The parasympathetic nerve plays a crucial role in our body’s functioning and overall well-being. It is a branch of the autonomic nervous system, which controls involuntary actions such as digestion, heart rate, and stress response. In this article, we will delve into the basics of the parasympathetic nerve, its impact on homeostasis, its role in the stress response, disorders related to its functioning, and the future of research in this field.
The Basics of the Parasympathetic Nerve
Before diving into the intricacies of the parasympathetic nerve, let’s first understand its definition and function. The parasympathetic nervous system is responsible for promoting relaxation and restoration in our body. It works opposite to the sympathetic nervous system, which triggers the “fight or flight” response.
The parasympathetic nervous system, also known as the “rest and digest” system, helps regulate vital bodily functions such as digestion, heart rate, and glandular secretions. It allows our body to conserve energy, repair tissues, and focus on essential tasks like food breakdown and nutrient absorption.
Now, let’s delve deeper into the anatomy of the parasympathetic nerve to gain a better understanding of its structure and function.
Definition and Function
The parasympathetic nervous system plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis, the body’s internal balance. It acts as a counterbalance to the sympathetic nervous system, ensuring that our body functions smoothly and efficiently.
One of the primary functions of the parasympathetic nervous system is to regulate digestion. When we eat, the parasympathetic nerve stimulates the release of digestive enzymes and increases blood flow to the digestive organs, allowing for optimal nutrient absorption. It also helps in the elimination of waste products by promoting peristalsis, the rhythmic contractions of the digestive tract.
In addition to digestion, the parasympathetic nervous system controls heart rate and blood pressure. It slows down the heart rate, allowing the heart to pump blood efficiently and reducing the workload on the cardiovascular system. This helps to maintain a stable blood pressure and prevent cardiovascular diseases.
The parasympathetic nerve also plays a vital role in regulating glandular secretions. It stimulates the production of saliva, tears, and other essential fluids that aid in digestion and lubrication. It also controls the release of hormones from various glands, ensuring proper hormonal balance in the body.
Anatomy of the Parasympathetic Nerve
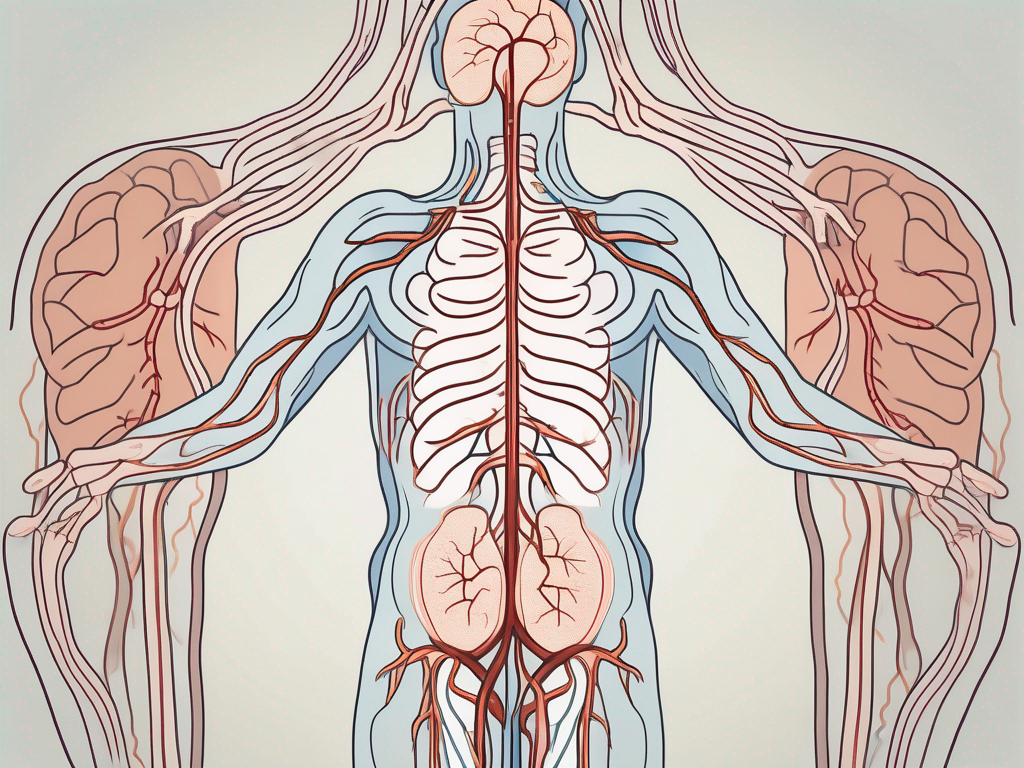
The parasympathetic nervous system consists of cranial nerves and sacral spinal nerves. The cranial nerves, including the vagus nerve, originate from the brainstem and innervate organs in the head, neck, chest, and abdomen. These cranial nerves carry parasympathetic signals to various target organs, allowing for precise control and regulation.
