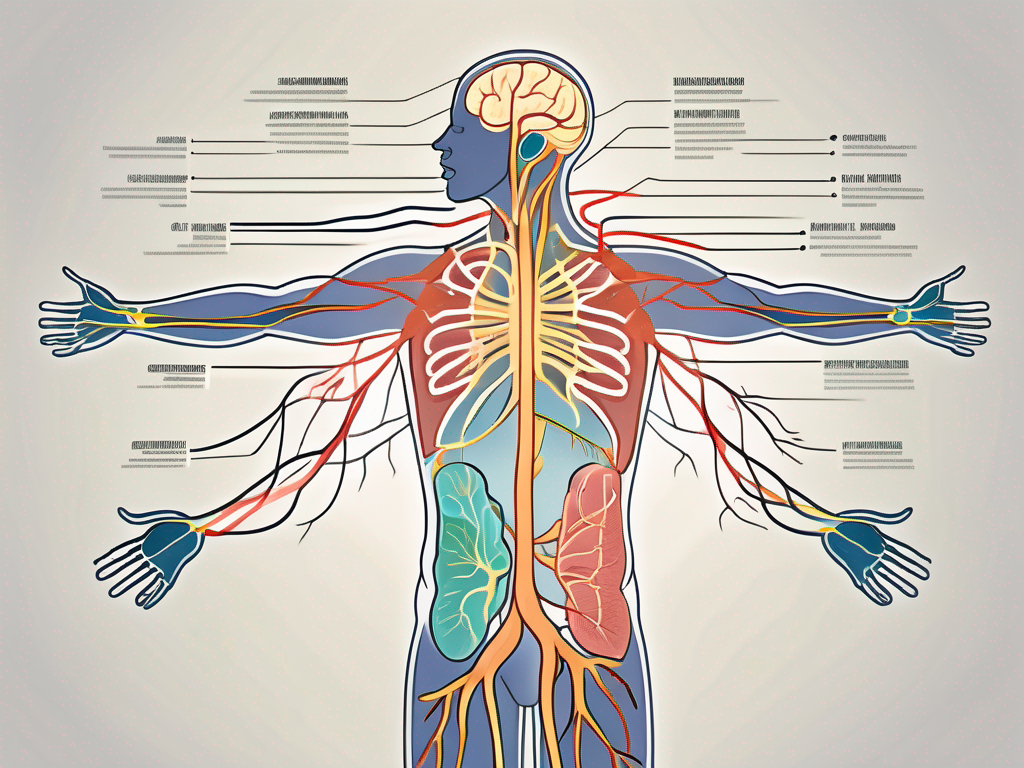
The parasympathetic nervous system is a crucial component of the human body’s complex nervous system. To fully understand its significance, it is essential to gain a comprehensive understanding of the nervous system as a whole. The nervous system plays a pivotal role in coordinating and controlling various bodily functions, ensuring our bodies operate efficiently and effectively.
Understanding the Nervous System
The nervous system is a complex network of cells and tissues that plays a crucial role in the functioning of the human body. It is responsible for transmitting signals throughout the body, allowing for rapid communication between different tissues and organs. This intricate system ensures that our body can respond to both internal and external stimuli in a coordinated and efficient manner.
The Role of the Nervous System
At its core, the nervous system acts as the body’s communication highway. It enables the transmission of electrical signals, known as nerve impulses, which carry information from one part of the body to another. These signals are essential for coordinating various bodily functions, such as movement, sensation, and even thought processes.
The nervous system consists of two primary divisions—the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS comprises the brain and spinal cord, which serve as the command center for the entire body. It is within the CNS that information is processed, decisions are made, and responses are initiated.
On the other hand, the peripheral nervous system consists of a vast network of nerves that extend throughout the body, linking the CNS to the various organs, muscles, and glands. These nerves act as messengers, carrying information to and from the CNS. They are responsible for relaying sensory information, such as touch, temperature, and pain, as well as motor signals that control muscle movement.
Divisions of the Nervous System
The peripheral nervous system can be further divided into two major subdivisions—the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system. The somatic nervous system controls voluntary movements and sensory perception. It allows us to consciously control our muscles and respond to external stimuli, such as picking up an object or feeling a gentle breeze on our skin.
