulation and advanced imaging techniques offer exciting possibilities. These innovations may provide new insights into the functioning of the parasympathetic system and pave the way for novel treatments.
Neurostimulation, in particular, holds great potential for the future of parasympathetic nerve research. This technique involves the use of electrical or magnetic impulses to stimulate specific nerves in the parasympathetic system. By precisely targeting these nerves, researchers can modulate their activity and potentially restore balance to the system. Neurostimulation has already shown promise in the treatment of various conditions, such as chronic pain and Parkinson’s disease. As scientists continue to refine this technique, it may become a valuable tool for managing parasympathetic-related disorders.
Advanced imaging techniques, such as positron emission tomography (PET) and diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), also offer exciting possibilities for future discoveries. These imaging modalities allow researchers to visualize the structure and function of the parasympathetic nerves in unprecedented detail. By studying the intricate connections and pathways of these nerves, scientists can gain a deeper understanding of their role in health and disease. This knowledge can then be translated into the development of targeted therapies that can restore normal parasympathetic function.
In conclusion, the future of parasympathetic nerve research is filled with promise and potential. Ongoing studies are shedding light on the underlying mechanisms of the parasympathetic system and its connection to various health conditions. With the advent of emerging technologies, such as neurostimulation and advanced imaging techniques, researchers are poised to make groundbreaking discoveries that could revolutionize healthcare and improve the lives of countless individuals.
Conclusion: The Parasympathetic Nervous System and You
In conclusion, the parasympathetic nervous system plays a vital role in maintaining our overall well-being. By promoting relaxation, regulating bodily functions, and fostering a sense of peace, it contributes to our physical, mental, and emotional health. Understanding the importance of parasympathetic nerve fibers empowers us to prioritize self-care and seek professional guidance when necessary.
Everyday Impacts of the Parasympathetic Nervous System
Recognizing the everyday impacts of the parasympathetic nervous system allows us to make informed choices that support its proper functioning. Engaging in activities such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, and regular exercise can help activate the parasympathetic system and promote relaxation.
Maintaining a Healthy Parasympathetic Nervous System
To maintain a healthy parasympathetic nervous system, it is crucial to prioritize self-care and adopt a holistic approach to well-being. This includes maintaining a balanced diet, getting adequate sleep, managing stress levels, and seeking professional healthcare when necessary. Your doctor can provide personalized guidance and support to ensure the optimal functioning of your parasympathetic system.
By understanding the role of parasympathetic nerve fibers and taking steps to support their functioning, we can enhance our overall quality of life and cultivate a sense of harmony within ourselves. Embracing this comprehensive guide to the parasympathetic nervous system empowers us to make informed decisions about our health and well-being.