The pelvic parasympathetic nerve plays a vital role in the complex functioning of the human body. This comprehensive guide aims to provide a detailed understanding of its anatomy, functions, disorders, diagnostic procedures, treatment options, and the future of research in this field. It is important to note that this article does not provide medical advice, and individuals experiencing any symptoms or concerns should consult with a qualified healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Anatomy of the Pelvic Parasympathetic Nerve
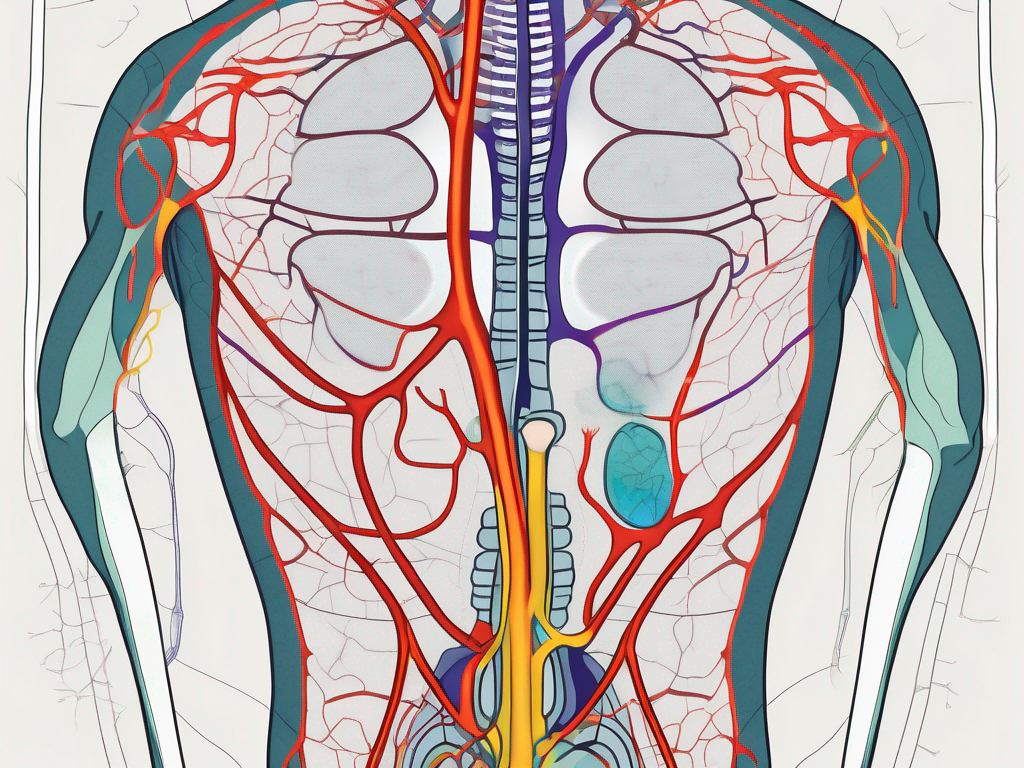
The pelvic parasympathetic nerve is an essential part of the autonomic nervous system, responsible for regulating and controlling various bodily functions. It arises from the sacral spinal cord and travels through the pelvic region. Understanding its location and structure is crucial in comprehending its functions and potential disorders.
Location and Structure of the Pelvic Parasympathetic Nerve
The pelvic parasympathetic nerve is situated in the lower part of the spinal cord, specifically in the sacral region. It consists of a network of nerve fibers that branch out to innervate various organs in the pelvic cavity, including the urinary system, reproductive organs, and parts of the digestive system.
Within the sacral region, the pelvic parasympathetic nerve is intricately intertwined with other nerves and blood vessels, forming a complex network. This network ensures efficient communication and coordination between the nerve fibers, allowing for the precise regulation of pelvic organ functions.
As the nerve travels through the pelvic region, it gives rise to numerous branches that extend to different areas. These branches reach out to the bladder, uterus, rectum, and other pelvic organs, delivering the necessary signals for their proper functioning. The intricate branching pattern of the nerve ensures that each organ receives the appropriate level of parasympathetic innervation.
Connection to the Central Nervous System
The pelvic parasympathetic nerve forms connections with the central nervous system, particularly the brain and the spinal cord, allowing for communication and coordination between these vital components. This connection plays a significant role in regulating and maintaining the functions of the pelvic organs.
At the level of the sacral spinal cord, the pelvic parasympathetic nerve fibers merge with other nerve fibers that originate from different regions of the body. This merging of fibers forms the sacral plexus, a complex network of nerves that serves as a hub for relaying signals between the pelvic organs and the central nervous system.
