The innervation provided by parasympathetic nerve fibers plays a crucial role in the functioning of our body. Understanding the parasympathetic nervous system and its impact on various organs and body functions is essential for exploring the vital role these nerve fibers play in our overall well-being.
Understanding the Parasympathetic Nervous System
The parasympathetic nervous system is one of the divisions of the autonomic nervous system, along with the sympathetic nervous system. While the sympathetic system is responsible for our fight-or-flight response, the parasympathetic system is often referred to as the “rest-and-digest” system. It counterbalances the sympathetic system by promoting relaxation and conserving energy.
When we think of the parasympathetic nervous system, we often think of a state of calm and tranquility. It is the system that allows us to unwind after a long day, to find solace in a peaceful environment, and to enjoy a good night’s sleep. But there is so much more to this intricate system that plays a vital role in our overall well-being.
The Role of Parasympathetic Nerve Fibers
Parasympathetic nerve fibers are responsible for transmitting signals from the central nervous system to various organs and glands. These fibers release the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, which binds to specific receptors in the target tissues and triggers a response.
Imagine a symphony orchestra, with each instrument playing its part to create a harmonious melody. Similarly, the parasympathetic nerve fibers work in perfect synchronization to maintain the delicate balance within our body. From regulating heart rate and digestion to promoting proper functioning of our reproductive system, these fibers are the conductors of our bodily functions.
The Anatomy of the Parasympathetic Nervous System
The parasympathetic nervous system consists of cranial nerves, which originate in the brain, and sacral nerves, which arise from the spinal cord. Cranial nerves, such as the vagus nerve, carry parasympathetic fibers to the head, neck, thoracic organs, and abdominal organs, while sacral nerves innervate the pelvic organs.
Think of the parasympathetic nervous system as a vast network of interconnected pathways, extending from the brain to every nook and cranny of our body. It is like a complex highway system, with each nerve fiber serving as a road that leads to a specific destination. These cranial and sacral nerves are the lifelines that ensure the smooth functioning of our vital organs, allowing us to experience the world through our senses and maintain optimal health.
Next time you find yourself in a state of deep relaxation, take a moment to appreciate the wonders of the parasympathetic nervous system. It is the unsung hero that keeps us grounded, restores our energy, and allows us to thrive in a world full of challenges and excitement.
The Connection Between Parasympathetic Nerve Fibers and Innervation
Innervation refers to the process of supplying nerves to a particular organ or part of the body. It is a complex and essential process that allows for the regulation of organ functions and the maintenance of homeostasis. One crucial player in the process of innervation is the parasympathetic nerve fibers.
Parasympathetic nerve fibers play a vital role in innervation by extending from their origin in the central nervous system and traveling through specific pathways to reach their target tissues. These fibers form intricate networks, allowing for the transmission of signals and the subsequent regulation of organ activity.
The Process of Innervation
The process of innervation involves a series of intricate steps that ensure the proper functioning of organs. Parasympathetic nerve fibers, being an integral part of this process, extend from the central nervous system, which includes the brain and spinal cord. From there, they travel through specific pathways, branching out like intricate highways, to reach their target tissues.
Once the parasympathetic nerve fibers reach their target tissues, they form synapses. Synapses are specialized junctions where the nerve fibers communicate with the target tissues, allowing for the transmission of signals. This communication is essential for the regulation of organ activity and maintaining optimal function.
How Parasympathetic Nerve Fibers Facilitate Innervation
The parasympathetic nervous system exerts its control over organs through a series of integrated responses. These responses are orchestrated by the parasympathetic nerve fibers, ensuring the proper functioning of various organs and systems within the body.
One way parasympathetic nerve fibers facilitate innervation is by stimulating glandular secretions. Glands throughout the body, such as salivary glands, lacrimal glands, and digestive glands, receive signals from the parasympathetic nervous system, leading to the production and release of necessary secretions. This stimulation ensures the proper functioning of these glands and aids in processes like digestion, lubrication, and protection.
