Parasympathetic nerve impulses play a vital role in the functioning of our bodies. These impulses are part of the autonomic nervous system, which controls involuntary bodily functions. To truly understand the role of parasympathetic nerve impulses, we must first have a clear understanding of the basics of the nervous system.
The Basics of the Nervous System
The nervous system is a complex network of cells, tissues, and organs that coordinate and control the activities of the body. It can be divided into two main parts: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
The central nervous system (CNS) consists of the brain and spinal cord. The brain, which weighs about three pounds, is the command center for the entire body. It is responsible for processing and interpreting information received from the sensory organs and sending out appropriate signals to the rest of the body. The spinal cord, on the other hand, is a long, thin bundle of nerves that extends from the base of the brain down to the lower back. It acts as a pathway for information to travel between the brain and the rest of the body.
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) includes all the nerves outside of the brain and spinal cord. These nerves, which are like electrical wires, transmit signals between the central nervous system and the rest of the body. The PNS can be further divided into two parts: the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system. The somatic nervous system controls voluntary movements, such as walking or picking up an object. The autonomic nervous system, on the other hand, controls involuntary actions, such as breathing or digestion.
The Structure of the Nervous System
The central nervous system (CNS) is protected by the skull and the spinal column. The brain, which is made up of billions of neurons, is divided into different regions, each responsible for specific functions. For example, the frontal lobe is involved in decision-making and problem-solving, while the occipital lobe is responsible for processing visual information. The spinal cord, which is surrounded by a protective layer called the spinal column, is made up of a series of interconnected nerves that transmit information to and from the brain.
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) consists of nerves that extend throughout the body. These nerves can be categorized into two types: sensory nerves and motor nerves. Sensory nerves carry information from the sensory organs, such as the eyes or skin, to the central nervous system. Motor nerves, on the other hand, carry signals from the central nervous system to the muscles and glands, allowing for movement and bodily functions.
The Function of the Nervous System
The primary function of the nervous system is to collect, process, and respond to information from both internal and external environments. It helps regulate bodily processes such as movement, sensation, and digestion. For example, when you touch a hot stove, sensory receptors in your skin send a signal to your brain, which then sends a signal to your muscles to move your hand away. This rapid response is made possible by the intricate network of neurons in the nervous system.
In addition to its role in coordinating movement and sensation, the nervous system also plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis, the body’s internal balance. It helps regulate body temperature, blood pressure, and heart rate, among other things. For example, when you exercise, your nervous system sends signals to increase your heart rate and dilate your blood vessels, ensuring that your muscles receive enough oxygen and nutrients.
Furthermore, the nervous system is involved in higher cognitive functions, such as memory, learning, and emotions. The brain, in particular, is responsible for processing and storing information, allowing us to learn new things and remember past experiences. It also plays a role in controlling emotions and behaviors, helping us respond appropriately to different situations.
In conclusion, the nervous system is a complex and intricate network that controls and coordinates the activities of the body. From the brain and spinal cord to the peripheral nerves, each component plays a vital role in ensuring that our bodies function properly. Whether it’s sensing the world around us, moving our muscles, or regulating our internal processes, the nervous system is involved in every aspect of our daily lives.
Introduction to Parasympathetic Nerve Impulses
The parasympathetic nervous system is one of the two divisions of the autonomic nervous system. It works in opposition to the sympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for the “fight or flight” response. The parasympathetic system is often referred to as the “rest and digest” system, as it promotes relaxation and conservation of energy.
When it comes to the regulation of bodily functions, the parasympathetic nervous system plays a crucial role. It helps maintain homeostasis by counterbalancing the effects of the sympathetic nervous system. While the sympathetic system prepares the body for action, the parasympathetic system ensures that the body can rest, recover, and perform essential functions.
What are Parasympathetic Nerve Impulses?