The vagus nerve, the longest cranial nerve, is responsible for the parasympathetic innervation of several organs, including the heart, lungs, stomach, and intestines. It helps regulate heart rate, respiratory rate, digestion, and many other vital functions.
On the other hand, the sacral spinal nerves arise from the lower part of the spinal cord and provide parasympathetic innervation to the pelvic organs. These nerves control functions such as bladder emptying, sexual arousal, and bowel movements.
Overall, the parasympathetic nervous system is a complex network of nerves that work together to maintain balance and promote relaxation in the body. Understanding its anatomy and function is essential in comprehending the intricate workings of our physiological processes.
The Parasympathetic Nervous System and Homeostasis
Homeostasis refers to the body’s ability to maintain stable internal conditions necessary for optimal functioning. It is a complex process that involves various physiological mechanisms working together to regulate temperature, pH levels, blood pressure, and other vital parameters. One of the key players in maintaining homeostasis is the parasympathetic nervous system.
The parasympathetic nervous system, also known as the “rest and digest” system, is responsible for promoting relaxation and conserving energy. It works in opposition to the sympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for the body’s “fight or flight” response. Together, these two systems maintain a delicate balance that allows the body to respond appropriately to different situations.
Role in Digestion
When it comes to digestion, the parasympathetic nerve plays a crucial role in ensuring the efficient breakdown and absorption of nutrients. It promotes the secretion of digestive enzymes, such as amylase, lipase, and protease, which are essential for breaking down carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, respectively. Additionally, the parasympathetic nerve increases blood flow to the digestive organs, including the stomach, liver, and intestines, ensuring that they receive an adequate supply of oxygen and nutrients.
Furthermore, the parasympathetic nerve enhances the contraction of smooth muscles in the gastrointestinal tract. These contractions, known as peristalsis, help propel food through the digestive system, allowing for proper digestion and absorption. Without the parasympathetic nervous system’s influence, digestion would be compromised, leading to various gastrointestinal issues such as indigestion, bloating, and nutrient deficiencies.
Impact on Heart Rate
In terms of heart rate regulation, the parasympathetic nervous system plays a vital role in maintaining a healthy cardiovascular system. It acts in opposition to the sympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for increasing heart rate and preparing the body for physical activity or stress. The parasympathetic nerve helps slow down the heart rate, allowing the heart to rest and recover.
When the body is at rest or engaged in non-strenuous activities, the parasympathetic nervous system dominates, ensuring that the heart rate remains within a healthy range. This state of rest and relaxation is essential for the heart’s overall health and longevity. However, during times of stress or physical exertion, the sympathetic nervous system takes over, increasing heart rate and redirecting blood flow to the muscles to prepare the body for action.
The balance between the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems is crucial for maintaining cardiovascular health. An imbalance in this delicate equilibrium can lead to various heart-related problems, including arrhythmias, high blood pressure, and even heart attacks.