Another crucial role of parasympathetic nerve fibers in innervation is the stimulation of smooth muscle contractions. Smooth muscles are found in various organs, including the gastrointestinal tract, respiratory system, and reproductive system. The parasympathetic nervous system, through its nerve fibers, regulates the contraction and relaxation of these smooth muscles, allowing for proper organ function. For example, in the digestive system, parasympathetic stimulation promotes peristalsis, the rhythmic contractions that propel food along the digestive tract.
Furthermore, parasympathetic nerve fibers play a role in regulating heart rate. The parasympathetic nervous system acts as a counterbalance to the sympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for the “fight or flight” response. When the parasympathetic nerve fibers are activated, they slow down the heart rate, promoting a state of rest and relaxation.
In addition to these functions, parasympathetic nerve fibers also play a role in controlling other vital processes, such as pupillary constriction, bronchoconstriction, and promoting sexual arousal.
Overall, the parasympathetic nerve fibers are integral to the process of innervation. Through their extensive network and communication with target tissues, they facilitate the regulation of organ functions, maintaining a state of balance and rest within the body. Understanding the connection between parasympathetic nerve fibers and innervation is crucial in comprehending the complex mechanisms that allow our bodies to function optimally.
Organs Innervated by Parasympathetic Nerve Fibers
Parasympathetic nerve fibers provide innervation to a wide range of organs in the body, each with its own unique functions and responses. Let’s explore some key examples:
The Heart and Parasympathetic Innervation
The parasympathetic nervous system plays a crucial role in regulating heart rate. Stimulation of parasympathetic fibers to the heart leads to a decrease in heart rate, allowing for a more measured and relaxed physiological state. This control over heart rate is vital for overall cardiovascular health.
Additionally, parasympathetic innervation of the heart also influences the force of contraction. Through the release of acetylcholine, the parasympathetic fibers help to decrease the strength of each heartbeat, allowing for efficient blood circulation and preventing unnecessary strain on the heart muscle.
Furthermore, the parasympathetic nervous system is involved in maintaining heart rhythm. By inhibiting the activity of the sinoatrial (SA) node, the natural pacemaker of the heart, parasympathetic innervation helps to regulate the regularity and consistency of the heart’s electrical impulses.
Digestive System and Parasympathetic Innervation
In the digestive system, parasympathetic innervation stimulates an array of functions, including increased salivary gland secretion, enhanced peristalsis in the intestines, increased gastric acid production, and relaxation of the sphincters. These actions aid in the breakdown of food, absorption of nutrients, and overall digestive efficiency.
Moreover, parasympathetic fibers also play a role in the regulation of blood flow to the digestive organs. By causing vasodilation of the blood vessels supplying the stomach, intestines, and other digestive structures, the parasympathetic nervous system ensures an adequate blood supply for optimal digestion and nutrient absorption.
Furthermore, parasympathetic innervation is involved in the activation of the enteric nervous system, which is a complex network of neurons within the walls of the digestive tract. This activation helps to coordinate various digestive processes, such as the release of digestive enzymes and the contraction of smooth muscles, ensuring the efficient movement of food along the gastrointestinal tract.