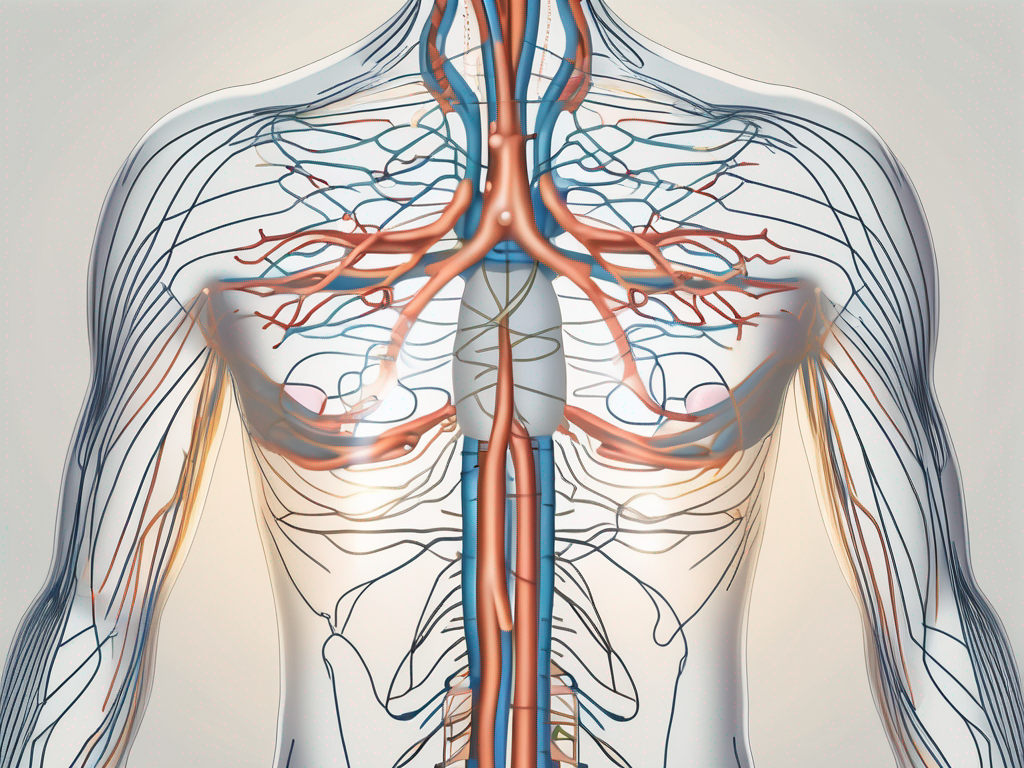
Parasympathetic nerve impulses are electrical signals that travel along parasympathetic nerve fibers. These impulses originate in specific regions of the CNS, namely the cranial nerves and the sacral spinal cord. They then travel through the peripheral nervous system (PNS) to various organs and glands, influencing their function.
When the body needs to slow down, the parasympathetic nervous system kicks into action. It sends out nerve impulses that help regulate heart rate, digestion, and other vital functions. These impulses are like messengers, delivering instructions to different parts of the body, ensuring that everything runs smoothly.
The Origin and Pathways of Parasympathetic Nerve Impulses
Parasympathetic nerve impulses originate in two main areas: the brainstem and the sacral spinal cord. The cranial nerves, specifically the vagus nerve, carry parasympathetic fibers that innervate organs in the head, neck, thorax, and abdomen. These fibers branch out and reach various target organs, such as the heart, lungs, liver, and intestines.
Meanwhile, the sacral spinal cord supplies parasympathetic fibers to the organs in the pelvis. These fibers travel through the pelvic nerves, influencing the function of the bladder, reproductive organs, and digestive system in that region.
It’s fascinating to think about the intricate network of nerves that make up the parasympathetic system. These nerves form pathways that connect the brain and spinal cord to different organs, allowing for precise control and coordination of bodily functions.
Overall, the parasympathetic nervous system is a vital part of our physiological well-being. It ensures that our bodies can rest, digest food properly, and maintain a state of calmness. Without the parasympathetic nerve impulses, our bodies would be in a constant state of heightened arousal, unable to recover and function optimally.
The Role of Parasympathetic Nerve Impulses in Body Functions
Now that we have a basic understanding of parasympathetic nerve impulses, let’s explore their roles in various body functions.
The parasympathetic nervous system, often referred to as the “rest and digest” system, is responsible for maintaining homeostasis in the body. It works in opposition to the sympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for the “fight or flight” response.
Parasympathetic Nerve Impulses and the Heart
The parasympathetic nervous system plays a crucial role in regulating heart rate and controlling blood pressure. Parasympathetic fibers from the vagus nerve slow down the heart rate by reducing the rate of electrical impulses conducted through the heart’s specialized cells. This helps maintain a steady and healthy heart rhythm.
Additionally, the parasympathetic system helps to regulate blood pressure by promoting vasodilation, which is the widening of blood vessels. This allows for increased blood flow and helps to lower blood pressure.
Parasympathetic Nerve Impulses and the Digestive System
The parasympathetic system stimulates the digestive process by increasing the production of digestive enzymes and promoting the relaxation of smooth muscles in the gastrointestinal tract. This allows for efficient digestion and absorption of nutrients.
Furthermore, the parasympathetic system stimulates the release of bile from the gallbladder, which is essential for the breakdown and absorption of fats. It also enhances blood flow to the digestive organs, ensuring that they receive the necessary oxygen and nutrients for optimal function.
Parasympathetic Nerve Impulses and the Respiratory System
In the respiratory system, parasympathetic nerve impulses help regulate breathing rate and depth. They cause constriction of the airways, which can be beneficial in certain situations such as preventing unwanted airflow or protecting the lungs from harmful substances. However, excessive constriction can lead to breathing difficulties.
Additionally, the parasympathetic system promotes bronchoconstriction, which is the narrowing of the airways. This helps to direct airflow to specific regions of the lungs, ensuring efficient gas exchange.