On the other hand, the autonomic nervous system regulates involuntary bodily functions, such as heart rate, digestion, and breathing. It operates without conscious control and ensures that essential processes continue to function smoothly, even when we are not actively thinking about them.
Within the autonomic nervous system, there are two main divisions—the sympathetic nervous system and the parasympathetic nervous system. The sympathetic nervous system is responsible for the body’s “fight or flight” response, which prepares us to respond to perceived threats or stressful situations. It increases heart rate, dilates blood vessels, and releases adrenaline, among other physiological changes.
In contrast, the parasympathetic nervous system promotes a state of relaxation and rest. It helps to conserve energy, slow down heart rate, and facilitate digestion. These two divisions of the autonomic nervous system work in harmony to maintain a balance in our body’s overall functioning.
Understanding the nervous system is essential for comprehending how our body functions and how it responds to various stimuli. By studying this intricate network of cells and tissues, scientists and medical professionals can gain insights into neurological disorders, develop new treatments, and improve overall human health.
The Parasympathetic Nervous System Defined
The parasympathetic nervous system is one of the two main branches of the autonomic nervous system (ANS), alongside its counterpart, the sympathetic nervous system. While the sympathetic nervous system prepares the body for action and stress responses, the parasympathetic nervous system works to restore the body to a calm and resting state.
The parasympathetic nervous system arises from the cranial and sacral regions of the spinal cord. Cranial nerves, including the vagus nerve, play a key role in transmitting parasympathetic signals to several vital organs, such as the heart, lungs, digestive system, and bladder.
The Anatomy of the Parasympathetic Nervous System
The parasympathetic nervous system consists of a complex network of nerves and ganglia that extend throughout the body. It is responsible for regulating various bodily functions and maintaining homeostasis. The cranial nerves, originating from the brainstem, carry parasympathetic signals to different organs and tissues.
One of the most important cranial nerves involved in the parasympathetic nervous system is the vagus nerve. It is the longest cranial nerve and plays a crucial role in regulating heart rate, digestion, and other vital functions. The vagus nerve branches out to different organs, including the heart, lungs, stomach, and intestines, to transmit parasympathetic signals and promote relaxation.
In addition to the cranial nerves, the parasympathetic nervous system also includes the sacral nerves. These nerves originate from the sacral region of the spinal cord and innervate the pelvic organs, such as the bladder and reproductive organs. They help control bladder function, sexual arousal, and other essential processes.
The Function of the Parasympathetic Nervous System
The parasympathetic nervous system primarily focuses on conserving energy and promoting relaxation. It facilitates essential bodily functions such as digestion, restful sleep, and recuperation. By slowing down the heart rate, stimulating digestion, and promoting proper bladder control, the parasympathetic nervous system helps the body maintain a state of equilibrium.
When the body is in a relaxed state, the parasympathetic nervous system promotes the release of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that helps transmit signals between nerve cells. Acetylcholine acts on various receptors in the body, triggering responses that promote relaxation and restoration. For example, it stimulates the release of digestive enzymes, increases blood flow to the digestive organs, and relaxes the muscles in the bladder, allowing for proper urine elimination.
In addition to its role in maintaining physiological balance, the parasympathetic nervous system also plays a crucial role in emotional well-being. It is often referred to as the “rest and digest” system, as it helps the body relax, unwind, and recover from stress. By activating the parasympathetic nervous system through activities like deep breathing, meditation, and gentle exercise, individuals can promote a sense of calm and reduce anxiety.
Overall, the parasympathetic nervous system is an essential component of the autonomic nervous system, working in harmony with the sympathetic nervous system to ensure the body functions optimally. Its role in promoting relaxation, digestion, and restoration highlights the importance of maintaining a balanced and healthy lifestyle to support the overall well-being of both the mind and body.
The Parasympathetic Nervous System vs. The Sympathetic Nervous System
Key Differences and Similarities
Although the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems work in harmony to maintain overall bodily balance, they exhibit distinct differences in their responses. While the parasympathetic nervous system promotes rest and relaxation, the sympathetic nervous system triggers the “fight or flight” response, preparing the body for potential danger or stress.
When it comes to the parasympathetic nervous system, it is often referred to as the “rest and digest” system. It is responsible for conserving energy and promoting activities that occur during a relaxed state. This includes activities such as digestion, urination, and sexual arousal. The parasympathetic system slows down heart rate, constricts the pupils, and stimulates salivation.