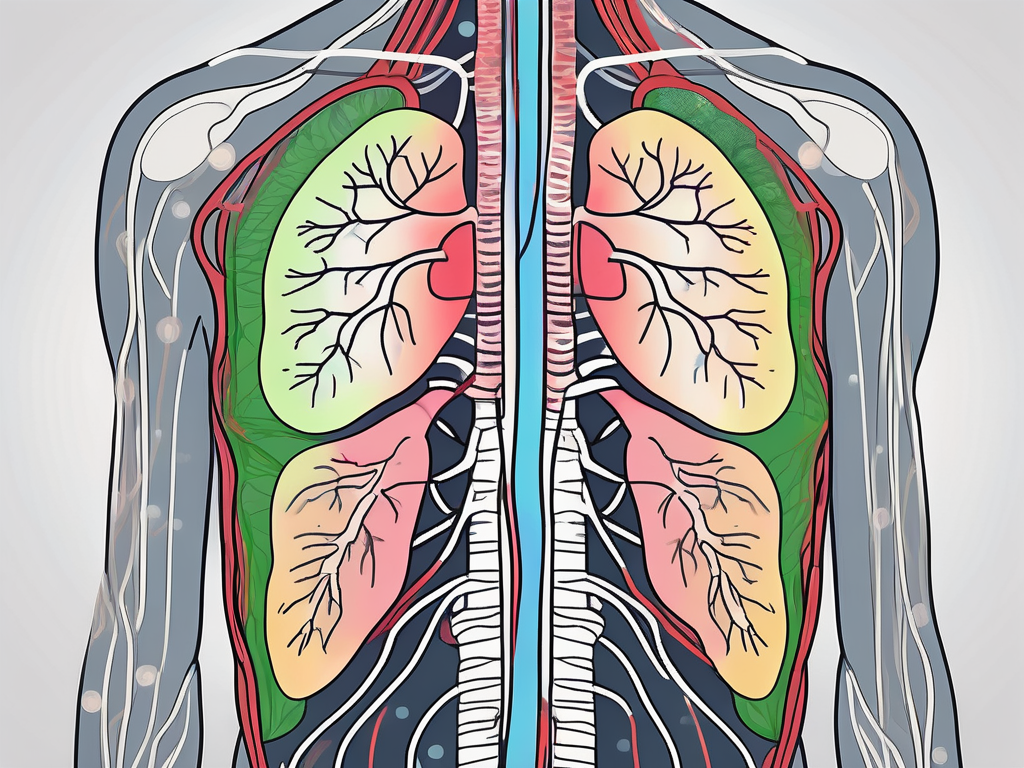
The Role of Parasympathetic Innervation in the Respiratory System
Parasympathetic innervation actively contributes to the regulation of the respiratory system. It influences bronchoconstriction and secretion of mucus in the airways, promoting efficient gas exchange between the lungs and the external environment. Proper parasympathetic control ensures optimal respiratory function.
Moreover, parasympathetic fibers also play a role in regulating the diameter of the blood vessels supplying the lungs. By causing vasodilation, the parasympathetic nervous system helps to ensure an adequate blood supply to the lungs, facilitating the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide during respiration.
Additionally, parasympathetic innervation is involved in the regulation of respiratory rate. By influencing the activity of the respiratory centers in the brainstem, the parasympathetic nervous system helps to control the depth and frequency of breathing, ensuring the body receives an adequate supply of oxygen and the removal of carbon dioxide.
The Impact of Parasympathetic Innervation on Body Functions
Parasympathetic innervation extends its influence beyond specific organs, contributing to broader body functions and maintaining equilibrium.
The parasympathetic nervous system plays a crucial role in maintaining the body’s overall homeostasis. It is responsible for regulating various physiological processes, including digestion, heart rate, and overall relaxation. Let’s explore some of the specific functions that parasympathetic innervation influences.
Parasympathetic Innervation and Rest-and-Digest Functions
The rest-and-digest response, triggered by parasympathetic activity, allows the body to conserve energy and promote recovery. This physiological state promotes digestion, nutrient absorption, and restorative processes within the body. When the parasympathetic nervous system is activated, blood flow is directed towards the digestive organs, enhancing their function and optimizing nutrient uptake.
Additionally, parasympathetic innervation stimulates the release of digestive enzymes and increases intestinal motility, ensuring efficient breakdown and absorption of nutrients. This process is crucial for maintaining a healthy digestive system and supporting overall metabolic function.
The Influence of Parasympathetic Innervation on Heart Rate
The parasympathetic nervous system counterbalances the sympathetic system’s influence on heart rate, ensuring a controlled and balanced rhythm. By regulating heart rate variability, parasympathetic innervation promotes cardiovascular health and helps maintain overall cardiac function.
When the body is in a relaxed state, parasympathetic activity dominates, leading to a decrease in heart rate. This decrease allows the heart to rest and recover, reducing the workload on this vital organ. By contrast, sympathetic activity, which is responsible for the fight-or-flight response, increases heart rate to prepare the body for action.