From the sacral plexus, the pelvic parasympathetic nerve fibers ascend towards the brain, forming connections with various regions involved in autonomic control. These connections allow for bidirectional communication, enabling the brain to regulate the activity of the pelvic organs and receive feedback regarding their status.
Furthermore, the pelvic parasympathetic nerve fibers also interact with the spinal cord, specifically in the sacral region. This interaction enables reflexive responses, such as the relaxation of the bladder during urination or the contraction of the uterus during childbirth.
Overall, the connection between the pelvic parasympathetic nerve and the central nervous system is essential for maintaining the balance and proper functioning of the pelvic organs. It allows for precise control and coordination of various bodily functions, ensuring optimal health and well-being.
Functions of the Pelvic Parasympathetic Nerve
The pelvic parasympathetic nerve is involved in several essential bodily functions. Understanding its functions is key to appreciating its impact on overall health and well-being.
The pelvic parasympathetic nerve, also known as the pelvic splanchnic nerve, is a branch of the sacral spinal nerves. It arises from the second, third, and fourth sacral segments of the spinal cord. This nerve plays a crucial role in the autonomic nervous system, specifically in the parasympathetic division.
Role in Digestive Processes
The pelvic parasympathetic nerve influences digestion by stimulating the smooth muscles and glands in the digestive tract. It helps regulate the secretion of digestive enzymes, gastric motility, and the absorption of nutrients. This nerve provides the necessary signals for the coordinated contraction and relaxation of the gastrointestinal muscles, allowing the food to move through the digestive system smoothly.
Moreover, the pelvic parasympathetic nerve plays a role in the regulation of blood flow to the digestive organs. It ensures that an adequate blood supply is provided to support the digestive processes. Any disruptions in this process can lead to digestive disorders and discomfort, such as constipation, diarrhea, or bloating.
Influence on Urinary Function
The pelvic parasympathetic nerve plays a significant role in controlling the bladder and urinary functions. It helps regulate the sensation of fullness, the coordination of bladder contraction, and the relaxation of the urinary sphincters. This nerve sends signals to the bladder, instructing it to contract when it is time to empty the urine.
Furthermore, the pelvic parasympathetic nerve also plays a role in the relaxation of the urinary sphincters, allowing the urine to flow out of the bladder. Dysfunction of this nerve can result in urinary incontinence or retention. Incontinence refers to the involuntary leakage of urine, while retention refers to the inability to empty the bladder completely.
Impact on Sexual Function
Another crucial aspect of the pelvic parasympathetic nerve is its influence on sexual function. It is responsible for the regulation of genital blood flow, erection in males, lubrication in females, and the coordination of sexual responses. This nerve plays a vital role in the physiological processes that occur during sexual arousal and intercourse.
In males, the pelvic parasympathetic nerve stimulates the release of nitric oxide, which leads to the dilation of blood vessels in the penis. This dilation allows for increased blood flow, resulting in an erection. In females, this nerve stimulates the production of vaginal lubrication, enhancing sexual pleasure and reducing discomfort during intercourse.
Additionally, the pelvic parasympathetic nerve coordinates the contraction of the pelvic floor muscles during orgasm. These contractions are essential for the pleasurable sensations experienced during sexual climax. Dysfunction of this nerve can lead to sexual dysfunction and fertility issues, affecting both physical and emotional well-being.
Disorders Related to the Pelvic Parasympathetic Nerve
Several disorders can affect the pelvic parasympathetic nerve, causing a range of symptoms and complications. Identifying these disorders is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment.
The pelvic parasympathetic nerve plays a crucial role in regulating various functions in the pelvic region. It is responsible for controlling the digestive system, urinary system, and sexual function. When this nerve is affected by certain conditions, it can lead to disruptions in these bodily functions.
Symptoms of Pelvic Parasympathetic Nerve Disorders
Pelvic parasympathetic nerve disorders can present with various symptoms depending on the specific affected functions. These can include digestive issues, such as constipation or diarrhea, urinary problems like frequent urination or inability to empty the bladder completely, and sexual dysfunction.
When the pelvic parasympathetic nerve is compromised, it can result in a cascade of symptoms that can significantly impact an individual’s daily life. Digestive issues can cause discomfort and affect the absorption of nutrients, leading to nutritional deficiencies. Urinary problems can cause frequent trips to the bathroom, disrupting sleep patterns and causing inconvenience. Sexual dysfunction can strain relationships and impact overall well-being.
Common Conditions Affecting the Pelvic Parasympathetic Nerve
Some common conditions affecting the pelvic parasympathetic nerve include pelvic organ prolapse, bladder dysfunction, irritable bowel syndrome, and sexual dysfunction. These conditions can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life and require medical attention for proper management.