In conclusion, the parasympathetic nervous system plays a vital role in maintaining homeostasis, particularly in digestion and heart rate regulation. Its impact on the digestive system ensures efficient nutrient breakdown and absorption, while its influence on heart rate helps maintain a healthy cardiovascular system. Understanding the intricate workings of the parasympathetic nervous system allows us to appreciate the complexity of the human body and the remarkable mechanisms it employs to maintain optimal functioning.
The Parasympathetic Nervous System and Stress Response
The parasympathetic nervous system also plays a significant role in the body’s response to stress. While the sympathetic nervous system triggers the “fight or flight” response, the parasympathetic nervous system activates the “rest and digest” response.
When we experience stress, our body undergoes a series of physiological changes. The sympathetic nervous system releases stress hormones like adrenaline, which prepare us for action. Our heart rate increases, blood pressure rises, and blood flow is redirected to our muscles, enabling us to respond quickly to potential threats.
However, the parasympathetic nervous system acts as a counterbalance to the sympathetic response. It helps our body recover and restore balance after a stressful event. This system promotes relaxation and supports various bodily functions, such as digestion and elimination.
The “Rest and Digest” Response
During times of stress, the parasympathetic nerve helps counterbalance the heightened sympathetic activity, allowing our body to recover and restore balance. It reduces heart rate, promotes relaxation, and supports digestive processes, ensuring that our body can effectively deal with stress and return to a state of equilibrium.
When the parasympathetic nervous system is activated, our heart rate decreases, blood pressure normalizes, and our muscles relax. This response allows our body to conserve energy and focus on essential functions like digestion and immune system activity.
Furthermore, the parasympathetic system stimulates the release of digestive enzymes and increases blood flow to the gastrointestinal tract. This enhanced blood flow aids in nutrient absorption and supports the breakdown of food, ensuring that our body can efficiently extract the necessary nutrients from our meals.
Balancing Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Activity
While both the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems are essential for our survival, maintaining a proper balance between them is crucial. Imbalances can lead to various health issues, including anxiety, gastrointestinal disorders, and cardiovascular problems.
Factors such as chronic stress, poor lifestyle habits, and certain medical conditions can disrupt the delicate equilibrium between these two systems. For example, individuals experiencing chronic stress may have an overactive sympathetic response and an underactive parasympathetic response, leading to a constant state of heightened alertness and difficulty relaxing.
Consulting with a healthcare professional can help in determining and managing any imbalances that may arise. They can provide guidance on stress management techniques, lifestyle modifications, and, if necessary, prescribe medications or therapies to restore the proper functioning of the autonomic nervous system.
In conclusion, the parasympathetic nervous system plays a vital role in our body’s response to stress. It acts as a counterbalance to the sympathetic response, allowing our body to recover and restore balance. By promoting relaxation and supporting essential functions like digestion, the parasympathetic system ensures that our body can effectively deal with stress and return to a state of equilibrium.
Disorders Related to the Parasympathetic Nervous System
In some cases, the parasympathetic nervous system may malfunction, leading to disorders that can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. Understanding the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options is key to managing these conditions effectively.
The parasympathetic nervous system is responsible for regulating various bodily functions, including digestion, heart rate, and sweating. When this system malfunctions, it can result in a range of disorders that affect different aspects of a person’s health.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Disorders related to the parasympathetic nervous system can manifest in various ways, including digestive problems, irregular heart rate, excessive sweating, and difficulty focusing. These symptoms can significantly impact an individual’s daily life, making it essential to seek medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Diagnosing disorders related to the parasympathetic nervous system can be challenging, as the symptoms can overlap with other conditions. Healthcare professionals will typically conduct a thorough evaluation, which may include a physical examination, medical history review, and specialized tests to assess the functioning of the parasympathetic nervous system.
One common diagnostic tool used is the autonomic function test, which measures the body’s response to various stimuli. This test helps determine if there is an imbalance in the parasympathetic nervous system and provides valuable insights into the underlying cause of the disorder.