Overall, the parasympathetic nervous system plays a vital role in maintaining the body’s internal balance and ensuring the proper functioning of various organ systems. By understanding its functions, we can appreciate the intricate mechanisms that allow our bodies to function optimally.
The Impact of Parasympathetic Nerve Impulses on Health and Disease
Understanding the impact of parasympathetic nerve impulses on health and disease can provide valuable insight into various bodily processes. It is important to note that disruptions in the normal functioning of the parasympathetic system can have significant implications.
The parasympathetic system, also known as the “rest and digest” system, plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis within the body. It works in opposition to the sympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for the “fight or flight” response. While the sympathetic system prepares the body for action, the parasympathetic system helps counterbalance these effects, promoting relaxation and calming the body.
One of the key ways in which parasympathetic nerve impulses impact health is through their role in the stress response. Chronic stress can dysregulate the delicate balance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems, potentially leading to increased susceptibility to stress-related disorders. When the parasympathetic system is not functioning optimally, individuals may experience symptoms such as increased heart rate, elevated blood pressure, and digestive disturbances.
Managing stress is crucial for maintaining a healthy parasympathetic system. Engaging in regular exercise, practicing meditation or mindfulness techniques, and seeking support from a healthcare professional can all be effective strategies for promoting relaxation and restoring balance to the nervous system.
Parasympathetic Nerve Impulses and Chronic Diseases
Research has shown that certain chronic diseases can affect the functioning of the parasympathetic system. For example, cardiovascular disease, which encompasses conditions such as hypertension and heart failure, can disrupt the normal regulatory mechanisms of the parasympathetic system. This can lead to imbalances in heart rate variability and contribute to the progression of the disease.
Gastrointestinal disorders, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), have also been linked to alterations in parasympathetic nerve impulses. The parasympathetic system plays a crucial role in regulating digestive processes, including the secretion of digestive enzymes and the movement of food through the gastrointestinal tract. Disruptions in this system can contribute to symptoms such as abdominal pain, bloating, and irregular bowel movements.
Understanding the interactions between chronic diseases and the parasympathetic system is essential for healthcare professionals in developing targeted treatments and interventions. By addressing the underlying dysregulation of the parasympathetic system, it may be possible to improve patient outcomes and alleviate symptoms associated with these conditions.
If you suspect any issues related to the parasympathetic system, it is always advisable to consult with a healthcare provider. They can conduct a thorough evaluation, including medical history, physical examination, and potentially specialized tests, to determine the underlying cause of any symptoms and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
The Future of Parasympathetic Nerve Research
The field of parasympathetic nerve research is continually evolving, with new advancements and discoveries being made. Let’s explore some of the current trends and potential applications of this research.
Current Trends in Parasympathetic Nerve Research
One current trend in parasympathetic nerve research is the exploration of its role in mental health disorders such as anxiety and depression. Researchers are investigating how modulating parasympathetic activity through techniques like vagus nerve stimulation can potentially alleviate symptoms and improve overall well-being.
Recent studies have shown promising results in using vagus nerve stimulation as a treatment for treatment-resistant depression. By targeting the parasympathetic nervous system, this technique aims to restore balance and regulate mood. This research opens up new possibilities for individuals who have not responded to traditional antidepressant medications.
Moreover, researchers are also examining the connection between parasympathetic nerve activity and anxiety disorders. By understanding how the parasympathetic system influences the body’s response to stress, scientists hope to develop more effective interventions. This could lead to the development of innovative therapies that target the parasympathetic nervous system, providing relief for individuals suffering from debilitating anxiety.
Potential Applications of Parasympathetic Nerve Research
As our understanding of the parasympathetic system grows, there is potential for developing new therapeutic approaches for various conditions. For example, targeted interventions could be designed to enhance parasympathetic activity in cases of heart rate irregularities or digestive disorders.
Heart rate irregularities, such as arrhythmias, can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. By investigating the role of the parasympathetic nervous system in regulating heart rate, researchers aim to develop treatments that specifically target this system. This could potentially lead to more effective and personalized therapies for individuals with heart conditions.
Similarly, digestive disorders, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), can cause significant discomfort and affect daily life. Parasympathetic nerve research may provide insights into the underlying mechanisms of these disorders, leading to the development of novel treatments. By modulating parasympathetic activity, researchers hope to alleviate symptoms and improve the overall well-being of individuals living with digestive disorders.
However, it’s important to remember that further research is needed to fully explore these possibilities. While the current trends and potential applications of parasympathetic nerve research show great promise, continued investigation and clinical trials are necessary to validate these findings and ensure their safety and efficacy.
Conclusion
In conclusion, parasympathetic nerve impulses play a critical role in maintaining the balance and proper functioning of various bodily systems. Understanding the intricacies of the parasympathetic system can help healthcare professionals identify and address potential disruptions, leading to improved patient care and outcomes. If you have any concerns about your own health or the functioning of your parasympathetic system, it is always best to consult with a healthcare provider who can provide expert guidance and support.