Pelvic organ prolapse occurs when the muscles and tissues that support the pelvic organs weaken, causing them to descend into the vaginal canal. This can put pressure on the pelvic parasympathetic nerve, leading to various symptoms such as urinary incontinence, constipation, and discomfort during sexual intercourse.
Bladder dysfunction refers to abnormalities in the storage and emptying of urine. When the pelvic parasympathetic nerve is affected, it can disrupt the coordination between the bladder muscles and the nerve signals, leading to urinary urgency, frequency, and incomplete emptying.
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a chronic gastrointestinal disorder that affects the large intestine. It can cause abdominal pain, bloating, and changes in bowel habits. When the pelvic parasympathetic nerve is involved, it can contribute to the development or exacerbation of IBS symptoms.
Sexual dysfunction can occur as a result of pelvic parasympathetic nerve disorders. It can manifest as erectile dysfunction in men or decreased sexual arousal and orgasmic difficulties in both men and women. These issues can have a significant impact on an individual’s self-esteem, relationships, and overall quality of life.
In conclusion, disorders related to the pelvic parasympathetic nerve can cause a wide range of symptoms and complications. Proper diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing these conditions and improving the quality of life for affected individuals.
Diagnostic Procedures for Pelvic Parasympathetic Nerve Disorders
Accurate diagnosis of pelvic parasympathetic nerve disorders is crucial for developing an effective treatment plan. Healthcare professionals employ various diagnostic procedures to evaluate the condition thoroughly.
Physical Examination and Patient History
Medical professionals typically begin the diagnostic process by conducting a comprehensive physical examination and taking a detailed patient history. This helps to identify any observable symptoms or patterns and gather relevant information about the individual’s health and lifestyle.
During the physical examination, the healthcare provider may palpate the abdomen and pelvic region to check for any tenderness or abnormalities. They may also perform a pelvic exam to assess the condition of the reproductive organs and look for any signs of inflammation or infection.
Simultaneously, the healthcare provider will engage in a detailed conversation with the patient to gather information about their medical history, including any previous pelvic surgeries, chronic illnesses, or medications they may be taking. They will also inquire about the patient’s lifestyle habits, such as exercise routines, dietary patterns, and stress levels, as these factors can contribute to pelvic nerve disorders.
Imaging and Laboratory Tests
In some cases, imaging techniques such as ultrasound, MRI, or CT scans may be employed to visualize the pelvic organs and identify any structural abnormalities or impingements. These non-invasive imaging procedures provide detailed images of the pelvic region, allowing healthcare professionals to assess the condition of the nerves and surrounding tissues.
Ultrasound, a commonly used imaging technique, uses sound waves to create real-time images of the pelvic organs. It can help identify conditions such as cysts, tumors, or abnormalities in the uterus, ovaries, or bladder.
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) and CT (Computed Tomography) scans provide more detailed images and can help identify nerve compression, inflammation, or other abnormalities that may be affecting the parasympathetic nerves in the pelvis.
Additionally, laboratory tests, including blood work and urinalysis, may be conducted to rule out other potential causes of symptoms. Blood tests can help assess hormone levels, detect infections or inflammatory markers, and evaluate organ function. Urinalysis can provide insights into kidney function and identify any urinary tract infections that may be contributing to the symptoms.
By combining the information gathered from physical examinations, patient history, and imaging or laboratory tests, healthcare professionals can form a comprehensive understanding of the pelvic parasympathetic nerve disorder and develop an appropriate treatment plan tailored to the individual’s needs.
Treatment Options for Pelvic Parasympathetic Nerve Disorders
Treatment options for pelvic parasympathetic nerve disorders aim to alleviate symptoms, improve quality of life, and restore normal function. It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on the individual’s specific condition and needs.
Pelvic parasympathetic nerve disorders can significantly impact a person’s daily life, causing discomfort and affecting various bodily functions. Fortunately, there are several treatment options available that can provide relief and help individuals regain control over their health.
One of the primary approaches to managing these disorders is through medication and non-surgical interventions. Depending on the nature and severity of the disorder, healthcare professionals may recommend various medications, such as muscle relaxants, pain relievers, or medications targeting specific symptoms. These medications can help reduce pain, relax muscles, and alleviate other distressing symptoms.
In addition to medication, non-surgical interventions play a crucial role in the treatment of pelvic parasympathetic nerve disorders. Physical therapy is often recommended as it can help strengthen the pelvic muscles, improve flexibility, and reduce pain. Through targeted exercises and stretches, physical therapists can assist individuals in regaining control over their pelvic floor muscles and restoring normal function.