On the other hand, the sympathetic nervous system is known as the “fight or flight” system. It prepares the body to react to stressful or dangerous situations. When the sympathetic system is activated, it increases heart rate, dilates the pupils, and inhibits digestion. It also triggers the release of stress hormones like adrenaline, which increases blood pressure and boosts energy levels.
Additionally, the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems differ in the neurotransmitters they release. The parasympathetic system predominantly utilizes acetylcholine, while the sympathetic system primarily employs norepinephrine. These neurotransmitters play a crucial role in transmitting signals between nerve cells and target organs.
Balancing Act: How They Work Together
As essential components of the autonomic nervous system, the parasympathetic and sympathetic systems work collaboratively to maintain bodily homeostasis. Although they often have opposing effects, their coordinated actions ensure that the body responds appropriately to different situations.
For example, during a stressful event, the sympathetic system initiates the fight or flight response. This response prepares the body to either confront the threat or flee from it. The heart rate increases, blood vessels constrict, and blood is redirected to the muscles, providing them with the necessary oxygen and nutrients to respond effectively.
While the sympathetic system is in full swing, the parasympathetic system remains active in the background, ready to restore the body to a calm state once the threat has passed. Once the danger has subsided, the parasympathetic system takes over, slowing down the heart rate, dilating blood vessels, and promoting digestion and relaxation.
It is important to note that the balance between the parasympathetic and sympathetic systems is crucial for overall health and well-being. An imbalance can lead to various health issues, such as chronic stress, digestive problems, and cardiovascular disorders. Therefore, maintaining a healthy balance between these two systems is essential for optimal physiological functioning.
Disorders of the Parasympathetic Nervous System
The parasympathetic nervous system plays a crucial role in maintaining the body’s homeostasis and regulating various bodily functions. However, when this system malfunctions, it can lead to the development of various health issues. Some common disorders associated with the parasympathetic nervous system include irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), gastroparesis, and disorders affecting bladder control.
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a chronic disorder that affects the large intestine. It is characterized by symptoms such as abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, and constipation. The parasympathetic nervous system, which controls the relaxation and contraction of the intestines, can contribute to the development of IBS symptoms when it is not functioning properly.
Gastroparesis is another disorder that can arise from parasympathetic dysfunction. It is a condition in which the stomach takes longer than usual to empty its contents into the small intestine. This can lead to symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, bloating, and a feeling of fullness after eating small amounts of food. The parasympathetic nervous system plays a role in regulating the movement and contractions of the stomach muscles, and its dysfunction can disrupt the normal digestive process.
Disorders affecting bladder control, such as overactive bladder or urinary retention, can also be linked to parasympathetic dysfunction. The parasympathetic nervous system helps regulate the relaxation and contraction of the bladder muscles, allowing for proper urine storage and elimination. When this system malfunctions, it can result in urinary difficulties, including frequent urination, urgency, or the inability to empty the bladder completely.
Treatment Options for Parasympathetic Disorders
If you suspect that you may be experiencing issues with your parasympathetic nervous system, it is crucial to consult with a medical professional. They will be able to provide an accurate diagnosis and suggest appropriate treatment options tailored to your specific condition.
Treatment for parasympathetic disorders may involve a combination of lifestyle modifications, stress reduction techniques, dietary changes, and medication when necessary. Stress reduction techniques, such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, and yoga, can help calm the nervous system and alleviate symptoms associated with parasympathetic dysfunction.
In some cases, dietary changes may be recommended to support the proper functioning of the parasympathetic nervous system. This may include consuming foods that are rich in nutrients, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Avoiding trigger foods, such as caffeine, alcohol, and spicy foods, may also be beneficial in managing symptoms.
Medication may be prescribed to help regulate the parasympathetic nervous system and alleviate symptoms. For example, antispasmodic medications can help relax the muscles of the intestines and bladder, while medications that increase gastric motility can aid in the emptying of the stomach.
In conclusion, disorders of the parasympathetic nervous system can have a significant impact on various bodily functions. Recognizing the symptoms and seeking appropriate medical attention is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment. With the right approach, individuals can effectively manage their parasympathetic disorders and improve their overall quality of life.