Parasympathetic innervation not only influences heart rate but also helps regulate blood pressure. By promoting vasodilation, the parasympathetic nervous system helps reduce peripheral resistance, allowing blood to flow more freely through the blood vessels. This mechanism contributes to maintaining healthy blood pressure levels and overall cardiovascular well-being.
Overall, the impact of parasympathetic innervation on body functions goes beyond specific organs. It plays a crucial role in promoting digestion, nutrient absorption, and restorative processes. Additionally, parasympathetic activity helps maintain a balanced heart rate and supports cardiovascular health. Understanding the intricate workings of the parasympathetic nervous system is essential for comprehending the body’s overall physiological equilibrium.
Disorders Related to Parasympathetic Innervation
While parasympathetic innervation is essential for normal bodily functions, certain disorders can affect its balance and lead to various health issues.
The parasympathetic nervous system, also known as the “rest and digest” system, is responsible for conserving energy and promoting relaxation. It works in opposition to the sympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for the “fight or flight” response. When the parasympathetic nervous system is disrupted, it can result in a range of disorders that impact different aspects of our health.
Symptoms of Parasympathetic Nervous System Disorders
Disorders related to parasympathetic innervation can manifest in numerous ways. Common symptoms may include excessive sweating, digestive disturbances, abnormal heart rate, difficulty breathing, and urinary problems. However, it is important to note that these symptoms can vary depending on the specific disorder and the affected organ or system.
Excessive sweating, also known as hyperhidrosis, can be a distressing symptom experienced by individuals with parasympathetic nervous system disorders. It can occur in localized areas or affect the entire body, leading to social embarrassment and discomfort.
Digestive disturbances, such as bloating, constipation, or diarrhea, can be indicative of parasympathetic innervation disorders affecting the gastrointestinal system. These disruptions can interfere with the body’s ability to properly break down and absorb nutrients, leading to nutritional deficiencies and other health complications.
Abnormal heart rate, known as arrhythmia, is another symptom commonly associated with parasympathetic nervous system disorders. It can manifest as a slow heart rate, known as bradycardia, or a rapid heart rate, known as tachycardia. These irregularities can have serious implications for cardiovascular health and may require medical intervention.
Difficulty breathing, also referred to as dyspnea, can occur in individuals with parasympathetic innervation disorders affecting the respiratory system. This can result in shortness of breath, wheezing, or a feeling of tightness in the chest, making it challenging to engage in physical activities or even perform simple tasks.
Urinary problems, such as urinary incontinence or urinary retention, can be distressing symptoms experienced by individuals with parasympathetic nervous system disorders affecting the urinary system. These issues can significantly impact a person’s quality of life and may require specialized treatment approaches.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management. They will be able to evaluate your symptoms, conduct necessary tests, and develop a personalized treatment plan to address the underlying disorder.
Treatment and Management of Parasympathetic Innervation Disorders
The treatment and management of parasympathetic innervation disorders depend on the specific condition and its underlying cause. Consulting with a doctor or specialist in neurology or cardiology is crucial for an accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plans.
Medication is often prescribed to manage the symptoms associated with parasympathetic nervous system disorders. For example, anticholinergic drugs may be used to reduce excessive sweating, while medications that regulate heart rate, such as beta-blockers, can be prescribed for individuals with arrhythmias.
Lifestyle modifications can also play a significant role in managing parasympathetic innervation disorders. These may include stress reduction techniques, such as meditation or yoga, which can help balance the autonomic nervous system. Additionally, dietary changes, such as avoiding trigger foods or incorporating fiber-rich foods, can help alleviate digestive disturbances.
Therapies that assist in alleviating symptoms and promoting overall well-being may be recommended as part of the treatment plan. These can include physical therapy to improve muscle control, biofeedback to regulate heart rate and breathing, or pelvic floor exercises to address urinary problems.
In conclusion, parasympathetic nerve fibers play a vital role in the innervation of various organs and body functions. Their involvement in regulating heart rate, facilitating digestion, maintaining respiratory efficiency, and promoting rest-and-digest functions highlights their significance in supporting our overall well-being. Understanding the intricacies of parasympathetic innervation and seeking appropriate medical advice when experiencing related symptoms ensures optimal health and enhances our quality of life.