Treatment and Management
While treatments for disorders related to the parasympathetic nervous system may vary depending on the specific condition, they often include a combination of lifestyle adjustments, medication, and therapies tailored to address the underlying causes.
Lifestyle adjustments may involve dietary changes to support digestive health, stress management techniques to regulate heart rate, and strategies to manage excessive sweating. These modifications can significantly improve symptoms and enhance overall well-being.
Medication may be prescribed to help regulate the parasympathetic nervous system and alleviate specific symptoms. For example, medications that target excessive sweating can be prescribed to reduce its occurrence and improve comfort.
Therapies such as physical therapy, occupational therapy, and psychotherapy can also play a crucial role in managing disorders related to the parasympathetic nervous system. These therapies aim to strengthen the body, improve function, and provide emotional support to individuals dealing with the challenges of these conditions.
It is crucial to work closely with healthcare professionals to determine the most suitable approach for managing disorders related to the parasympathetic nervous system. Regular follow-ups and open communication with the healthcare team are essential to monitor progress, adjust treatment plans if needed, and address any concerns or questions that may arise.
The Future of Parasympathetic Nervous System Research
As our understanding of the parasympathetic nervous system continues to evolve, exciting advancements in research are on the horizon. Scientists are exploring the potential therapeutic applications of stimulating or modulating the parasympathetic nerve to treat various conditions.
The parasympathetic nervous system, often referred to as the “rest and digest” system, is responsible for promoting relaxation, conserving energy, and maintaining homeostasis in the body. It works in opposition to the sympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for the “fight or flight” response.
Recent studies have shown that parasympathetic nerve stimulation may hold promise in managing anxiety disorders. By activating the parasympathetic nervous system, researchers believe that it may help reduce anxiety symptoms and promote a sense of calmness. This could potentially revolutionize the treatment of anxiety, offering a non-pharmacological approach that targets the root cause of the disorder.
Another area of research focuses on the potential of parasympathetic nerve stimulation in promoting better sleep. Sleep disorders, such as insomnia, affect millions of people worldwide and can have a significant impact on overall health and well-being. By understanding the role of the parasympathetic nervous system in sleep regulation, scientists hope to develop targeted interventions that can improve sleep quality and duration.
In addition to anxiety and sleep disorders, researchers are also exploring the potential of parasympathetic nerve stimulation in enhancing digestion. The parasympathetic nervous system plays a crucial role in regulating digestive processes, such as the secretion of digestive enzymes and the movement of food through the gastrointestinal tract. By modulating the parasympathetic nerve, scientists aim to develop interventions that can improve digestion and alleviate gastrointestinal disorders.
Unanswered Questions and Future Directions
While significant progress has been made in parasympathetic nerve research, many questions still remain unanswered. Future studies will explore how the parasympathetic nervous system interacts with other bodily systems and how it can be harnessed to improve overall health and well-being.
One area of interest is the connection between the parasympathetic nervous system and the immune system. Research suggests that the parasympathetic nerve may play a role in regulating immune responses, inflammation, and autoimmune disorders. Understanding this connection could lead to the development of novel therapies for immune-related conditions.
Furthermore, researchers are also investigating the potential of non-invasive techniques for parasympathetic nerve stimulation. Currently, most interventions involve invasive procedures, such as electrical stimulation or surgical implantation of devices. Non-invasive methods, such as transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation, are being explored as a safer and more accessible alternative.
Continued research in this field will undoubtedly contribute to better understanding and potential breakthroughs. By unraveling the intricacies of the parasympathetic nervous system, scientists hope to unlock its full therapeutic potential and improve the lives of individuals with various health conditions.
In conclusion, the parasympathetic nerve plays a crucial role in the body by regulating digestion, heart rate, and stress response. Understanding its functioning, impact on homeostasis, and disorders related to it is essential for maintaining optimal health. As research in this field progresses, the potential for enhanced therapies and treatments holds great promise. If you suspect any issues related to the parasympathetic nervous system, it is always wise to consult with a healthcare professional who can guide you on the appropriate steps to take.