Maintaining a Healthy Parasympathetic Nervous System
The parasympathetic nervous system plays a crucial role in maintaining balance and promoting relaxation in the body. It is responsible for conserving energy, slowing down the heart rate, and promoting digestion and rest. To ensure the optimal functioning of your parasympathetic nervous system, there are several lifestyle changes you can implement.
Lifestyle Changes for Better Functioning
Engaging in regular exercise is one of the most effective ways to support the health of your parasympathetic nervous system. Exercise not only helps to reduce stress and anxiety but also stimulates the release of endorphins, which are natural mood boosters. Whether it’s going for a brisk walk, practicing yoga, or participating in a team sport, finding an activity that you enjoy and can incorporate into your routine is key.
In addition to exercise, practicing relaxation techniques can also have a positive impact on your parasympathetic nervous system. Deep breathing exercises, such as diaphragmatic breathing or alternate nostril breathing, can help activate the relaxation response and promote a sense of calm. Meditation, mindfulness, and progressive muscle relaxation are other techniques that can help reduce stress and support the functioning of your parasympathetic system.
Adequate sleep is another essential factor in maintaining a healthy parasympathetic nervous system. During sleep, the body has a chance to rest, repair, and rejuvenate. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night to ensure that your parasympathetic system has the opportunity to function optimally. Establishing a bedtime routine, creating a comfortable sleep environment, and avoiding stimulating activities before bed can all contribute to a good night’s sleep.
Furthermore, the food you consume can greatly impact the health of your parasympathetic nervous system. Opt for a balanced diet that includes plenty of nutrient-dense foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. These foods provide the necessary vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support overall nervous system health. Additionally, staying hydrated by drinking an adequate amount of water throughout the day is vital for optimal nervous system function.
The Impact of Stress on the Parasympathetic Nervous System
Chronic stress can have a detrimental impact on the parasympathetic nervous system, disrupting its ability to restore balance and maintain proper functioning. When the body is constantly exposed to stressors, such as work pressure, relationship problems, or financial difficulties, the sympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for the body’s fight-or-flight response, becomes overactive. This can lead to a decrease in parasympathetic activity and an imbalance in the autonomic nervous system.
It is essential to find healthy stress management techniques that work for you to mitigate the negative effects of stress on the parasympathetic system. Engaging in regular exercise, as mentioned earlier, can help reduce stress levels and promote relaxation. Finding hobbies or activities that bring you joy and allow you to unwind can also be beneficial. Whether it’s painting, playing a musical instrument, or gardening, engaging in activities that you enjoy can help shift your focus away from stress and activate your parasympathetic nervous system.
Seeking support from friends, family, or a therapist can also be instrumental in managing stress and supporting the health of your parasympathetic system. Talking about your concerns and emotions with someone you trust can provide a sense of relief and help you gain perspective on stressful situations. Additionally, practicing self-care activities, such as taking a warm bath, practicing mindfulness, or listening to calming music, can help activate the relaxation response and counteract the effects of chronic stress.
In conclusion, maintaining a healthy parasympathetic nervous system requires making lifestyle changes that support relaxation, stress management, and overall well-being. By incorporating regular exercise, relaxation techniques, adequate sleep, and a balanced diet into your daily routine, you can promote the optimal functioning of your parasympathetic system and enhance your overall quality of life.
The Future of Parasympathetic Nervous System Research
Emerging Trends in Neuroscience
Ongoing research in the field of neuroscience continues to shed light on the intricacies of the parasympathetic nervous system. Advancements in technology and innovative scientific methods are enabling researchers to deepen their understanding of how the parasympathetic system interacts with other bodily systems, providing valuable insights into its potential therapeutic applications.
Potential Implications for Health and Medicine
As our knowledge of the parasympathetic nervous system expands, there is significant potential for advancements in health and medicine. Targeted interventions and therapies may emerge in the future, facilitating the treatment of disorders linked to parasympathetic dysfunction and improving overall well-being.
In conclusion, the parasympathetic nervous system is a vital component of the intricate human nervous system. Understanding its role, functioning, and potential disorders can help individuals prioritize their overall nervous system health. If you suspect any issues related to the parasympathetic nervous system, it is always advisable to seek guidance from a qualified healthcare professional, who can provide expert advice for your specific situation.