Biofeedback is another non-surgical intervention that can be beneficial for individuals with pelvic parasympathetic nerve disorders. This technique involves using sensors to provide real-time feedback on muscle activity, allowing individuals to learn how to control and relax their pelvic muscles effectively. By gaining awareness and control over these muscles, individuals can experience a reduction in symptoms and an improvement in overall quality of life.
Lifestyle modifications are also an essential aspect of treatment for pelvic parasympathetic nerve disorders. Healthcare professionals may recommend dietary changes, such as avoiding trigger foods and increasing fiber intake, to manage symptoms like constipation or diarrhea. Additionally, stress management techniques, such as meditation or yoga, can help reduce stress levels and alleviate symptoms.
While medication and non-surgical interventions are often effective in managing pelvic parasympathetic nerve disorders, there are cases where surgical treatments and procedures may be necessary. These interventions are typically reserved for more severe cases or when there are underlying structural issues or nerve impingements that require correction.
Surgical treatments aim to repair or remove any abnormalities in the pelvic area, restoring proper function and alleviating symptoms. However, it is essential to note that surgical interventions carry risks and should only be considered after careful consideration and consultation with a specialist.
In conclusion, treatment options for pelvic parasympathetic nerve disorders encompass a range of approaches, including medication, non-surgical interventions, and, in some cases, surgical treatments. By working closely with healthcare professionals, individuals can find a treatment plan that addresses their specific needs and helps them regain control over their health and well-being.
The Future of Pelvic Parasympathetic Nerve Research
Advancements in medical research continue to shed light on the intricate workings of the pelvic parasympathetic nerve. Ongoing studies focus on emerging therapies, techniques, and the role of technology in understanding this complex nerve network.
The pelvic parasympathetic nerve, also known as the pelvic splanchnic nerve, is a crucial component of the body’s autonomic nervous system. It plays a vital role in regulating various bodily functions, including digestion, urinary function, and sexual function. Understanding the intricacies of this nerve is essential for diagnosing and treating disorders that can arise from its dysfunction.
Emerging Therapies and Techniques
Researchers are exploring innovative therapies and techniques to improve the diagnosis and treatment of pelvic parasympathetic nerve disorders. These may include targeted drug therapies, nerve stimulation techniques, and advanced imaging technologies to aid in more accurate diagnosis.
Targeted drug therapies aim to specifically address the underlying causes of pelvic parasympathetic nerve disorders. By targeting the affected pathways or receptors, these therapies can potentially restore normal function and alleviate symptoms. Nerve stimulation techniques, such as electrical stimulation or biofeedback, can help retrain the nerves and restore their proper functioning.
Advanced imaging technologies, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and positron emission tomography (PET), provide detailed visualization of the pelvic parasympathetic nerve and surrounding structures. These imaging techniques allow researchers to identify any abnormalities or damage to the nerve, guiding treatment decisions and monitoring the effectiveness of interventions.
The Role of Technology in Understanding the Pelvic Parasympathetic Nerve
Technology plays a crucial role in advancing our understanding of the pelvic parasympathetic nerve. Techniques such as nerve mapping, neuroimaging, and the use of artificial intelligence in data analysis are instrumental in unraveling the complexities of this intricate nerve network. These advancements pave the way for improved diagnosis, treatment, and overall patient care.
Nerve mapping involves the precise identification and mapping of the pelvic parasympathetic nerve fibers. This technique helps researchers understand the nerve’s pathways and connections, enabling targeted interventions and therapies. Neuroimaging techniques, such as functional MRI (fMRI) and diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), provide insights into the functional and structural aspects of the nerve, aiding in the identification of abnormalities and guiding treatment decisions.
Artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms are increasingly being used to analyze complex data sets related to the pelvic parasympathetic nerve. These algorithms can identify patterns, predict outcomes, and assist in personalized treatment planning. AI-powered diagnostic tools can enhance the accuracy and efficiency of diagnosing pelvic parasympathetic nerve disorders, leading to more effective and timely interventions.
In conclusion, the pelvic parasympathetic nerve is an integral component of the body’s autonomic nervous system, influencing digestive processes, urinary function, and sexual function. Disorders related to this nerve can lead to a range of symptoms and complications, requiring accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Diagnostic procedures, including physical examination, patient history, imaging, and laboratory tests, help identify these disorders. Treatment options may include medication, non-surgical interventions, or surgical procedures, depending on the individual’s condition.
Ongoing research in this field focuses on emerging therapies, techniques, and the utilization of technology to advance our understanding of the pelvic parasympathetic nerve. By exploring innovative approaches and harnessing the power of technology, researchers aim to improve the lives of individuals affected by pelvic parasympathetic nerve disorders. It is essential to seek professional medical advice and consultation for any symptoms or concerns related to this nerve for proper management and care.